Physical Therapy after Microdiscectomy
If spine pain becomes so severe that it disrupts daily life or is accompanied by swelling, tenderness, or redness, it’s important to seek medical attention.
At Complete Orthopedics, our expert spine specialists are adept at treating spine pain through both surgical and non-surgical means. We examine symptoms, diagnose the condition, and recommend suitable treatments, including surgery if necessary.
Serving New York City and Long Island, we partner with six hospitals to offer cutting-edge spine surgery and comprehensive orthopedic care. You can schedule a consultation with our orthopedic surgeons online or by phone.
Learn about the common causes of spine pain and the treatment options available, including when surgery might be the best choice.
Overview
Physical therapy forms an essential part of the rehabilitation following microdiscectomy surgery. Microdiscectomy surgery involves the removal of the herniated intervertebral disc to help patients suffering from back pain and sciatica. Following the surgery, physical therapy helps in both strengthening the muscles of the back and increasing the flexibility to prevent future herniations and complications.
Microdiscectomy
Microdiscectomy is a minimally invasive spine surgery commonly done for the surgical management of sciatica. Sciatica usually occurs as a result of the prolapse of an intervertebral disc. The intervertebral disc may prolapse as a result of age-related wear and tear or due to trauma as a result of fall or repetitive action.
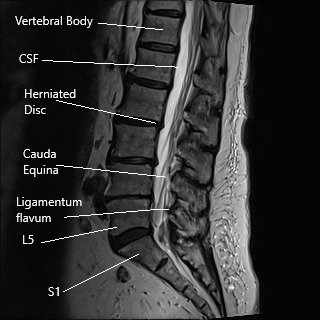
MRI of the lumbar spine in sagittal section.
Sciatica is usually managed with nonsurgical treatment and surgical treatment is only indicated in patients who have had no relief with the non-surgical measures. Microdiscectomy surgery involves a small incision in the lower back. The spine surgeon separates or cuts the muscles and tissues to reach the diseased disc. The herniated disc is then removed and pressure over the spinal nerve is relieved.
The surgeon then repairs and closes the incision in layers. A bandage is applied at the incision area and the incision usually heals in about 10 – 14 days.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy is usually held off during the initial postoperative period and is started around 2 weeks when the incision heals. During the initial 2 weeks, the post-operative pain subsides and the patients may no longer require narcotic pain medications. However, some physicians may recommend starting the physical therapy earlier or later than 2 weeks depending upon the patient’s condition.
Although targeted exercises may be withheld for about 2 weeks, the patients are advised to stay active after surgery by walking around and avoid complete bed rest.
Walking boosts blood flow throughout the body and helps to build cardiovascular endurance. The increased blood flow brings in more nutrients and oxygen to the tissues cut during surgery to help them heal.
Targeted physical therapy after microdiscectomy is aimed to strengthen the muscles around the diseased disc and also increase flexibility. The strength is achieved with graduated and repetitive exercises targeting the lower back muscles. Flexibility is increased with the help of targeted stretching.
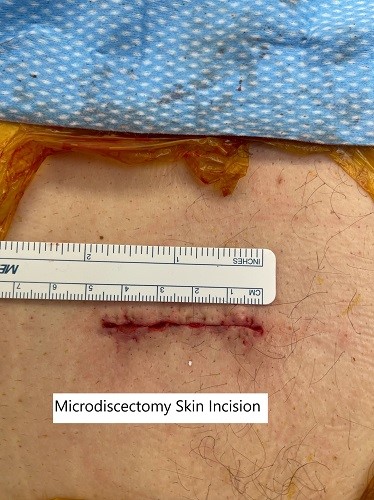
Intraoperative image showing the surgical skin incision after closure.
The physical therapist works with the patients to improve posture and gait. Maintenance of a proper posture is important to prevent excess strain on the ligaments and to prevent muscle deconditioning. Proper posture during the early postoperative period helps in the early healing of the tissues.
Prone and supine leg raises are strengthening exercises due the lower back and the abdominal muscles. The lower back muscles are activated when the exercise is performed by lying on the belly (prone) and the abdominal muscles are activated when lying on the back (supine).
In prone leg raise, the patients lay on their belly and slowly raise the leg backwards up in the air. The leg is held in the position for 1-2 mins and the exercise is repeated similarly with the other leg. Supine leg raise is performed similarly with the patients laying on their back and raising one leg while keeping it straight.
The abdominal muscles provide support in the front of the spine while the back muscles provide support from the back. The support acts as a deterrent to disc prolapse.
Alternate knees to the chest is another exercise for strengthening spine flexion. The patients while lying on their back with their knees bent try to bring one knee towards the chest with the help of their hands. The exercise is repeated similarly with the other knee.
Similarly exercise for strengthening the core muscles involves lying on the back with knees bent. The patients tried to flatten their lower back to touch the ground and hold their muscles in the position for 1-2 mins.
Core strengthening and hip strengthening exercises are also performed under supervision of the therapist to help in early recovery. The exercises not only strengthen the muscles but also decrease postoperative pain. Physical therapy allows the therapist and the physician to assess the patient’s ability to return to work.
Workplace analysis may also be performed by the therapist to aid in their smooth return to activities. Physical therapy forms one of the most important aspects of postoperative recovery of the patients.
With proper therapy, patients return to their baseline activists sooner and have decreased incidence of complications such as reherniation after microdiscectomy. Speak with your surgeon regarding physical therapy after microdiscectomy.
Importance of Postoperative Physical Therapy
Postoperative physical therapy aims to address several key aspects of recovery:
Pain Management: Postoperative pain can be managed effectively through targeted physical therapy exercises that help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Functional Recovery: Physical therapy helps restore the normal function of the spine and surrounding muscles, allowing patients to return to their daily activities more quickly.
Prevention of Recurrence: A structured physical therapy program can help strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, reducing the risk of recurrent disc herniation.
Conclusion
The success of microscopic endoscopic discectomy is greatly enhanced by a well-structured and compliant postoperative physical therapy program. By following a phased approach to rehabilitation, patients can achieve significant improvements in pain, disability, and overall function, while minimizing the risk of recurrence. The importance of patient education and adherence to the prescribed exercises cannot be overstated, as they are key factors in achieving the best possible outcomes.
Do you have more questions?
When should physical therapy begin after surgery?
Physical therapy typically begins one month after surgery, starting with gentle exercises and gradually progressing to more intensive rehabilitation as the healing process advances.
What types of exercises are included in the early phase of physical therapy?
Early phase exercises focus on gentle mobilization, such as pelvic tilts, abdominal bracing, and maintaining proper posture to minimize pain and prevent complications.
How does the dynamic phase of physical therapy help in recovery?
The dynamic phase (7 weeks to 6 months post-surgery) involves more challenging exercises to strengthen the core and back muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance overall stability, reducing the risk of future injuries.
What is the focus of the physical therapy program from 4-6 weeks post-surgery?
During this phase, the focus is on increasing mobility, initiating gentle strengthening exercises for the core and lower back, and emphasizing proper posture to support the healing process.
What activities can patients resume six months after surgery?
Six months post-surgery, patients can gradually return to normal activities and sports, focusing on low-impact, high-resistance exercises like swimming and cycling, and progressively reintroducing sport-specific drills.
What are the signs of a recurrent disc herniation?
Signs of a recurrent disc herniation include a return of symptoms such as lower back pain, leg pain, numbness, or weakness, similar to the symptoms experienced before the initial surgery.
How can patients prevent recurrence of lumbar disc herniation?
Patients can prevent recurrence by adhering to their physical therapy program, maintaining a strong core, practicing good posture, avoiding excessive strain on the spine, and staying active with appropriate exercises.
Can physical therapy help reduce the risk of needing repeat surgery?
Yes, a structured physical therapy program can significantly reduce the risk of recurrent disc herniation and the need for repeat surgery by strengthening the muscles supporting the spine and improving overall spinal stability.
Are there any risks associated with starting physical therapy too early?
Starting physical therapy too early can place excessive strain on the healing tissues, potentially leading to complications or delaying recovery. It is important to follow the recommended timeline and guidelines provided by the healthcare team.
What is the Visual Analog Scale (VAS), and how is it used in recovery?
The Visual Analog Scale (VAS) is a tool used to measure pain intensity. Patients rate their pain on a scale from 0 to 10, with 0 indicating no pain and 10 indicating the most severe pain. It helps track changes in pain levels during recovery.
What should patients avoid during the early postoperative period?
During the early postoperative period, patients should avoid activities that involve lifting, bending, twisting, or hyperextending the lumbar spine. They should also avoid prolonged sitting or standing and refrain from driving for at least two weeks.
What is the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI), and why is it important?
The Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) measures a patient’s degree of disability due to lower back pain. It assesses various aspects of daily life, including pain intensity, personal care, lifting, walking, sitting, standing, sleeping, social life, traveling, and employment/homemaking. It is important for evaluating the impact of surgery and physical therapy on a patient’s quality of life.
How does compliance with the physical therapy program affect outcomes?
Compliance with the physical therapy program is crucial for achieving the best outcomes. Regular participation in prescribed exercises helps strengthen the spine, reduce pain, improve function, and prevent recurrence of disc herniation.
What are some common exercises recommended in the later stages of physical therapy?
Common exercises in the later stages include dynamic lumbar stabilization exercises, core strengthening exercises (like planks and bird-dogs), proprioceptive exercises, and sport-specific training to gradually return to full activity.
How often should patients attend physical therapy sessions?
The frequency of physical therapy sessions may vary, but patients are typically advised to attend sessions 1-2 times per week initially, with adjustments based on progress and individual needs. Home exercises should be performed daily.
What role does patient education play in postoperative recovery?
Patient education is vital for ensuring that patients understand the importance of following their physical therapy program, practicing good posture, avoiding risky activities, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support their recovery.
Can physical therapy help with other conditions besides disc herniation?
Yes, physical therapy can help with a wide range of musculoskeletal conditions, including arthritis, tendonitis, muscle strains, joint injuries, and post-surgical rehabilitation for various orthopedic procedures.
How can patients manage pain during the rehabilitation process?
Patients can manage pain through a combination of prescribed pain medications, physical therapy exercises, heat or cold therapy, proper rest, and maintaining an active lifestyle within the recommended guidelines.
. How can patients ensure long-term success after microscopic endoscopic discectomy?
Long-term success can be ensured by adhering to the physical therapy program, maintaining a regular exercise routine, practicing good posture and body mechanics, staying active, and avoiding activities that may strain the spine. Regular follow-up visits with the healthcare provider are also important to monitor progress and address any concerns.
What should patients do if they experience increased pain or new symptoms during rehabilitation?
If patients experience increased pain or new symptoms, they should immediately contact their healthcare provider for evaluation. Adjustments to the physical therapy program or further medical assessment may be necessary.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
