Fractures of the Spine
If spine pain intensifies, disrupts daily activities, or is accompanied by swelling and redness, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. At Complete Orthopedics, our experienced team specializes in addressing spine issues with customized treatment plans and surgical options. We prioritize understanding your symptoms, identifying the underlying causes, and recommending the most appropriate treatments or surgeries.
Our clinics are conveniently located across New York City and Long Island, and we partner with six leading hospitals to ensure you receive top-quality care for spine issues. Schedule an appointment with one of our orthopedic surgeons online or by phone. Learn about the causes and treatments for spine pain and determine when surgery might be necessary.
Overview
Fractures of the vertebral column commonly result from motor vehicle accidents, a fall from a height, gunshot injuries, or sports injuries. The compression fractures of the vertebra commonly result in trivial falls in the elderly population as a result of osteoporosis. The fractures of the spine may sometimes be managed with conservative treatment such as bracing but occasionally may require operative management.
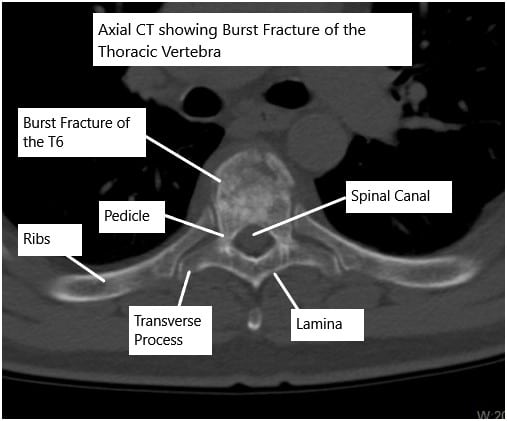
CT scan of the thoracic spine showing a burst fracture of the T6 vertebra.
The vertebral column consists of vertebra stacked on each other providing a safe conduit for the spinal cord. The spinal cord transmits signals from the brain that help in the movement of the four limbs. The spinal cord also gives branches known as spinal nerves at each level that travel to the part they supply.
Symptoms
The symptoms of spine fractures depend upon the nature of fracture and the inciting event leading to fracture. The spine fractures resulting from high-intensity injuries such as fall from height or motor vehicle accident usually involve injuries to other organs/body-parts as well. On the other hand, osteoporotic compression fractures are usually asymptomatic for a period of time.
Commonly the mid-back or the lower back is involved in spine fractures and the symptoms depend upon the part of the segment fractured. The fractures of the mid and the lower back may be potentially dangerous due to the narrow spinal canal. The blood supply of the spine is also precarious in the thoracolumbar area and the area acts as a fulcrum of motion of the spine.
In cases where only the front of the vertebra gets fractured and the back of the vertebrae is intact, it is known as the flexion type of spine fracture. These fractures usually do not result in loss of neurological function and are considered stable fractures.
Usually, as a result of fall from a height, both the front and the back of the vertebral body lose height. These types of fractures are known as burst fractures and may be associated with neurological injuries.
Extension fractures typically occur as a result of motor vehicle accidents where the pelvis is stabilized by the car seatbelt and the upper spine moves forward. The extension fractures may lead to instability of the spine and neurological injury.
Fracture dislocation injuries involve a fracture of a part of the vertebrae with damage to the soft tissue structures required for stabilizing the spine. These injuries may lead to serious damage to the spinal cord.
Whiplash injuries are common in the neck due to excessive forward and backward motion of the spine in a motor vehicle accident. The various ligaments and muscles attached to the vertebral column may be torn or strained to lead to instability. There may be bulging of intervertebral disks leading to spinal cord compression.
The symptoms of spinal fractures depend upon the level involved. There is severe pain in the spine which gets worse on movement. The involvement of the spinal cord or spinal nerves may lead to weakness and numbness in the legs in the case of thoracic and lumbar involvement. There may be a loss of bowel and bladder control.
In the case where the spine fracture is sustained because of trauma, the patients need emergency management. Once the patients are stabilized at the hospital, a thorough evaluation of their injuries is made. The physician tests for the neurological integrity in the patient and any signs suggesting neurological damage.
Types of Spine Fractures
Compression Fractures: Often caused by osteoporosis, these fractures occur when the vertebrae collapse under pressure. They are common in older adults and can cause chronic pain and deformity.
Burst Fractures: These result from severe trauma, leading to the vertebra breaking into multiple pieces. Burst fractures can cause spinal cord injury due to bone fragments pressing against the cord.
Flexion-Distraction Fractures: Also known as Chance fractures, these are typically associated with high-speed car accidents where the body is thrown forward, causing the spine to flex and then extend violently.
Fracture-Dislocations: These are severe injuries where the vertebrae are fractured and displaced. They often involve spinal cord injury and require immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis
Radiological tests are done which include X-rays, CT scans, and MRI. The radiological studies help determine the nature of fracture and the degree of spinal cord damage. The radiological studies also help in planning surgical management if needed.
Treatment
The treatment depends upon the type of fracture, the segment involved, other injuries and their treatment, and the presence or absence of neurological injury. Flexion type injuries or stable fractures are generally treated with bracing of the spine for 2-3 months and physical rehabilitation once the fracture unites.
In cases of spinal instability or neurological damage, surgical management is usually done in the form of laminectomy with spine stabilization. The stabilization is usually done in the form of fusion with screws and rods in the adjacent vertebrae. In compression fractures of the spine resulting from osteoporosis, kyphoplasty or vertebroplasty may be done.
The ultimate goal of surgery is to relieve the pressure on the spinal cord and stabilize the segment involved. The surgery may be performed from the front, from the sides, or from the back.
As with any surgery, there may be a risk of complications in the form of bleeding, infection, instrument failure, blood clots, spinal fluid leakage, non-union of the fracture, etc. The spine surgeries are followed by a period of extensive rehabilitation and the ultimate return to previous activity depends upon the initial spine damage.
Complications
Complications from spine fractures can be serious and include:
- Chronic Pain: Persistent pain even after the fracture has healed.
- Deformity: Such as kyphosis, where the spine curves abnormally.
- Neurological Deficits: Permanent loss of function or sensation below the level of the injury.
- Paralysis: In severe cases involving the spinal cord.
Prevention and Management of Osteoporosis-Related Fractures
Osteoporosis is a significant risk factor for spine fractures, especially in older adults. Managing osteoporosis involves:
- Medication: Drugs like bisphosphonates help strengthen bones.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, regular weight-bearing exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Fall Prevention: Ensuring home safety to prevent falls, which are a common cause of fractures in osteoporotic individuals.
Conclusion
Spine fractures are a serious medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment to prevent long-term complications. Understanding the types of fractures, their symptoms, and treatment options can help in managing these injuries effectively and improving outcomes for those affected. Regular check-ups and osteoporosis management are essential in preventing fractures, especially in at-risk populations like older adults.
Do you have more questions?
What causes spine fractures?
Spine fractures can be caused by trauma such as car accidents, falls, sports injuries, or conditions like osteoporosis weakening the bones.
Can osteoporosis lead to spine fractures?
Yes, osteoporosis weakens bones, making them more prone to compression fractures, especially in older adults.
Are all spine fractures equally severe?
No, the severity of spine fractures varies depending on factors like the type of fracture, location, and involvement of the spinal cord or nerves.
How can I tell if I have a spine fracture?
Symptoms include severe back or neck pain, numbness or tingling, weakness, or loss of bladder or bowel control. Imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans help diagnose spine fractures.
What are the treatment options for spine fractures?
Treatment varies from conservative management with pain relief and physical therapy to surgical intervention for severe fractures, depending on the type and severity.
What is involved in surgical treatment for spine fractures?
Surgical options include spinal fusion to stabilize the spine or decompression surgery to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
How effective is rehabilitation after spine fracture treatment?
Rehabilitation, including physical therapy, is crucial for recovery, helping restore strength, flexibility, and function.
Can spine fractures lead to long-term complications?
Yes, complications can include chronic pain, deformity, neurological deficits, or even paralysis in severe cases involving spinal cord injury.
Can spine fractures be prevented?
Prevention strategies include managing osteoporosis with medication, lifestyle changes like proper nutrition and exercise, and fall prevention measures.
What are the risks associated with osteoporosis-related fractures?
Osteoporosis-related fractures can lead to chronic pain, deformity, loss of independence, and increased mortality, particularly in older adults.
Is surgery always necessary for spine fractures?
No, surgery is reserved for severe fractures with spinal instability or neurological involvement. Minor fractures may be managed conservatively.
How long does it take to recover from a spine fracture?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the fracture and the chosen treatment approach, but it typically involves weeks to months of rehabilitation.
Can spine fractures cause permanent disability?
Yes, severe spine fractures, especially those involving spinal cord injury, can result in permanent neurological deficits or paralysis.
Are there any complications associated with surgical treatment for spine fractures?
Complications can include infection, blood clots, nerve injury, or failure of the surgical hardware.
Can spine fractures recur after treatment?
While rare, spine fractures can recur, especially in individuals with osteoporosis or those involved in high-risk activities.
Is there a difference in treatment for different types of spine fractures?
Yes, treatment varies based on the type and severity of the fracture, as well as the patient’s overall health and individual circumstances.
Will I need to wear a brace after spine fracture treatment?
It depends on the type and severity of the fracture. Some patients may benefit from wearing a brace to support the spine during healing.
What is the success rate of surgical treatment for spine fractures?
Success rates vary depending on factors like the type of fracture, patient’s overall health, and surgical technique, but outcomes are generally favorable for appropriately selected patients.
Can spine fractures cause psychological effects?
Yes, coping with the physical limitations and potential long-term consequences of spine fractures can lead to psychological distress, including anxiety and depression
How can I prevent falls and reduce my risk of spine fractures?
Fall prevention measures include removing hazards at home, installing grab bars and handrails, wearing proper footwear, and participating in balance exercises.
Will I need to take medication for osteoporosis indefinitely?
The duration of osteoporosis medication depends on individual risk factors, response to treatment, and ongoing assessment by a healthcare provider.
Can spine fractures affect my ability to work or perform daily activities?
Yes, spine fractures, especially if they result in chronic pain or disability, can impact a person’s ability to work or engage in activities of daily living.
Are there any dietary supplements that can help with spine fracture recovery?
Calcium and vitamin D supplements are often recommended to support bone health and aid in fracture healing, but it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
What should I do if I suspect I have a spine fracture?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms like severe back or neck pain, numbness or weakness, or loss of bladder or bowel control. A healthcare provider can perform a thorough evaluation and recommend appropriate treatment.
Can spine fractures lead to other spinal conditions like arthritis?
Yes, spine fractures can increase the risk of developing conditions like spinal arthritis, especially if the fracture causes joint instability or abnormal alignment.
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.

