Facet Joint Syndrome
If spine pain becomes more severe, interferes with daily activities, or is accompanied by swelling and redness, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. At Complete Orthopedics, our expert team specializes in addressing spine problems with customized treatment plans and surgical solutions. We focus on understanding your symptoms, identifying the underlying causes, and recommending the most suitable treatments or surgeries.
Our clinics are conveniently located throughout New York City and Long Island, and we have affiliations with six top hospitals, ensuring you receive the highest quality care for spine conditions. Schedule an appointment with one of our orthopedic surgeons online or by phone. Learn about the causes and treatments for spine pain and understand when surgery might be necessary.
Oveview
Facet joint syndrome is a condition resulting from degeneration of the facet joints in the vertebral column. The facet joint syndrome commonly affects the facet joints in the cervical spine or the lumbar spine. The patients suffering from facet joint syndrome may complain of neck pain or low back pain. The pain may be localized to the involved area or may radiate to other parts of the body.
Anatomy of Lumbar Spine
The facet joints provide stability to the vertebral column and aid in the movement of the spinal column. Each vertebra has two pairs of facet joints, one pair facing upwards connecting with the vertebrae above and the other pair facing downwards, connecting with the vertebra below. The facet joints through sliding and gliding motion, help in bending, extending, and twisting the spine.
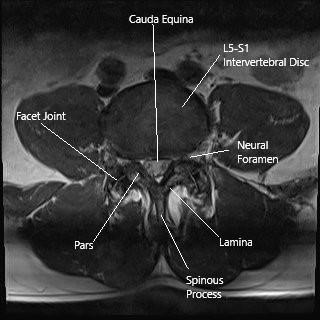
Axial section of the lumbar spine showing the facet joints.
The facet joint like some other joints in the body are synovial joints which are covered by a joint capsule. The ends of the bones forming the facet joints are covered with a protective tissue known as the articular cartilage. The capsule of the joint secretes a watery thin fluid called synovial fluid to lubricate and nourish the joint.
Facet Joint Syndrome Causes
With advancing age the intervertebral disk between the adjoining vertebrae loses water content that may lead to small tears in the disk. The loss of water content of the disk leads to loss of disk height. The instability from loss of disk height may lead to additional stress on the facet joints leading to facet joint degeneration.
The wear and tear of the joint leads to loss of articular cartilage and thinning of the joint capsule. The inner synovial lining of the joint capsule gets inflamed causing pain. The degeneration of the facet joint leads to the rubbing of the bones and the resulting instability may result in the formation of bone spurs. The bone spurs may impinge the exiting nerve roots and cause radiculopathy.
Facet joint degeneration may also occur in patients who are involved in excessive movements of the spine. The repetitive bending, extending, and twisting motions on the facet joint may lead to wear and tear of the facet joints. The wear and tear are especially common in the lumbar spine as the lumbar spine is the major weight-bearing part of the spine.
Cervical spine facet joint syndrome may result from traumatic neck injuries such as whiplash injury. The mid-back known as the thoracic spine is rarely affected by facet joint syndrome as the segment has little movement secondary to the attachment of the ribs.
Facet Joint Syndrome Symptoms
The symptoms of facet nerve syndrome result from irritation of the joint during motion as the bones devoid of the cartilage rub against each other. The irritated and inflamed joint sends a signal to the brain via the medial branch nerve causing the sensation of pain.
The pain is usually a dull ache located in the segment of the involved spine. The pain gets worse after periods of inactivity and may be associated with stiffness. The pain may refer to the buttocks or upper thighs in the case of lumbar facet joint syndrome. In the case of cervical facet joint syndrome, the pain may refer to the upper back and shoulders. The pain gets worse on activities such as bending backward and twisting movements.
The patients may experience relief on activities that offload the weight from the joint such as bending forward and sitting. The bone spurs may impinge upon the nerve roots and cause symptoms of radiculopathy. The radiculopathy symptoms consist of shooting pain down the leg/foot in case of lumbar involvement and shooting pain down the arm/hand in case of cervical involvement.
Facet Joint Syndrome Diagnosis & Management
The diagnosis of facet joint syndrome is made by a spine orthopedic surgeon after a detailed history and examination. The physician will extract a detailed history of the symptoms and the events leading to them. Various physical examination tests are done to localize the segment of the spine involved and rule out other causes of pain.
A detailed neurological examination is done to look for any motor sensory loss and signs of radiculopathy. Radiological tests are usually followed in the form of an X-ray and an MRI. The facet joints along with any bone spurs are usually visualized on an X-ray. The MRI allows detailed visualization of soft tissue structures.
A diagnostic facet nerve injection test may be done in patients with facet joint syndrome. The procedure involves the injection of a mixture of lidocaine (a numbing medication) and cortisone (a steroid medication) in the facet joint under fluoroscopic guidance. If the patient experiences immediate relief due to the action of lidocaine, a diagnosis of facet joint syndrome is likely.
The facet joint injection also serves as a therapeutic tool in such patients. Multiple injections may be administered over time leading to prolonged periods of relief. The cortisone in the injection reduces inflammation in the joint and the surrounding tissues leading to relief.
Conservative management in the form of medications such as NSAIDs and muscle relaxants, heat and cold therapy, and physical therapy are usually the first line of treatment in the management of facet joint syndrome. The physical therapy is directed towards posture training and muscle strengthening exercises. Physical therapy along with medications provides significant relief in the vast majority of the patients.
Surgical management is reserved for patients who are unable to benefit from conservative management. The initial surgical options include facet nerve injections and radiofrequency ablation of the medial branch nerve. Surgeries such as lumbar fusion are rarely performed in patients in whom all other treatment options have been tried and failed.
Prognosis
The prognosis for Facet Joint Syndrome varies depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. Many individuals experience significant relief with appropriate management, though the condition may be chronic and require ongoing treatment to manage symptoms. With a combination of medical treatments, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications, most patients can achieve a good quality of life and maintain their daily activities
Preventive Measures
Preventing Facet Joint Syndrome involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and taking measures to protect the spine:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps strengthen the muscles supporting the spine. Activities such as swimming, walking, and yoga can improve flexibility and reduce the risk of joint degeneration
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients helps maintain an optimal weight and supports overall joint health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, calcium, and vitamin D are particularly beneficial
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Ensuring proper posture at work and during daily activities reduces strain on the spine. Using supportive chairs, adjusting computer monitors to eye level, and taking regular breaks to stretch can help maintain spinal health
- Avoiding Heavy Lifting: When lifting objects, it is essential to use proper techniques, such as bending at the knees and keeping the back straight, to prevent injury to the spine and facet joints
Conclusion
Facet Joint Syndrome is a common condition that can cause significant discomfort and affect daily activities. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help manage the condition effectively and improve the quality of life for those affected. With a combination of medical interventions, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and preventive measures, individuals with Facet Joint Syndrome can achieve long-term relief and maintain their daily functions. For more detailed information and guidance, consulting healthcare professionals and referring to comprehensive reviews and guidelines on facet joint interventions is recommended
Do you have more questions?
What exactly are facet joints and their function?
Facet joints are small synovial joints located between and behind adjacent vertebrae in the spine. They provide stability and help guide motion, allowing for flexion, extension, and rotation of the spine. These joints are critical for maintaining the spine’s flexibility while preventing excessive movement that could damage the spinal cord and nerves.
How does Facet Joint Syndrome develop?
Facet Joint Syndrome develops primarily due to degenerative changes in the facet joints, often from aging. The cartilage in the joints wears down, leading to arthritis and inflammation. Injury, repetitive stress, poor posture, obesity, and genetic predispositions can also contribute to its development.
What are the main symptoms of Facet Joint Syndrome?
The main symptoms include:
- Localized pain in the lower back, middle back, or neck.
- Radiating pain to the buttocks, thighs, or shoulders.
- Stiffness and reduced mobility, particularly after inactivity.
- Tenderness around the affected joints.
- Increased pain with movement, such as twisting, bending, or lifting.
How is Facet Joint Syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves:
- Medical history and physical examination to assess pain points and mobility.
- Imaging studies like X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to visualize joint degeneration.
- Diagnostic injections where a local anesthetic is injected into the joint; relief from this injection confirms the facet joint as the pain source.
What non-surgical treatments are available for Facet Joint Syndrome?
Non-surgical treatments include:
- Medications such as pain relievers and muscle relaxants.
- Physical therapy with exercises to strengthen and stretch supporting muscles.
- Interventional procedures like facet joint injections and radiofrequency ablation.
- Lifestyle modifications including weight management and posture improvement.
How effective are facet joint injections?
Facet joint injections, typically containing steroids, can be very effective in reducing inflammation and pain. They provide temporary relief, which can last from several weeks to months. This procedure is often used when other conservative treatments have not been effective.
What is radiofrequency ablation and how does it help?
Radiofrequency ablation uses heat generated by radio waves to disrupt the nerve supply to the painful facet joint. This procedure can provide longer-term pain relief, often lasting from 6 months to 2 years, by effectively “turning off” the pain signals from the affected joint.
When is surgery considered for Facet Joint Syndrome?
Surgery is considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief. Procedures like spinal fusion or facet joint replacement may be performed to stabilize the spine and alleviate pain by addressing the structural issues in the joints.
Can Facet Joint Syndrome be prevented?
While it can’t always be prevented, you can reduce the risk by maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, engaging in regular exercise, and using proper techniques when lifting objects to avoid injury.
Is Facet Joint Syndrome a chronic condition?
Yes, it can be a chronic condition. However, with appropriate management, including medical treatments, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications, many patients can control their symptoms effectively and maintain a good quality of life.
Are there any specific exercises recommended for Facet Joint Syndrome?
Exercises that strengthen the core muscles and improve flexibility are recommended. Low-impact activities like swimming, walking, and yoga can be beneficial. It’s best to work with a physical therapist to develop a tailored exercise program.
How do weight and obesity affect Facet Joint Syndrome?
Excess weight increases the load on the spine, accelerating the wear and tear on the facet joints. Managing weight through a healthy diet and regular exercise can reduce the strain on the spine and alleviate symptoms.
How long does it take to see improvements with treatment?
The time frame for improvement varies. Some patients may see relief within a few weeks of starting treatment, while others may take longer. Consistent adherence to treatment plans, including physical therapy and lifestyle modifications, is essential for optimal results.
What role does physical therapy play in managing Facet Joint Syndrome?
Physical therapy plays a crucial role by:
- Improving spinal stability and flexibility.
- Reducing muscle tension and pain.
- Teaching proper body mechanics and posture.
- Providing personalized exercise programs to strengthen supporting muscles.
Can poor posture alone cause Facet Joint Syndrome?
While poor posture alone may not directly cause Facet Joint Syndrome, it can contribute significantly to the condition by placing undue stress on the spine and facet joints, accelerating degenerative changes.
What are the potential side effects of facet joint injections?
Potential side effects include:
- Temporary increase in pain at the injection site.
- Infection.
- Bleeding.
- Allergic reactions to the injected substances.
- Nerve damage, though rare.
How often can I receive facet joint injections?
Facet joint injections can be administered several times a year, depending on the patient’s response and pain levels. Typically, injections are spaced out by at least a few months to prevent overuse of steroids and potential side effects.
Are there any alternative therapies for Facet Joint Syndrome?
Alternative therapies may include:
- Acupuncture.
- Chiropractic care.
- Massage therapy.
- Mind-body techniques like yoga and meditation.
These therapies can complement conventional treatments but should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
How does aging affect the facet joints?
Aging leads to the degeneration of cartilage in the facet joints, resulting in arthritis. The joints lose their smooth surface, causing pain and inflammation. Aging also leads to decreased flexibility and strength, contributing to joint stress.
Is Facet Joint Syndrome the same as arthritis?
Facet Joint Syndrome is a type of arthritis affecting the facet joints in the spine. It involves similar degenerative processes and symptoms, including pain and stiffness, as seen in other types of arthritis.
Can children or adolescents develop Facet Joint Syndrome?
While rare, children and adolescents can develop Facet Joint Syndrome, typically due to trauma or congenital abnormalities. It is more commonly seen in adults due to degenerative changes.
What dietary changes can help manage Facet Joint Syndrome?
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help manage inflammation. Avoiding processed foods, excessive sugar, and unhealthy fats is also beneficial.
How do I know if my back pain is from Facet Joint Syndrome or another condition?
A thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider, including a physical exam, imaging studies, and possibly diagnostic injections, is necessary to determine if back pain is from Facet Joint Syndrome or another condition, such as a herniated disc or spinal stenosis.
Can facet joint problems lead to other complications?
If left untreated, Facet Joint Syndrome can lead to chronic pain and reduced mobility. Severe degeneration can cause spinal instability and may contribute to the development of other conditions like spinal stenosis or spondylolisthesis.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
