Case Study: Knee Arthroscopy with Synovectomy Surgery
performed to 36 year-old male patient
One surgical method we use to treat synovitis and other conditions that affect our synovium is a synovectomy. A thin membrane called synovium lines the interior of joints including the knee, shoulder, and elbow. The removal of the inflammatory synovium is known as a synovectomy. Three to four months after surgery, the majority of patients recover fully.
Patient presented today is male, 36 years of age. He complains his left knee is in terrible pain. He also presented his X-ray result. There are mild osteoarthritic degenerative changes but no acute fractures found. He had tried conservative management but no benefit.
MRI of Left knee
We agreed to go with 3 Tesla MRI of Left knee to final the diagnosis. We also discussed treatment options including Physical Therapy, Injection and also Surgery. Patient will continue to do the Ice/Heat Therapy for it helps a little on his knee condition.
After a week MRI results received and discussed to the patient- showed that aside from joint effusion, there are some degenerative changes seen in the patellofemoral compartment and posterior aspect of the medial tibial plateau which could be related to focal PVNS.
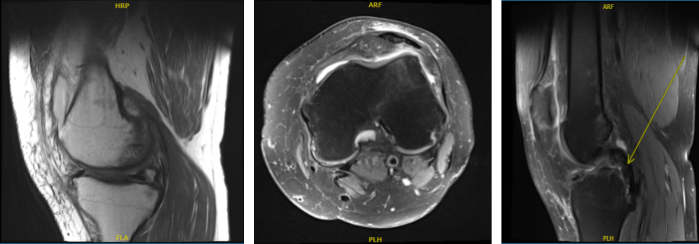
MRI of Left knee
We discussed treatment options and the patient opted for surgical management. We discussed the risks and benefits including infection, bleeding, inability to relieve the pain, recurrence of the tumor, complications including blood clots, complications including death. The patient understood and signed the informed consent.
The patient was taken to the operating room where he was placed on a well-padded operating room table. The patient was given sedation. 30 cc of equal quantity of 2% Lidocaine and 5% Marcaine was mixed and injected into the left knee joint. A tourniquet was applied.
Preoperative antibiotics were given in the form of Ancef. The tourniquet was elevated. The left knee was prepped and draped aseptically in the usual fashion. Local infiltration with 5% Marcaine was done at the site of the medial and lateral anterior portals. A timeout was called.
A lateral incision was given for the anterior portal for the arthroscope. The arthroscope was entered into the patellofemoral joint where synovitis was seen in the suprapatellar region.
There was Grade II to Grade III chondral damage on the posterior surface of the patella. The arthroscope was entered into the medial compartment where there was no meniscal tear. The cartilage was intact. There was synovitis in the medial compartment.
A medial anterior portal was made using the spinal needle. Examination of the anterior chondral notch showed an intact ACL. Examination of the lateral compartment showed a tear of the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus. There was synovitis in the lateral compartment also.
The shaver was used to do the synovectomy in the medial compartment as well as the lateral compartment. Shaving was done for doing meniscectomy of the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus. Up biter was also used for the meniscectomy.
Now the shaver and the arthroscope were entered into the patellofemoral compartment where extensive synovectomy of the synovium from the suprapatellar pouch as well as the medial and lateral gutter was performed. The chondral lesion of the posterior patella pouch was also debrided with the use of a shaver. After thorough irrigation pictures were taken and saved.
The knee was thoroughly irrigated. Closure was done with the use of 3-0 nylon. 9 cc of .5% Marcaine mixed with 40 mg of Depo Medrol was injected into the knee. Dressing was done with the use of Xeroform, 4 x 8s, Webril and ACE wrap. The tourniquet was released. The patient was moved to the recovery room in stable condition.
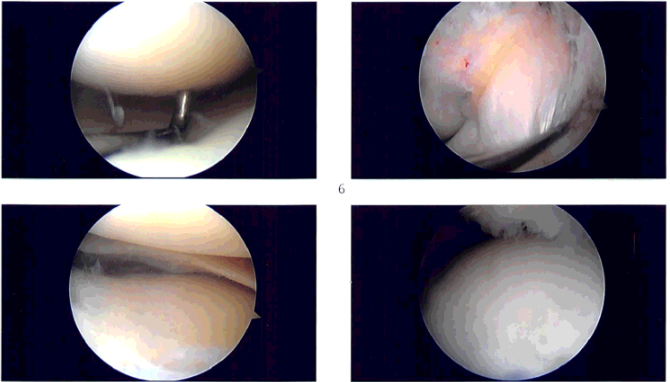
Intraoperative images
After one-week post operative, a patient seen in the office has extensive bruising around the knee and is using a cane, no X-ray were needed but recommended to have a Synovial biopsy to reconfirm the patient’s condition.
Post Operative Exam: General Appearance: swelling and tenderness and wound clean and dry, no warmth, appropriate range of motion, and neurovascular intact.
For four-week postoperative patients still have swelling and bruising but still improving using cane and weight-bearing is tolerable. By this time, we both agreed to start physical therapy.
Patient underwent Physical Therapy for four weeks, and got well and recovered easily on his surgery. Physical Therapy played an important role in his recovery for he is able to return to work after 8 week post-surgery.
Disclaimer – Patient’s name, age, sex, dates, events have been changed or modified to protect patient privacy.
I am Vedant Vaksha, Fellowship trained Spine, Sports and Arthroscopic Surgeon at Complete Orthopedics. I take care of patients with ailments of the neck, back, shoulder, knee, elbow and ankle. I personally approve this content and have written most of it myself.
Please take a look at my profile page and don't hesitate to come in and talk.

