Case Study: Custom Total Knee Replacement in
Left Knee Arthritis with prior Hardware on the Lateral Tibial Plateau
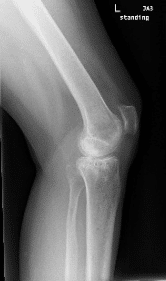
X-ray of a left knee.
The patient was a 55 year old female presenting to the office with complaints of worsening left knee pain for the last three years. The patient was referred to us by one of our previous patients and was working as a guidance counselor in a school. The patient stated that she had sustained a slip and fall in 2017 fracturing her left upper leg. She was hospitalized and was treated with open reduction and internal fixation of the left lateral tibial plateau.
She subsequently resumed her activities but over the past year, started experiencing worsening left knee pain. The pain was described as sharp to dull ache with worsened on activities such as walking, climbing stairs, bending, kneeling and getting up from a chair.
The pain has recently been disturbing her sleep. She stated she was under tremendous emotional stress due to pain in her daily activities.
She had restricted her activities due to pain and tried conservative management in the form of physical therapy, cortisone injections, braces, and heat pads but with minimal relief.
The patient was a former smoker having quit ten years ago and had comorbidities of hypothyroidism and hypertension. She is currently using a cane as a walking aid.
On physical examination, she demonstrated tenderness on the medial joint line and medial patellar facet. She was uncomfortable with the examination due to pain. After a thorough evaluation and imaging studies, she was advised about the hardware removal from the lateral tibial plateau with subsequent total knee replacement using custom implants and instruments.
She was thoroughly advised about the potential risk of infection and skin dehiscence post-surgery. The patient agreed to the treatment plan.
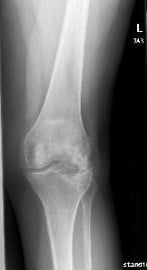
X-ray showing AP and lateral views of the left knee post removal of the lateral plateau plate.
The patient was brought to the operating room and anesthesia was obtained by the anesthesiologist. Tourniquet cuff was placed over the left thigh and left lower extremity was then draped and prepped in the usual sterile manner. Esmarch was used and the knee was exsanguinated.
The earlier incision was used for exposure. Skin and subcutaneous tissues were incised and the dissection was carried down to the plate. The plate was exposed. screws were removed. and the plate was removed. Three bone biopsy tissues were sent for culture and sensitivity. The additional tissue was sent for histopathology.
Thorough lavage was given. The injection was given with Marcaine and epinephrine. Cutaneous tissues were closed 0-Vicryl. Subcuticular tissues were closed with 2-0 Vicryl. The skin was closed Steri-strips. Sterile dressing was then applied over the wound. The patient was then transferred to the postoperative care unit in stable condition.
The bone biopsy tissues sent for pathological evaluation with culture and sensitivity came back negative for infection. The wound was allowed to heal. The patient was advised a total knee replacement after 3 months.
Imaging studies revealed tricompartmental osteoarthritis, most severely affecting the medial compartment with a post-traumatic deformity of the proximal tibia.
CT scan of the knee with the hip and ankle was performed to obtain data about the patient’s anatomy and biomechanics. A 3 D model was formed and was used to construct patient-specific implants and instruments. A preoperative plan was created to assist in surgical planning.
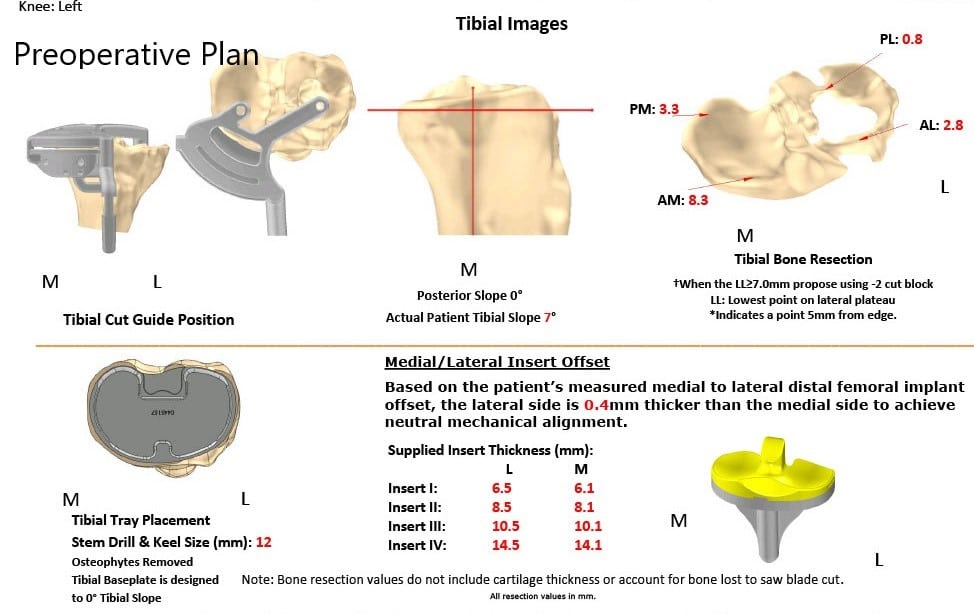
Complete Orthopedics patient specific surgical plan for a custom total knee replacement in left knee arthritis with prior Hardware on the lateral tibial plateau.
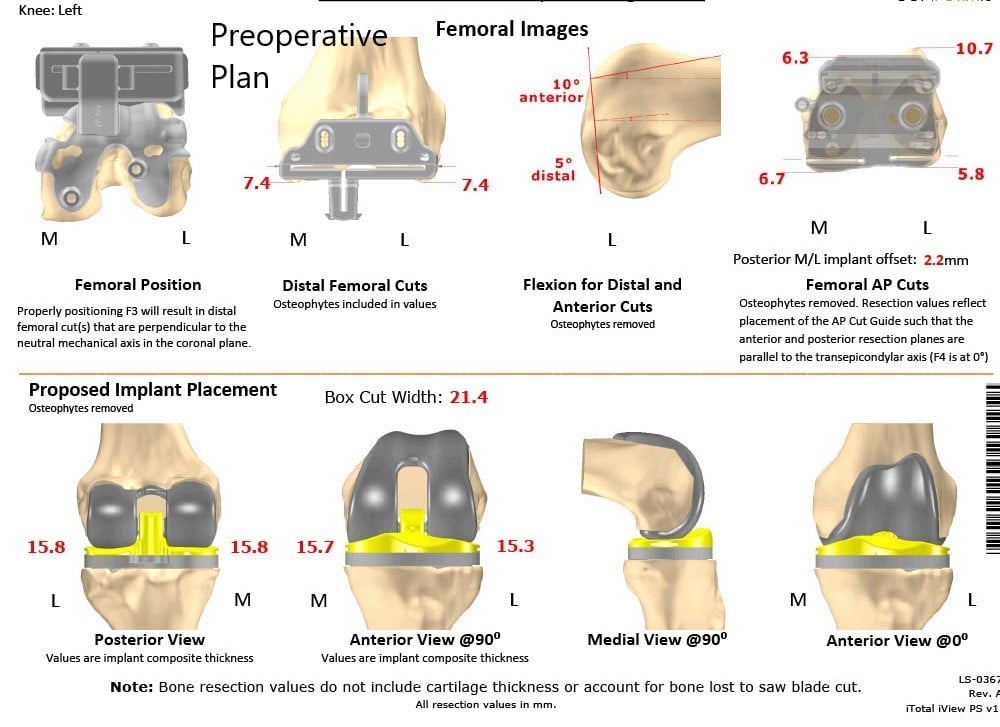
Complete Orthopedics patient specific surgical plan for a custom total knee replacement in left knee arthritis with prior hardware on the lateral tibial plateau (scan 2)
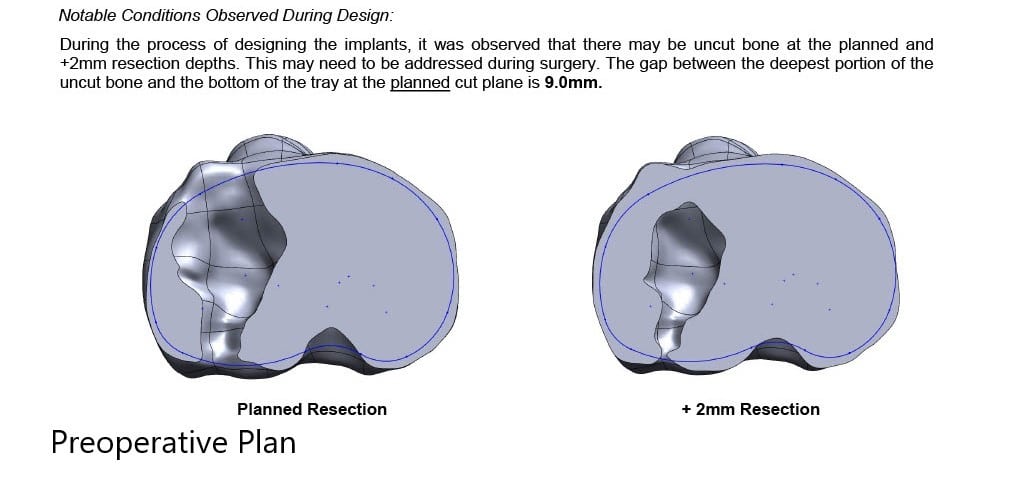
Complete Orthopedics patient specific surgical plan for a custom total knee replacement in left knee arthritis with prior hardware on the lateral tibial plateau (scan 3)
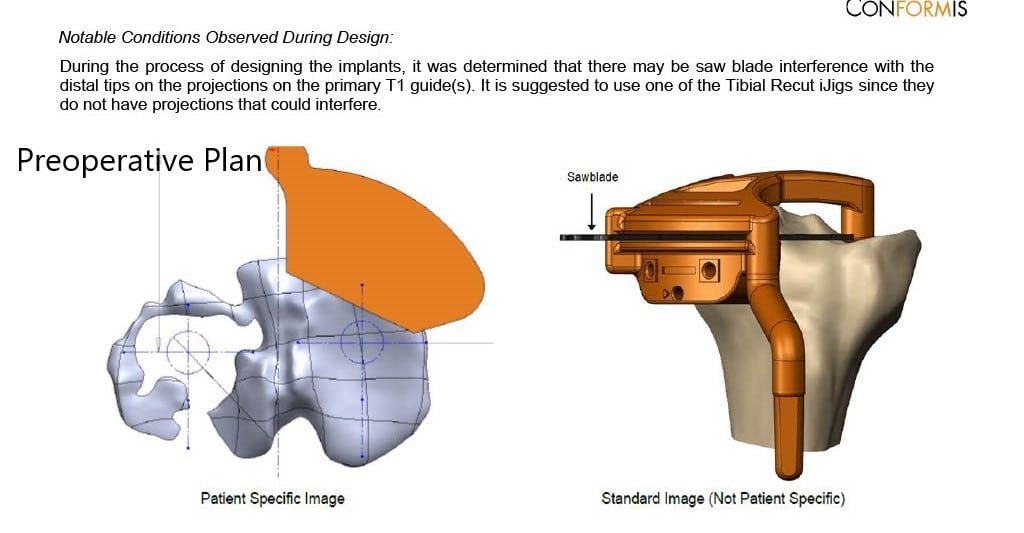
Complete Orthopedics patient specific surgical plan for a custom total knee replacement in left knee arthritis with prior hardware on the lateral tibial plateau (scan 4)
The patient underwent a custom left total knee replacement with iTotal tibial tray with iTotal femoral implant with iTotal poly 32 mm patella with a 6-mm polyethylene insert.
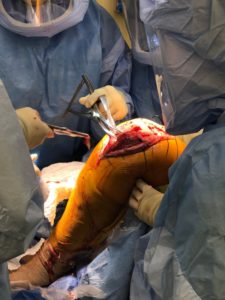
In consultation with the plastic surgeon, it was decided to make the medial incision a few centimeters away from the initial lateral incision. The skin and subcutaneous tissues were incised. A medial parapatellar arthrotomy was performed.
The tibia was then subluxed. The cruciates were then debrided. The customized gig was used for making the tibial resection. Additional loss was encountered on the lateral tibial plateau and that the bone from the lateral tibial plateau was sent for analysis.
Attention was then turned towards the femur. The customized guides were used for the distal resection for the chamfer cuts as well as the notch cuts.
Laminar spreaders were used medially and laterally and the meniscus were then debrided. Soft scar tissue was debrided and posterior osteophytes were then removed. The flexion and extension gap was balanced.
The patellar resection was performed. Drill holes were made in the patella. Patella was then placed into position. The trial femur was then placed in the position followed by the trial tibia after preparation of the tibial surface.
Poly was then placed into position. The knee was then trialed through a full physiological range of motion. The patellar tracking was good. Full-extension was obtained. Full flexion was obtained.
The trial components were then removed. Thorough lavage was given. The femur was cemented into position. Excess cement was removed. The tibia was cemented into position. Excess cement was removed. The poly was then placed into position.
The knee was then held in full extension with a bump under the ankle. The patella was then cemented into position and excess cement was removed. The patella was held in position with a patellar clamp.
After the cement hardened, a thorough lavage was given. Medial parapatellar arthrotomy was closed with O Vicryl and Stratafix. Cutaneous tissues ware closed with 2-O Vicryl.
Subcuticular tissues were closed with 2-0 Vicryl, and the skin was then closed. The closure was done by the plastic surgeon. A sterile dressing was then applied over the wound. The patient was then placed in a knee immobilizer and then transferred to the postoperative care unit in stable condition.
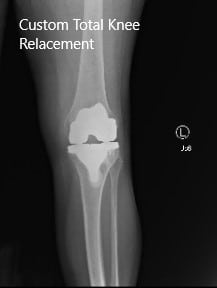
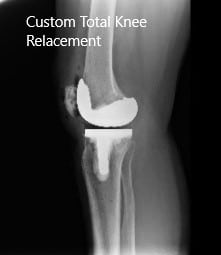
Post-Operative X-ray images showing AP and Lateral view:
The patient had an excellent recovery post arthroplasty. Her surgical wound was clean, dry and intact. The patient underwent an extensive program of physical therapy and a home exercise program.
During subsequent visits, she demonstrated a full range of motion with no pain. She stated she is now able to carry her daily activities without pain. She has since returned to work stating that she feels more motivated towards her work.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
