Case Study: Shoulder Arthroscopy: Rotator Cuff Repair
in a 42 year-old female
Surgery to repair a damaged tendon in the shoulder is known as a rotator cuff repair. A rotator cuff tear may be repaired via arthroscopy, open surgery, or a combination of the two methods. Reattaching the tendon to the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) is the most common procedure used in this surgery to repair a torn rotator cuff.
The patient is a 42 year-old female visiting the office with complaints of right shoulder pain. She has previously been operated on for knee scope last month. She has been recovering fine. Her right shoulder has not been responding to conservative treatment.
We discussed treatment options and she opted for surgical management. We discussed risks and benefits including infection, bleeding, injury to adjacent nerves and vessels, failure to heal, need for repeat surgery, arthritis, rehabilitation among others.
We discussed systemic complications including blood clots, cardiac, pulmonary, neurological complications including death. The patient understood and signed an informed consent.
The patient was taken to the operating room, where a supraclavicular block was given. General anesthesia was induced. The patient was put in the left lateral position with the right shoulder up. The right shoulder was prepped and draped aseptically in the usual fashion. Time-out was called.
Preoperative antibiotic was given. An entry portal was made through the soft spot posterolateral border of the acromion. Arthroscope was inserted into the glenohumeral joint. Anterosuperior portal was made with the use of spinal needle and cannula was inserted.
Examination of the joint showed fraying of the subscapularis tendon with partial tear. Biceps tendon was intact. There was high-grade articular side tear of the rotator cuff infraspinatus, which was debrided with the use of a shaver.
Examination of the labrum and tenodesis were very normal. Debridement of subscapularis tendon was done with the use of a shaver. Debridement of the rotator cuff tendon was also done. Pictures were taken and saved. The arthroscope was inserted in the subacromial bursa and a shaver was introduced.
Subacromial decompression performed. Examination arthritis. The tear could be found in the region of the infraspinatus, which was debrided. repaired. Healicoil Smith & Nephew doubled four-tail Healicoil anchor was used and inserted on the tapping.
One suture of the anchor was used far anteriorly and posteriorly and tied onto the was performed with the use of After closure, good repair of the rotator cuff was achieved. Acromioplasty was performed with the use of Coblation wand followed by #6-0 burr.
Distal clavicle excision was also performed with the use of Coblation wand followed by use of burr from the posterior as well as anterior portal. Final pictures were taken and saved. Then the shoulder was thoroughly irrigated and draped.
Closure was done with use of # 3-0 nylon. Dressing was done with the use of Xeroform, 4 x 8, ABD and tape. The patient was put in shoulder immobilizer and moved to recovery in a stable condition.
The patient’s status post right shoulder arthroscopic rotator cuff repair, DCR, ACR done, she has gone through right knee arthroscopic surgery, medial and lateral meniscectomy and chondroplasty in the past months ago.
Exactly one week after the surgery of her shoulder, she is here for her postoperative visit, no x-rays are needed. She is using a shoulder sling but not the pillow, she denies fever, chills and her knee is improving gradually but her shoulder is still hurting.
We discussed using the abduction pillow and avoiding active exercises of the right shoulder. After discussing treatment options, we have decided to proceed with a home exercise program for rehabilitation of the shoulder. We removed the stitches during the visit.
We will continue with ice and elevation of the shoulder to decrease swelling and pain. We will wean them off any narcotic medications and progress to anti-inflammatories and Tylenol as long as there are no contraindications to these medications.
We also discussed the risk and benefits and common side effects of taking these medications. The patient will be back in three weeks’ time to evaluate her progress.
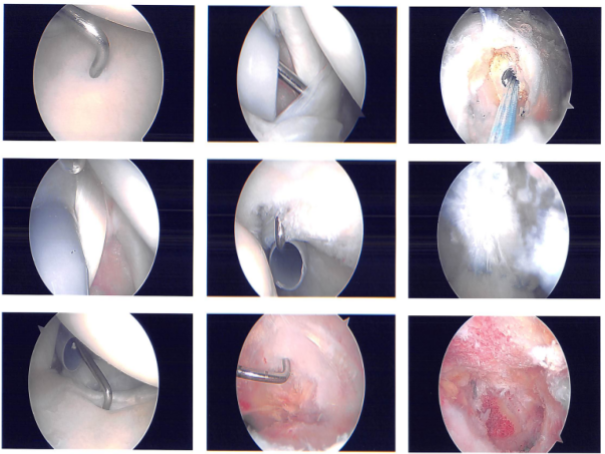
Intraoperative images
After three weeks the patient is seen in the office for her follow up checkup, no x-rays are needed. She is using shoulder sling but not the pillow, she denies fever, chills and her knee and shoulder are improving gradually.
After discussing treatment options, we have decided to proceed with a home exercise program for rehabilitation of the shoulder. We will continue with ice and elevation of the shoulder to decrease swelling and pain.
We also discussed with the patient that she may need surgery for left shoulder also but for the time being we agreed to go with conservative management for now. The patient follows up with a checkup after 4 weeks.
The patient seen in the office after a month for her follow up checkup, no x-rays are needed. She is improving. No brace or splint. She denies fever, chills and her knee and shoulder are improving gradually.
The patient did well after surgery and her shoulder is improving. Through regular visits and continued physical therapy, the patient healed and recovered.
Disclaimer – Patient’s name, age, sex, dates, events have been changed or modified to protect patient privacy

Dr. Vedant Vaksha
I am Vedant Vaksha, Fellowship trained Spine, Sports and Arthroscopic Surgeon at Complete Orthopedics. I take care of patients with ailments of the neck, back, shoulder, knee, elbow and ankle. I personally approve this content and have written most of it myself.
Please take a look at my profile page and don't hesitate to come in and talk.
