Case Study: Shoulder Arthroscopy: Rotator Cuff Repair
Acromioplasty and Subacromial Decompression
and Distal Clavicle Excision in a 43 year-old patient
Surgery to repair a damaged tendon in the shoulder is known as a rotator cuff repair. Both shoulder arthroscopy, which employs tiny incisions, and a big incision are options for doing the treatment. A collection of muscles and tendons that create a cuff across the shoulder is known as the rotator cuff.
An arthroscopic operation called subacromial decompression is used to remove a portion of the acromion’s undersurface as well as to loosen up the coracoacromial arch’s tight ligament.
By raising the shoulder’s roof, additional space is created beneath for the rotator cuff tendons. While the distal clavicle excision surgery is used to relieve shoulder discomfort and impairment brought on by arthritis or impingement by removing the outside portion of the clavicle.
A 43 year-old patient visited our office with complaints regarding left and right shoulder and neck pain since. Tried anti-inflammatory meds with no relief. For aggravating factors, patients report lifting, twisting, and nighttime. For location, left. For quality, she reported aching, throbbing, and frequent.
For timing, she reported acute, nighttime, and recurrent. For associated symptoms, she reported no weakness, no numbness, no tingling, no swelling, no redness, no warmth, no ecchymosis, no catching/locking, no popping/clicking, no buckling, no grinding, no instability, no radiation, no drainage, no fever, no chills, no weight loss, no change in bowel/bladder habits, and no tenderness. For previous surgery, none.
After discussing the options for treatment and the risks of injection, the patient wished to proceed with the injection to reduce pain and swelling. After a sterile prep, 3cc of 1% ropivacaine, 3cc of 0.5% marcaine and 80mg of depo-medrol were injected into the left shoulder subacromial space.
The patient tolerated the procedure well and there were no complications. Post injection pain, blood sugar elevation, skin discoloration, fatty atrophy and the signs of infection were discussed in detail.
The patient presented an MRI result that showed multifocal rotator cuff tendinosis with a delaminating high-grade partial-thickness intrasubstance insertional tear at the confluence of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons.
Mild tendinosis of the intra-articular portion of the biceps tendon. Mild degeneration with fraying/tearing at the base of the superior labrum. Very mild acromioclavicular joint arthrosis. Mild subacromial-subdeltoid bursitis.
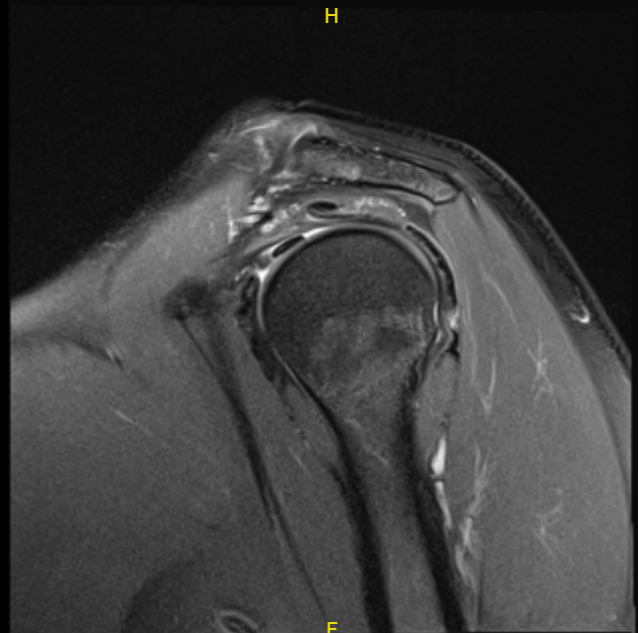
MRI-3T left shoulder non-contrast
The patient was taken to the operating room where supraclavicular block was done on the left side. This was followed by general anesthesia. The patient was put in the right lateral position with the left shoulder up. Preoperative antibiotics in the form of 2 g of Ancef and 1 g of tranexamic acid were given.
Left shoulder was prepped and draped aseptically in the usual fashion. Anterior portal was made in the soft spot posterior to the left shoulder. Trocar was inserted into the glenohumeral joint. Arthroscope was Inserted.
The anterosuperior entry portal was made with a spinal needle under arthroscopic supervision. Incision was given and examination of the cuff was space. with a spur. Probe was inserted from the anterosuperior portal. Glenoid as well as humerus as well as the scapula. The rotator Pictures were taken.
Trocar was inserted through the subscapularis and bursectomy was performed. Examination showed acromial roughening Examination of the rotator cuff showed high-grade partial-thickness tear in the anterior margin of the supraspinatus as well as in the rotator interval. The subscapularis was intact.
The decision was made to close the rotator cuff interval with the suture. The spinal needle was used to pass the PDS suture laterally and FirstPass was used to pass the suture medially. The arthroscope was entered into the glenohumeral joint to pass the suture superficial to the biceps tendon.
Once the suture was checked that it was not around the biceps tendon, the rotator cuff interval and the supraspinatus tear were closed with sliding knots. Acromioplasty was performed with the use of Coblation wand followed by burr.
Distal clavicle excision was also performed given the arthritis present. Coblation wand followed by burr was used to excise about a centimeter of the distal clavicle. The final pictures were taken and saved.
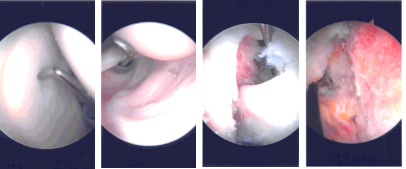
Intraoperative Arthroscopy Images
The shoulder was irrigated and drained. Closure was done using #3-0 nylon. Dressing was done using Xeroform, 4 x 4, ABD, and tape. Shoulder immobilizer was applied. The patient was extubated and moved to recover in a stable condition.
The patient was seen for post operative check up. We have decided to do formal physical therapy as well as a home exercise program for rehabilitation of the shoulder. The patient did well after the surgery and continued physical therapy. Patient checked in for a follow up visit after a month and saw significant improvement on her shoulder.
Disclaimer – Patient’s name, age, sex, dates, events have been changed or modified to protect patient privacy.

Dr. Vedant Vaksha
I am Vedant Vaksha, Fellowship trained Spine, Sports and Arthroscopic Surgeon at Complete Orthopedics. I take care of patients with ailments of the neck, back, shoulder, knee, elbow and ankle. I personally approve this content and have written most of it myself.
Please take a look at my profile page and don't hesitate to come in and talk.
