Scoliosis
Scoliosis is the abnormal side to side curvature of the spine. The shape and size of the vertebrae in the cervical, thoracic and sacral segments result in a characteristic double ‘’S’’ shape of the vertebral column. The cervical spine is naturally bent with an inward curve, the thoracic is bent with an outward curve and the lumbar is bent with an inward curve. The natural curves of the spine help the spine in bearing weight and provide more flexibility in movement.
Scoliosis is defined as an abnormal “S” or “C” shaped curve in the side to side direction. The actual deformity is much more complex and occurs in the three dimensional space. Scoliosis may be classified according to the age of onset and the underlying cause of scoliosis.
Idiopathic scoliosis has no known cause of the abnormal curvature of the spine. Idiopathic scoliosis may be Infantile idiopathic scoliosis that affects children aged 3 or less. Juvenile idiopathic scoliosis affects children aged 4-10 and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis affects adolescents aged 10 – 18 years of age.
Adult scoliosis may be a remnant of adolescent scoliosis that was treated or left untreated. Degenerative spine conditions may cause scoliosis in the lower spine of the adults. Scoliosis may also occur as a part of a presentation of a syndromic disease. Neuromuscular diseases such as cerebral palsy may also cause scoliosis. In congenital scoliosis, the child is born with scoliosis.
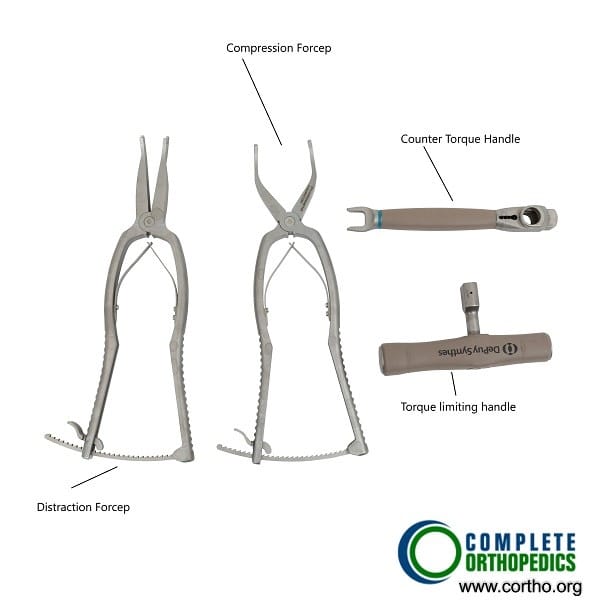
Compression and distraction instruments used in scoliosis surgery
Scoliosis Symptoms
The symptoms of scoliosis may just be limited to cosmetic abnormality. The patient with scoliosis may have uneven shoulders or waist. The head may not seem correctly placed in the line between the pelvis. The body may lean towards one side as the patient walks.
Back pain commonly accompanied scoliosis as the curve progresses. The patient usually complains of breathing difficulty as the severity of the curve increases. The heat and other organs may be affected in severe curves with curvature more than 100 degrees.
Scoliosis Diagnosis
The diagnosis of scoliosis is made by the Orthopaedic spine surgeon after extracting thorough history and conducting physical examination. The diagnosis of scoliosis is aided with radiological studies that also help in planning the surgery if needed and to check the progression of the curve.
Special views of the X-ray are needed to correctly calculate the degree of scoliosis and further classify the disease. CT scan results in a more detailed image of the bony spine and an MRI gives information of the soft tissue structures in the spine (nerves, spinal cord, ligaments, disk, etc).
Scoliosis Management
Most cases of infantile scoliosis resolve on their own by the age of 3 years. The physicians usually follow the patients every 6 months to check the progression of the curve. Infantiles in whom the progression of the curve is more than 5 degrees in a year may require casting to halt the progression and mould the deformity. The cast is changed every 2-4 months.
After a successful cast treatment bracing may be started. The bracing may also be done in children who do not tolerate casting. The operative procedure is reserved for patients in whom the curve progresses despite the casting/bracing.
Juvenile scoliosis with mild curves are regularly followed up every 6 months. Moderate scoliosis may be managed with bracing/casting and severe curves may require corrective surgery.
The surgery may involve fusion of the vertebrae either from the back or both from the front and the back. The fusion surgeries in children may result in abnormal prominence of the ribs in the case of posterior fusion and severe loss of height in case of combined fusion. Fusion led instruments such as growing rods and VEPTR (vertical expandable prosthetic titanium rib) system or growth modulation may be used to prevent the complications of fusion procedure.
Adolescent scoliosis is usually managed with frequent observation and bracing. The surgical correction of scoliosis in adolescents is done in cases of significant cosmetic deformity, uncontrolled pain and severe curves (>50 degrees).
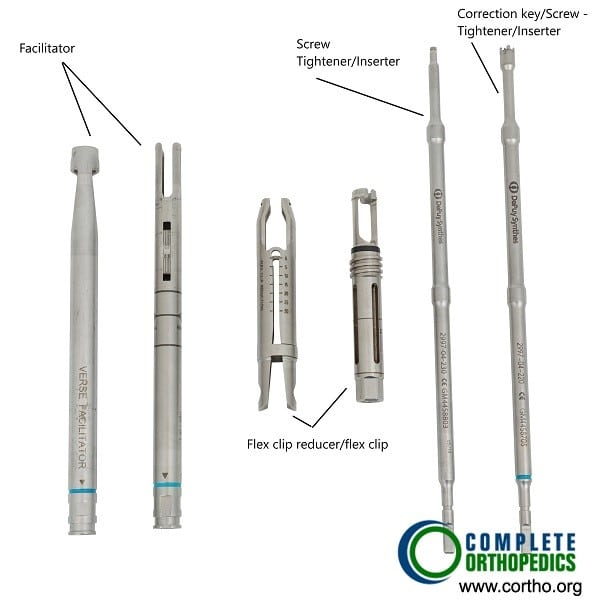

Reduction and de-rotation instruments used in Scoliosis surgery
The surgery may involve fusion of the facet joints or the vertebrae from the back with the help of screws/wires/cables. The prominent ribs may be corrected during the surgery. The corrective surgery may also be performed from the front in some patients. The corrective surgeries aim to correct the deformity and fuse the vertebrae to prevent further progression.
As with any surgical procedure there may be complications after the surgery. There may be neurological injury, infection, collapse of the lung or in some cases liquid/air may fill inside the chest cavity. There may also be a risk of failure of the surgery.
Do you have more questions?
What is the main cause of scoliosis?
Most cases of scoliosis are idiopathic, meaning there is no known cause. It often appears during adolescence, particularly in girls. However, congenital, neuromuscular, and syndromic forms have specific causes like abnormal vertebral formation or underlying neurological conditions.
How is scoliosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis begins with a physical examination, including the forward bending test. If scoliosis is suspected, X-rays are used to measure the degree of the spinal curvature. Additional tests, like MRIs, may be performed in more complex cases to rule out neurological causes.
Can scoliosis be prevented?
Idiopathic scoliosis cannot be prevented since its cause is unknown. Congenital scoliosis, which occurs due to spine malformations at birth, is also not preventable. Preventive strategies are not applicable for the majority of scoliosis types.
What are the risks if scoliosis is left untreated?
If untreated, curves greater than 50 degrees often continue to worsen, potentially leading to severe spinal deformities, chronic pain, and in rare cases, cardiopulmonary complications if the curve impinges on the lungs and heart.
What is the difference between structural and non-structural scoliosis?
Structural scoliosis involves a permanent curve with vertebral rotation, often requiring treatment. Non-structural scoliosis, or functional scoliosis, is a temporary curve without vertebral rotation and is often caused by factors like muscle spasms or differences in leg length.
What is the typical age when scoliosis develops?
Idiopathic scoliosis typically develops during adolescence, between the ages of 10 and 15, coinciding with growth spurts. However, congenital scoliosis is present at birth, and neuromuscular scoliosis can develop at any age depending on the underlying condition.
How often does scoliosis progress into adulthood?
Curves less than 30 degrees typically do not progress into adulthood after skeletal maturity. However, curves greater than 50 degrees tend to progress by about 1 degree per year, even after growth has stopped.
How does scoliosis affect physical activity?
Most individuals with mild to moderate scoliosis can engage in normal physical activity without restrictions. For severe cases, activities involving excessive twisting of the spine may need to be limited. Post-surgery, patients are often advised to avoid high-impact activities for a period to allow the spine to heal.
Can scoliosis cause back pain?
While back pain is not a common presenting symptom of idiopathic scoliosis, about 25% of adolescents with scoliosis report some back pain. Severe cases, or scoliosis related to other conditions, may cause significant pain due to muscle imbalances or nerve compression.
Is scoliosis hereditary?
Yes, there is a genetic component to scoliosis. Children and siblings of patients with idiopathic scoliosis have a higher likelihood of developing the condition. However, scoliosis does not follow a simple pattern of inheritance, and other factors likely play a role.
At what point is surgery recommended for scoliosis?
Surgery is generally recommended for curves greater than 45-50 degrees in growing patients or for curves that continue to progress after skeletal maturity. It is also considered when the patient experiences significant discomfort or deformity that affects daily activities.
Will bracing correct scoliosis?
Bracing does not correct scoliosis but is intended to prevent the curve from worsening during growth. It is most effective for curves between 25 and 40 degrees in growing children. Compliance with wearing the brace is crucial for its success.
What does scoliosis surgery involve?
The most common surgery for scoliosis is spinal fusion, which involves correcting the curve using rods, hooks, screws, and wires, then fusing the vertebrae with bone grafts. This procedure stabilizes the spine and prevents further progression of the curve.
Are there risks associated with scoliosis surgery?
As with any major surgery, there are risks, including infection, bleeding, nerve damage, or complications related to the anesthesia. However, advancements in surgical techniques have significantly improved safety and outcomes.
Can adults with scoliosis still be treated?
Yes, adults with scoliosis can be treated, although treatment options differ from those for children. Pain management, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery may be considered. Surgical correction in adults can improve symptoms but may not achieve the same level of curve correction as in children.
Can scoliosis cause respiratory or heart problems?
Severe scoliosis (usually curves greater than 90 degrees) can impact the chest cavity, restricting lung function and, in rare cases, putting pressure on the heart. This is more likely to occur if scoliosis is left untreated and allowed to progress.
What happens if scoliosis is detected after the child has stopped growing?
If scoliosis is detected after skeletal maturity, treatment options like bracing are no longer effective. Observation and periodic monitoring are used for smaller curves, while surgery may be considered for larger curves or if symptoms such as pain develop.
Is scoliosis screening necessary for children?
Screening programs for scoliosis, such as school-based screenings, are debated. Some organizations recommend routine screening for children between 10 and 14 years, while others argue that the benefits of routine screening are unclear, as it may lead to overdiagnosis.
Will scoliosis limit career choices?
For most individuals, scoliosis does not limit career choices or everyday activities. However, those with severe scoliosis, or who have undergone spinal surgery, may need to avoid careers that involve heavy lifting or physical strain on the back.
How can a parent help their child manage scoliosis?
Parents can help by ensuring their child attends regular medical check-ups, adheres to bracing schedules, and maintains a healthy lifestyle that includes physical activity. Providing emotional support is equally important, especially if the child is struggling with body image concerns.
Can scoliosis recur after surgery?
Once the spine has been fused during surgery, the area is stabilized, and the curve should not progress further. However, in rare cases, complications can occur that may require additional surgery, such as rod breakage or failure of the fusion to take hold.
Can scoliosis lead to arthritis?
Severe scoliosis can contribute to the early development of degenerative changes or arthritis in the spine due to abnormal wear and tear on the joints. This is more common in adults with untreated scoliosis.
How effective is physical therapy for scoliosis?
Physical therapy is generally used as an adjunct to other treatments for scoliosis, particularly for pain relief and improving flexibility. However, it is not a cure for scoliosis. Therapy can help improve posture and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine.
Is scoliosis painful for most patients?
Mild to moderate scoliosis is often painless and may not cause symptoms. However, more severe cases can cause discomfort, particularly in the lower back, and may lead to muscle fatigue. Postural imbalances due to scoliosis can also lead to pain over time.
What lifestyle changes can help manage scoliosis symptoms?
Staying physically active, maintaining good posture, and managing body weight can help alleviate symptoms of scoliosis. In some cases, modifications to workspaces and daily habits may reduce strain on the back.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
