Case Study: Management of Patellar Tendon Rupture
in a 70-year-old Male
A 70-year-old male reportedly had a fall stumbling down the stairs followed by pain and swelling in the left knee and left foot. The patient was taken to the ER where a left cuboid fracture was diagnosed on X-ray. He had a below-knee walking splint applied in the ER but was unable to walk. Subsequent examination suggested a rupture of the extensor mechanism of the left knee.
A sulcus was palpable in front of the left knee and the patient was unable to perform a straight leg raise test. The examination of the bilateral hips and spine was normal. There was ecchymosis in front of the left knee. X-ray of the left knee revealed a patella Alta and the presence of soft tissue swelling.
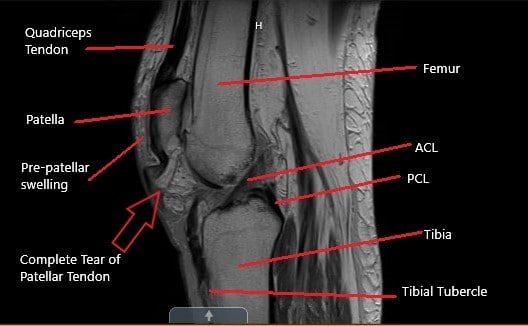
MRI of the knee in the sagittal section showing a complete tear of the patellar tendon.
MRI of the left knee suggested a full-thickness midsubstance tear of the patellar tendon with approximately 1.7 cm fluid gap and associated patella Alta. There was diffuse infiltration/edema within the infrapatellar and prepatellar fat. The patient is a retired banker and had an active lifestyle before the injury.
The patient’s past medical history was significant for chronic kidney disease, chronic bronchitis, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. The patient’s current medications include enalapril, hydrochlorothiazide, atorvastatin, and albuterol inhaler.
Various treatment options were discussed at length with the patient. The patient agreed to surgical management. The risks and benefits including failure, infection, bleeding, nonhealing, need for repeat surgery and reconstruction, knee stiffness, rehabilitation, systemic complications like blood clots, cardiac, pulmonary, neurological complications, and even death were discussed at length with the patient. The patient understood and signed the informed consent.
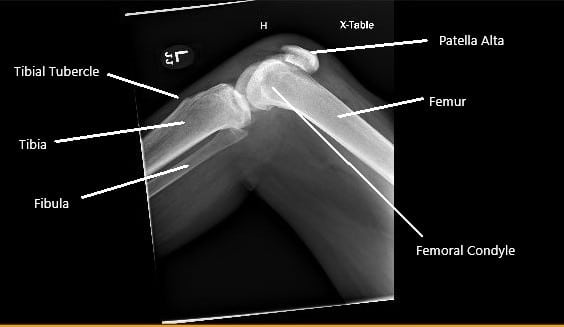
X-ray of the right knee showing patella Alta secondary to the rupture of the patellar tendon.
PREOPERATIVE DIAGNOSES:
- Left mid substance patellar tendon rupture.
- Fracture cuboid, left foot.
POSTOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS:
- Left mid substance patellar tendon rupture.
- Fracture cuboid, left foot.
OPERATION: Patellar tendon repair primary with augmentation using dermal allograft and sutures using SwiveLock and anchors.
PROCEDURE: The patient was taken to the operating room. The anesthesiologist did an adductor block. General anesthesia was induced. The left short-leg splint was removed before the procedure.
The left lower extremity was prepped and draped aseptically in a usual fashion. A high thigh tourniquet was applied. The Time out was called. Preoperative antibiotics are given. A thigh tourniquet was inflated to 325 mmHg.
The incision was planned from the anterior part of the patellar to the tibial tuberosity. A midline incision was given. With sharp and blunt dissection, a patellar tendon was reached, which was found to be ruptured with ragged margins.
The tear was extending into the lateral and medial patellar tendon. The knee was opened and washed thoroughly with irrigation. The ragged margins of the patellar tendon were removed. The primary repair of the patellar tendon was planned.
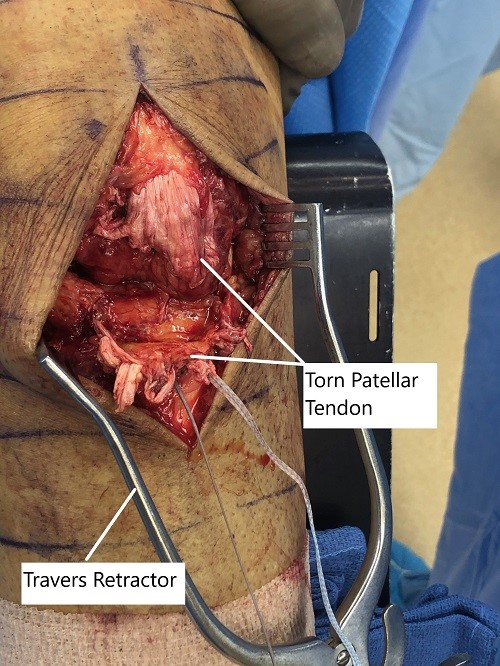
Intraoperative image showing the torn patellar tendon.
A 2 mm fiber tape x4 was used to put Krackow suture, one on either side on the proximal and distal end of the patellar. The tails of the sutures were in the midline. Now, the lower wall of the patellar was exposed, posterior to the patellar side. It was cleaned with the use of curette and Bovie. The bone was decorticated and two drill holes were done and planning for suture anchors.
Four drill suture anchors were brought on either side of the patellar, posterior to the patellar tendon. The sutures were brought to the front through the patellar tendon and reticulum using a suture passer.
Once they were brought up, the tails of the suture in the midsubstance of the patella were tied to each other using four knots separately. The knots were buried and cut. An Arthroflex was opened. It was put on the patellar tendon and sealed proximally.
The distal one-third of the graft was removed and little of access. The allograft was found to cover the patellar tendon and is to eternity. Now the two sutures from each side of the suture anchors proximal were crossed, one set was crossed and one set was taken straightening, put in the tibia lateral to the tibial tuberosity using SwiveLock on either side. Excellent configuration was achieved.

Intraoperative image showing the repaired patellar tendon with overlying allograft.
The knee was flexed in 30 degrees at that time. Then the patellar tendon repair was stopped. The allograft was posterior to the sutures opposing to the patellar tendon repair in the patellar tendon. The wound was again washed.
The patellar retinaculum was repaired on either side using #2 FiberWire. The sutures and towards the center of the patellar retinaculum were incorporated into the Arthroflex graft.
The wound was again washed and closure was done using Vicryl #2-0 for subcutaneous and Monocryl #3-0 for the skin. The dressing was done using Prineo. The further dressing was done using Webril and Ace wrap. A posterior short-leg splint was re-applied. A long knee brace was applied.
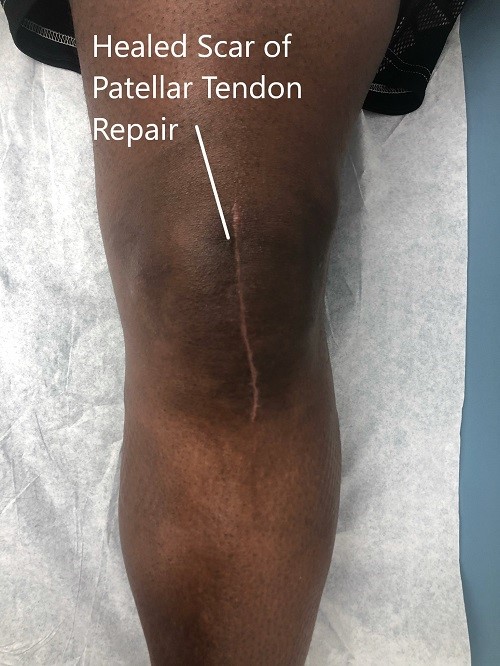
Postoperative images at 2 months follow up.
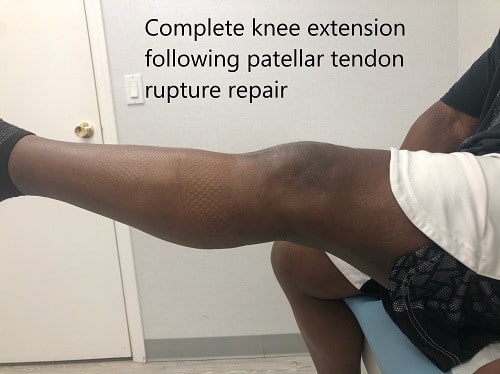
Postoperative images at 2 months follow up.
Disclaimer – Patient’s name, age, sex, dates, events have been changed or modified to protect patient privacy.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
