Case Study: Arthroscopic Meniscectomy and
Chondroplasty Of The Left Knee In A 63-Year-Old Female
The patient was seen as an outpatient with complaints of pain on the inner side of the left knee following a car accident. The patient has a history of ACL repair and medial meniscus surgery on the left knee about 5 years back form an outside physician.
The pain is mild in intensity located on the left knee. The pain is constant and does disturb sleep. The pain is not associated with swelling, bruising, tingling, radiating pain, weakness, bowel or bladder abnormality, gait problem, giving way, or limping. The problem has been getting worse since it started. Walking, bending, and climbing stairs make the symptoms worse. Rest makes the symptoms better.
The patient has a medical history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia. She is currently on Metoprolol and Atorvastatin. She has no known drug allergies. She has been doing physical therapy and there has been no improvement in pain in the left knee.
On general physical examination, the patient is calm conscious cooperative, and well oriented to time, place, and person. Upon examination of the left knee, the patient has tender to palpation along the medial joint line and has a small effusion elicited by the patellar tap.
The medial and lateral facets of the patella are non-tender on palpation. The patient has no discomfort with McMurray’s maneuvers, and the knee is stable. There is 5/5 strength in the bilateral lower extremity and distal neurovascular is intact. There are no erythema, warmth, or skin lesions present.
Knee flexion (Normal: 140 degrees) – 120 degrees with discomfort.
Extension (Normal: 5 degrees) – 0 degree with discomfort.
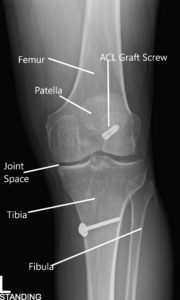
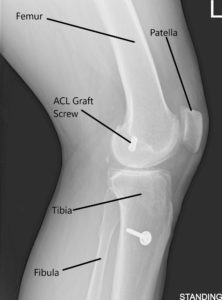
X-ray of the left knee in AP and Lateral views.
An X-ray of the left kee suggested a moderate narrowing of the medial joint compartment and status post ACL reconstruction.
She had an MRI which showed tearing of the medial meniscus at the meniscocapsular junction and posterior horn-body junction. There was tri-compartmental cartilage loss.
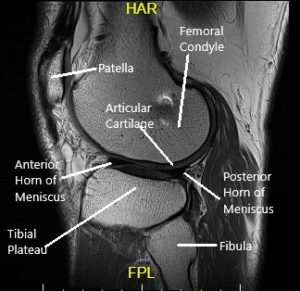

Sagittal MRI view of the left knee.
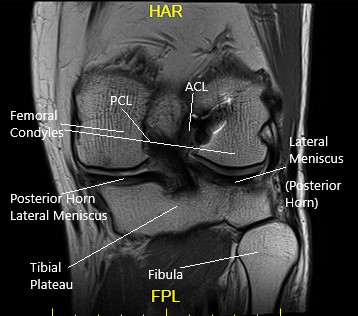
Coronal MRI view of the left knee.
PREOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Medial meniscus tear at the meniscocapsular junction of the left knee.
POSTOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS:
- Medial meniscus tear at the meniscocapsular junction of the left knee.
- Medial margin tear and fraying of lateral meniscus left knee
- Patellofemoral and Medial femoral condyle arthritis left knee
OPERATION:
- Arthroscopic Left knee arthroscopic medial meniscal repair all inside the left knee.
- Arthroscopic Chondroplasty of the patellofemoral joint and medial femoral condyle of the left knee
- Arthroscopic Meniscectomy of lateral meniscus left knee
- Arthroscopic Microfracture of the intertrochlear notch left knee.
The patient was taken to the operating room, where he was placed on the well-padded operating room table. Left lower extremity was prepped and draped aseptically in a usual fashion with a tourniquet applied on the lower thigh.
Time-out was called. A left lateral entry portal was made. An arthroscope was introduced. The medial entry portal was made using a spinal needle.
Examination of the knee showed grade 3 to grade 4 arthritis of the trochlea, grade 2 to grade 3 arthritis of the lateral facet of the patella, grade 2 to grade 3 arthritis of the medial femoral condyle, previous repair of the medial meniscus because of the sutures as well as long tear of the meniscocapsular junction of the medial meniscus of the left knee.
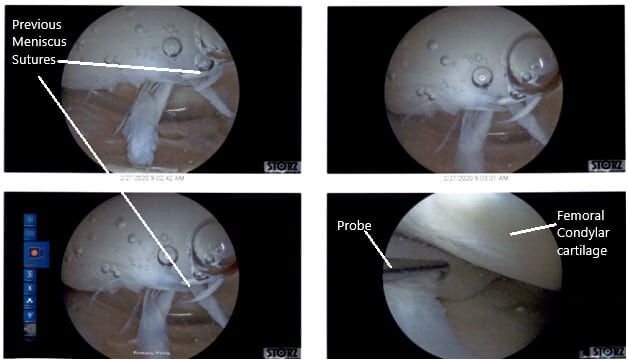
Intraoperative Arthroscopic Views of the left knee.
There were some medial margin tearing and fraying of the lateral meniscus which was taken care of with the shaver and meniscectomy performed to stable margins. The ACL (history of ACL reconstruction) showed fraying in the intertrochlear notch, but the ACL was intact.
Debridement of the ACL was performed. Clean up of the meniscocapsular junction of the medial meniscus was performed. The rasping of the meniscus as well as the capsule was performed in preparation for the repair using a shaver and arthroscopic rasps. Chondroplasty of the medial femoral condyle, trochlea, patellar lateral facet was performed. Decisional for repair was undertaken.
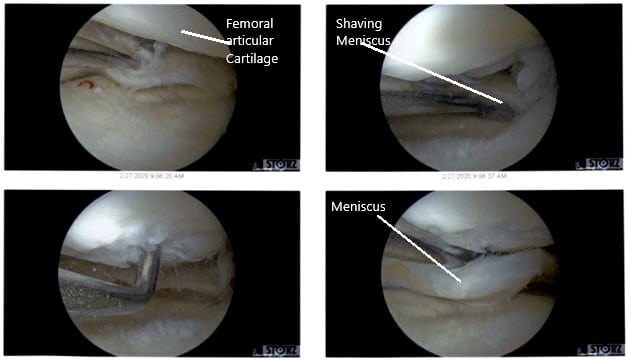
Intraoperative Arthroscopic Views of the left knee.
All inside the repair of the medial meniscus was performed using FasT fixers, five curved, two reversed curved in a sequential fashion. Following the repair, the meniscus was found to be stable. Final pictures were taken.

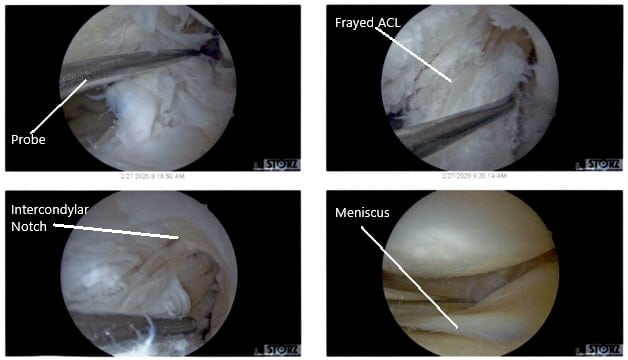
Intraoperative Arthroscopic Views of the left knee.
The knee was thoroughly irrigated. The scope was removed and the knee was drained. The closure was performed with nylon #4-0. The dressing was done using 4x4s, ABD, Webril, and Ace wrap. Knee immobilizer was applied. Postoperatively, the patient was to be partial weight-bearing with crutches.
Disclaimer – Patient’s name, age, sex, dates, events have been changed or modified to protect patient privacy.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
