Spine Tumors
Spinal tumors are an abnormal growth of tissue within or surrounding the spinal cord. The abnormal growth of the tissues is unchecked by the natural cellular mechanisms to halt the growth. Depending upon their cancerous (metastatic) potential, they may be benign (noncancerous), low-grade cancerous, or highly cancerous.
The spinal tumors may arise from the spinal column directly, which are known as primary spinal tumors. The tumors may also be implanted in the spinal column from another body part/organ known as secondary tumors or metastasis.
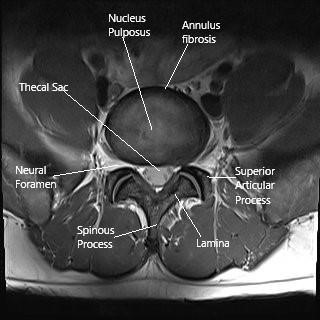
MRI of the lumbar spine in the axial section.
The spinal tumors are further classified depending upon their location in relation to the spinal cord. Intradural extramedullary tumors are contained within the spinal cord’s lining (dura mater) but outside the spinal cord tissue. Intradural intramedullary tumors are located inside the tissue of the spinal cord. Extramedullary tumors are situated outside the lining of the spinal cord and commonly arise from the vertebral bodies.
Intradural Extramedullary Tumors
The intradural extramedullary tumors represent the majority of the primary central nervous system spinal tumors. These tumors being outside the spinal cord tissue but inside their lining create a pressure effect on the cord. These are usually associated with back pain, which is more intense at night.
The tumors may also cause compression syndromes like cauda equina or central cord compression. There may be loss of bowel bladder function with weakness and numbness of the extremities. Patients may also complain of a radicular pattern of pain due to compression of specific nerve roots.
Schwannoma and Meningioma are common intradural extramedullary tumors. Schwannomas commonly affect middle-aged men/women and are mostly non cancerous. Schwannomas may be associated with a genetic disease known as Neurofibromatosis type 2.
Meningiomas occur more frequently in women and commonly affect the mid-back (thoracic spine). As with schwannomas, meningiomas are also commonly associated with neurofibromatosis type 2.
Intradural Intramedullary Tumors
The spinal tumors that arise within the spinal cord tissue often initially present with bowel/bladder dysfunction. These tumors often occur in children but may also affect adults. Patients often complain of weakness of the limbs associated with numbness in one or more regions along with bladder/bowel dysfunction.
Ependymomas and astrocytomas are intramedullary tumors arising from the spinal cord tissue. Astrocytomas commonly affect children and adults in their third decade. Ependymoma affects the spinal cord, often causing shape changes in the vertebral bodies.
Extradural Tumors
The extradural tumors are located outside the spinal cord’s lining and are commonly a result of advancing cancer in another part of the body. Cancer, in another part of the body, such as the prostate or breast, may spread to the spine when left unchecked. The tumor cells may reach the spine via blood or the CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) from their primary location. Rarely lymphomas may occur in the spine, usually affecting the cervical spine.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of spinal tumors is made after thorough clinical examinations along with radiological tests and tissue biopsies. An X-ray is usually the first test done in case of a suspected spine tumor and is usually followed by an MRI that can clearly define the spine’s soft tissue structures. Multiple areas may be subjected to radiological tests to look for metastasis and to find the primary tumor in case of spine metastasis. Other radiological tests, such as bone scans, may be used.
Tissue biopsies are performed to diagnose correctly and may also be used to stage the tumor. The biopsied tissue may help the surgeon decide between the various treatment options that may be used for best results.
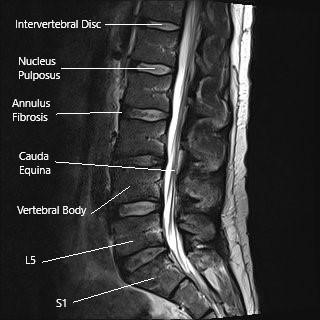
MRI of lumbar spine in sagittal section
Management
The treatment of spine tumors depends upon various factors such as the type of tumor, size, location, stage, age of the patient, etc. The treatment usually involves surgical resection of the tumor followed by chemotherapy or radiation therapy. With the advancement of spinal surgical techniques and early detection by imaging, most patients have an excellent prognosis with treatment.
Do you have more questions?
How common are spine tumors?
Primary spine tumors are rare, while metastatic spine tumors are more common, affecting up to 70% of cancer patients.
What types of spine tumors are most common?
The most common types of spine tumors are metastatic tumors. Among primary tumors, hemangiomas (benign vascular tumors) are common, followed by osteoid osteomas, osteoblastomas, and chondrosarcomas.
How are spine tumors diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically begins with imaging studies like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI. A biopsy may be performed to determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant and to guide treatment.
What is the prognosis for patients with spine tumors?
The prognosis depends on the type of tumor. Benign tumors generally have an excellent prognosis after surgical removal. The prognosis for metastatic tumors varies, depending on the type of primary cancer and how early the tumor is detected.
Can spine tumors be benign?
Yes, benign tumors like osteoid osteomas, osteoblastomas, and hemangiomas can occur in the spine. While non-cancerous, they may still cause symptoms and require treatment if they compress the spinal cord or nerves.
What role does MRI play in diagnosing spine tumors?
MRI is crucial for evaluating soft tissue structures, bone marrow involvement, and the relationship of the tumor to the spinal cord and nerves. It provides detailed information that helps in planning treatment.
Is surgery always necessary for spine tumors?
Surgery is often recommended for symptomatic spine tumors, especially if they cause neurological symptoms, spinal instability, or pain. However, for some benign tumors or tumors responding well to chemotherapy or radiation, surgery may not be necessary.
What are the surgical options for spine tumors?
Surgical options include tumor removal, spinal stabilization (with rods and screws), vertebroplasty (cement augmentation), and, in some cases, total en bloc spondylectomy (removal of an entire vertebra).
How are metastatic spine tumors treated?
Treatment for metastatic tumors often focuses on palliative care, including pain relief, radiation therapy, and surgery to stabilize the spine if necessary. Chemotherapy may be used depending on the type of primary cancer.
What is vertebroplasty, and when is it used?
Vertebroplasty involves injecting bone cement into the vertebra to stabilize it and relieve pain, often used in cases where the vertebra has weakened due to tumor growth or fracture.
Can spine tumors cause paralysis?
Yes, if a spine tumor compresses the spinal cord or nerves, it can lead to neurological deficits, including paralysis. Immediate treatment is crucial to prevent permanent damage.
What is the likelihood of a spine tumor recurring after surgery?
Recurrence depends on the type of tumor and how completely it was removed. Benign tumors like osteoid osteomas rarely recur if fully excised. Malignant tumors, however, may recur, particularly if not completely removed.
What is the role of radiation therapy in treating spine tumors?
Radiation therapy is used to shrink tumors, relieve pain, and improve neurological function. It is especially effective for metastatic tumors and some malignant primary tumors that are not amenable to surgery.
How can I tell if my back pain is from a spine tumor and not something else?
Back pain from spine tumors often has specific characteristics, such as worsening at night, being persistent despite rest, and being associated with other symptoms like numbness or weakness. Imaging studies are needed for a definitive diagnosis.
What is stereotactic radiosurgery, and how is it used for spine tumors?
Stereotactic radiosurgery is a precise form of radiation that delivers high doses of radiation directly to the tumor with minimal damage to surrounding tissues. It is often used for metastatic tumors and some primary tumors.
Can children develop spine tumors?
Yes, though rare, children can develop both benign and malignant spine tumors. Common pediatric spine tumors include osteoid osteomas, osteoblastomas, and Ewing’s sarcoma.
How do spine tumors affect mobility?
Spine tumors can impair mobility by causing pain, spinal instability, or neurological symptoms like weakness or paralysis. Treatment is aimed at relieving these symptoms and restoring mobility where possible.
Is there a genetic predisposition to developing spine tumors?
Some spine tumors, particularly primary tumors like chordoma, may have genetic links, but most occur sporadically without a known family history or genetic cause.
What happens if a spine tumor is left untreated?
If left untreated, spine tumors can grow, causing increased pain, spinal instability, and neurological deficits, including paralysis. Malignant tumors may metastasize to other areas of the body.
How are primary malignant spine tumors treated differently from metastatic tumors?
Primary malignant tumors are often treated with a combination of surgery (aiming for complete removal) and radiation or chemotherapy, depending on the type of cancer. Metastatic tumors typically focus on relieving symptoms, stabilizing the spine, and slowing tumor growth rather than aiming for a cure.
How long is the recovery period after surgery for spine tumors?
Recovery time depends on the type of surgery and the patient’s overall health. Minimally invasive procedures may require only a few weeks of recovery, while more extensive surgeries, like en bloc spondylectomy, may require several months.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
