Case Study: Custom Unilateral Knee
Replacement in a 74-year-old Female
A 71-year-old female presented to our office with complaints of bilateral knee pain (right greater than left) for the past four years. The patient stated that the pain was getting worse over time despite conservative management in forms of physical therapy, knee injections, and pain medications. The pain severely affected his daily activities such as walking and climbing stairs.
The patient was assessed at the office for surgical management of knee arthritis and was found a suitable candidate for total knee arthroplasty of the right knee. The patient was offered a custom knee replacement system. Risks, benefits, and alternatives were discussed thoroughly, and the patient went ahead for the procedure. The custom knee replacement system includes custom patient-specific implants with custom instrumentation.
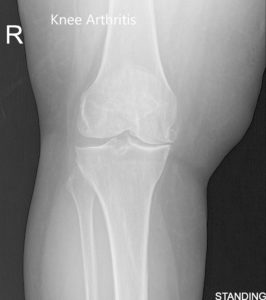
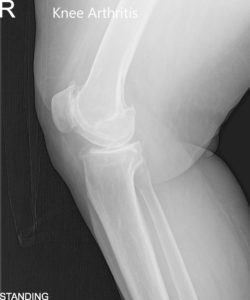
Pre-Operative AP and Lateral X-Ray views of the Right Knee
A preoperative CT scan of the right knee including the hip and ankle were obtained a few weeks prior to the surgery. The CT scan images are used to construct a 3D model of the patient’s anatomy. The information from the CT scan was used to create a unique patient-specific implant and instruments.
The instruments which were specific to the patient aided in reducing the amount of bone cut during surgery. The correctly sized patient-specific implant works in unison with the soft tissues of the knee resulting in a more natural feeling knee. The custom knee reduces the need to compromise soft tissues to work with an implant as in the case of off the shelf implants.
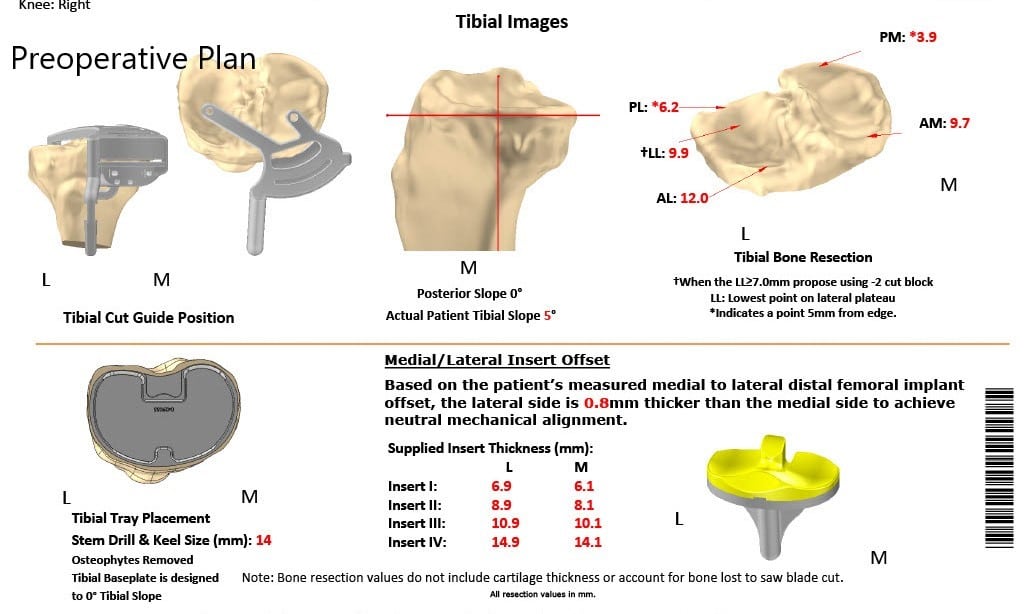
Complete Orthopedics patient-specific surgical plan for a custom unilateral knee replacement in a 74-year-old female.
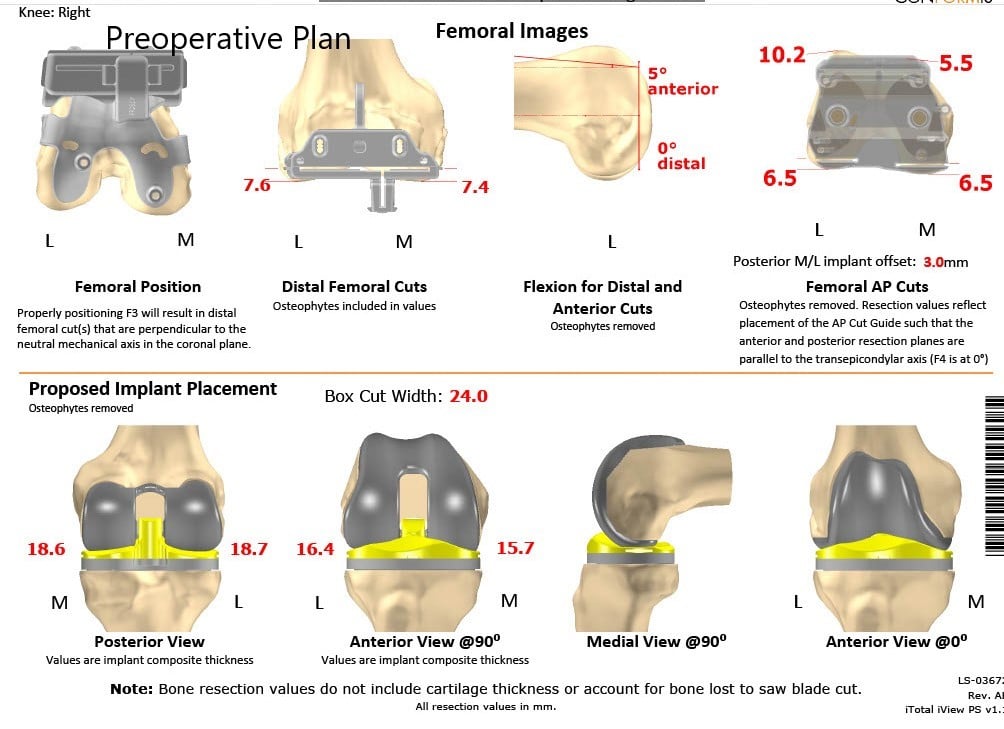
Complete Orthopedics patient-specific surgical plan for a custom unilateral knee replacement in a 74-year-old female (scan 2)
Operative reports:
The patient underwent Right Total Knee arthroplasty using custom total posterior stabilized knee with 14mm posterior stabilized polyethylene implant with custom tibial tray and patellar component.
The patient was brought to the operating room and anesthesia was obtained by the anesthesiologist. The patient was differently positioned and the right knee was then draped and prepped in the usual sterile manner. The cuff was placed over the right thigh. Time-out was performed. Antibiotics were given. Tourniquet was elevated after exsanguinating the limb.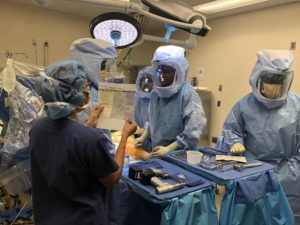
Skin, subcutaneous tissue were incised. Medial parapatellar arthrotomy was performed. The tibial surface was exposed and the jigs were then placed on the tibial surface and the tibial resection was performed. The resection angle was checked.
The tibia was drilled and broached. Attention was then turned towards the femur. The distal cut was made using the custom instrumentation. Anterior, posterior and chamfer cuts were made using custom instrumentation. The notch cut was then performed using custom instrumentation.
The laminar spreaders were used medially and laterally and the meniscus and the cruciates were then debrided. Posterior osteophytes were then removed. Attention was then turned towards the patella. The patellar resection was performed. Drill holes were made in the patella and the trial patella was then placed into position.
Attention was then turned towards the femur. The trial femur was placed into position followed by the trial tibia, and the trial poly was then placed into position. Knee was ranged through a full range of motion. The patellar tracking was excellent, stability was excellent. Gap balancing was excellent.
Trial components were then removed. Femur was cemented into position. Excess cement was removed. The tibia was then cemented into position. Excess cement was removed. The poly was then placed over the tibia and the knee was then reduced and held in full extension with a bump under the ankle. Patella was then cemented into position. Excess cement was removed.
After the cement hardened, the patellar clamp was removed. Medial parapatellar arthrotomy was closed with number 1 Vicryl and with Variax barbed suture.
Cutaneous tissues were closed with 0 Vicryl. Subcutaneous tissue closed with 2-0 Vicryl. The skin was closed using staples. Sterile dressing was then applied over the wound. The patient was then transferred to the postoperative care unit in stable condition.
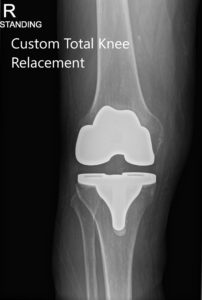
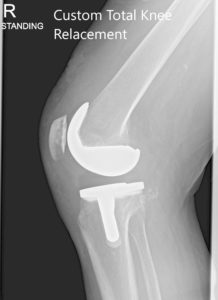
Post Operative X-ray of the patient’s right knee showing AP and Lateral Views
The patient was able to walk the same day after surgery and reported an excellent range of motion of the knee in the subsequent visits. She was able to drive and continue his daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs pain-free after a period of physical therapy. In the following subsequent post-operative visits, she reported no stiffness in the right knee with an excellent range of motion. The patient had excellent recovery from left knee arthritis pain due to offloading of weight from successful right total knee arthroplasty.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
