General Guideline Principles for Opioids: Initiating Transitioning
and Managing Long-Term Oral Opioids for workers
compensation patients
The New York State workers compensation board has developed these guidelines to help physicians, podiatrists, and other healthcare professionals provide appropriate treatment for Opioids: Initiating Transitioning and Managing Long-Term Oral Opioids.
These Workers Compensation Board guidelines are intended to assist healthcare professionals in making decisions regarding the appropriate level of care for their patients with ankle and foot disorders.
The guidelines are not a substitute for clinical judgement or professional experience. The ultimate decision regarding care must be made by the patient in consultation with his or her healthcare provider.
Opioids: Initiating Transitioning and Managing Long-Term Oral Opioids
Long haul Utilisation of Narcotics in the Narcotic Guileless Patient: Narcotic Helpful Preliminary
Overview of Opioids: Initiating Transitioning and Managing Long-Term Oral Opioids
A narcotic preliminary is a timeframe during which the viability of utilizing narcotics is tried to check whether the objectives of expanded capability and diminished pain are met. While considering long haul narcotic use, doctors ought to ensure that:
-
Other agony the executive’s systems, including physical, conduct and non-narcotic measures have fizzled, and
-
An effective narcotic preliminary somewhere in the range of 30 and 60 days, during which the patient exhibited maintained improvement in capability and torment levels, has been finished.
-
Patients ought to be observed week by week.
Objectives and Targets of Narcotic Preliminary of Opioids: Initiating Transitioning and Managing Long-Term Oral Opioids
An effective preliminary ought to meet the accompanying objectives:
-
Further developed capability, including return to work as well as expansion in exercises of day-to-day living, and basically a 30% decrease in pain,1 upheld by approved objective proportions of further developed capability and torment which ought to be plainly recorded. (See General Standards A.1, Clinical Consideration; A.3, Positive Patient Reaction; and A.4, Rethink Treatment.).
-
No critical antagonistic incidental effects; and
-
No unusual medication related ways of behaving.
If preliminary objectives are not met inside 30 to 60 days, the preliminary ought to be suspended, narcotics tightened/ceased, and another option approach taken to treating the aggravation.
In a specific level of patients, it will become obvious right on time in the time for testing that they are not answering this method of treatment.
For these patients, to limit the gamble of unfriendly clinical results like clinical reliance, the narcotic preliminary ought to be stopped when clinically doable. This direction ought to not be understood as requiring an entire 60-day time for testing.
Hazard Appraisal/Delineation of Opioids: Initiating Transitioning and Managing Long-Term Oral Opioids
Before considering a restorative narcotic preliminary, physical, and mental evaluation, including a full assessment for liquor or illicit drug use, reliance or misuse, ought to be directed.
-
Evaluating for likely comorbidities and hazard factors is critical so that expected gamble can be checked likewise. Individual or family background of substance misuse is the most grounded prescient component for abuse.
-
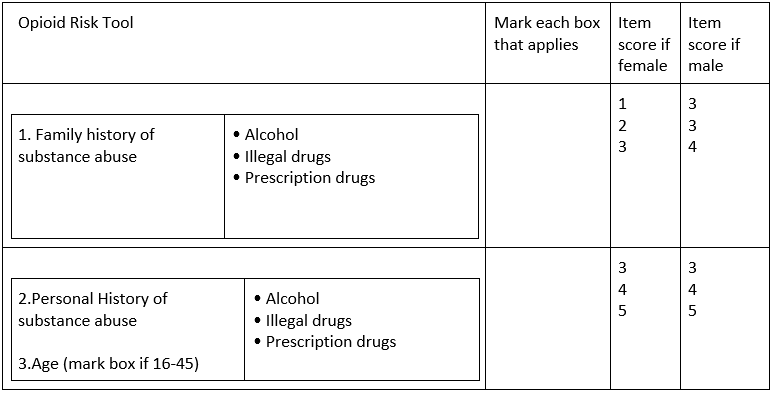
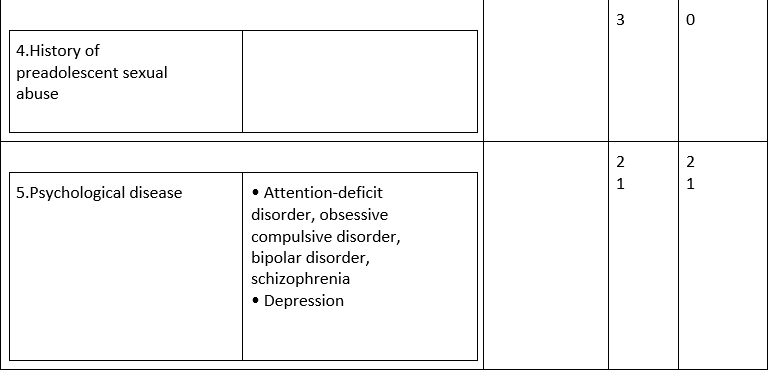
Evaluation of substance misuse, abuse, or compulsion risk, utilizing the Narcotic Gamble Device an approved clinical instrument (See Table 2: Narcotic Gamble Apparatus
-
The patient ought to be defined as to low, medium, or high risk for misuse.
-
High-risk patients are those with dynamic substance maltreatment of any sort or a background marked by solution narcotic misuse. As a rule, these patients shouldn’t be put on constant narcotics.
-
High-risk patients who are considered proper for constant narcotic treatment ought to be dealt with by a doctor spend significant time in compulsion medication.
-
Patients with a background marked by substance misuse or then again other psychosocial risk factors ought to be co-dealt with a doctor gaining practical experience in fixation medication.
-
Restorative Preliminary Rules (Narcotic Guileless Patient)/ Therapeutic Trial Criteria (Opioid-Naïve Patient)
While considering narcotic treatment in a narcotic gullible patient, the following preliminary measures should be met:
-
The disappointment of torment the board choices counting dynamic treatments, mental social treatment, torment self-administration methods, and other proper clinical methods.
-
Cautious assessment and documentation of the patient’s torment condition, general ailment, psychosocial history, mental status, and substance use history.
-
No untreated psychosocial issues driving or entangling the clinical show.
-
Narcotics ought to be viewed as just when the potential advantages are probably going to offset potential hurt and the clinician will resolve to proceed checking the impacts of treatment, counting an arrangement to end narcotic treatment if vital.
-
The preliminary ought to begin with a standard evaluation of capability and agony.
-
The treatment plan ought to incorporate continuation of fitting adjuvant treatments reliable with proposals in the New York Non-Intense Agony Clinical Treatment Rules to ease agony and help the patient adapt to the condition.
-
The treatment plan ought to incorporate fitting coordination of care.
-
The patient ought to have a careful comprehension of all the assumptions for narcotic use including the requirement for a restorative preliminary.
-
The doctor and patient should concur upon characterized useful as well as agony objectives.
-
The full range of aftereffects ought to be checked on, furthermore, a Patient Informed Assent for Narcotic Treatment Structure making sense of the dangers and advantages of narcotics must be endorsed by the patient and the doctor. (See Index F)
-
A composed Patient Comprehension for Narcotic Treatment Structure illustrating the supplier’s and patient’s obligations in narcotic treatment (counting affirmation that remedies will be acquired from a solitary expert) should be endorsed by the patient also, doctor. (See Addendum G)
-
Doctors recommending narcotic treatment should follow I-STOP and other pertinent regulation.
-
Doctors’ ought to finish the schooling suggested by the FDA, specifically the Gamble Assessment and Relief Methodologies (REMS).
Table 2: Opioid Risk Tool (ORT)
Therapeutic Trial
-
There is no proof that any one narcotic is better than some other for introductory treatment.
-
The preliminary ought to record supported improvement in torment control (essentially a 30% decrease on approved torment gauges) and worked on practical status, including get back to work as well as expansion in capacity to perform exercises of day-to-day living.
-
While directing a preliminary of narcotic treatment, begin with a low dose, increment slowly and screen narcotic viability until ideal portion is achieved. (See Reference section D: Dosing Limits for Chosen Narcotics)
-
Follow-up each seven to ten days is encouraged to titrate measurement and survey clinical viability.
-
During measurement titration, encourage the patient to keep away from taking part in wellbeing delicate word related and nonoccupational exercises, including yet not restricted to: working engine vehicles or other fueled gear; working at levels or in bound spaces; working gear or hardware with high probability of cut, cut or smash wounds; utilization of burnable or acidic synthetic substances; or participating in any movement where decreased readiness or smartness could represent a danger to work environment or public security, until a steady measurement is laid out and it is sure that the narcotic doesn’t cause sedation.
-
Pee Medication Testing (UDT) – See Area F.3.d, Pee Drug Testing (UDT) for Checking Narcotic Treatment.
-
Arbitrary pill counts. Unannounced pill counts are prescribed as demonstrated by risk classes or hazard factors.
-
If objectives are not being met the narcotic preliminary ought to be rethought.
Long haul Utilization of Narcotics: Changing/Overseeing Patients on
Overview of Existing Narcotic Treatment
The doctor treating a patient on long haul narcotics ought to start a re-appraisal/re-assessment of the patient’s clinical status, progressing to the executives and treatment as indicated by the standards for safe long haul narcotic administration and rules for streamlining narcotic consideration. (See Segments F.2.c and F.3)
Patients WHO ARE ON long haul narcotics shouldn’t have their drugs ceased basically because they have not met the preliminary models or the rules for safe long haul narcotic administration nitty gritty in this rule.
It ought to be noticed that the New York Non-Intense Agony Clinical Therapy Rules doesn’t need the end of narcotics for this subset of patients who have been on long haul narcotic treatment.
The objective is to change to the guidelines of care recognized beneath and stay away from sudden suspension of narcotics in patients who have been getting long haul treatment preceding the inception of the New York Non-Acute Agony Clinical Treatment Rules.
Approach
-
Cautious re-assessment and documentation of the patient’s torment condition, general ailment, psychosocial history, mental status, and substance use history to decide the adequacy and security of existing narcotic treatment.
-
Physical and mental as well as mental evaluation including a full assessment for liquor or chronic drug use, reliance, or misuse.
-
Chance Evaluation: Evaluating for potential comorbidities and hazard factors is significant so that expected chance can be checked appropriately.
-
Note: Individual or family background of substance misuse is the most grounded prescient element for abuse.
-
Chance Delineation: The patient ought to be separated as to low, medium, or high gamble for misuse in view of ways of behaving, approved clinical instruments and earlier history of misuse.
-
The gamble of substance misuse, abuse or enslavement ought to be evaluated by suggested and approved clinical instruments (See Table 2: Narcotic Gamble Apparatus
-
-
At the point when assessment distinguishes untreated psychosocial issues driving or convoluting the clinical show, suitable reference ought to be advertised.
-
Distinguishing proof and additionally continuation of fitting adjuvant non-narcotic treatments steady with proposals in the New York Non-Intense Agony Clinical Therapy Rules to alleviate torment, further develop capability and help the patient adapt to the condition.
-
Lay out an underlying continuous timetable for normal observing and re-assessment to decide the viability and security of the current narcotic treatment, need for adjustment/suspension of narcotics, creating plan for observing including UDT, pill count, need for specialty meeting/co-the board, commencement of non-narcotic adjuvant treatments, survey and fulfillment of Patient Comprehension for Narcotic Treatment Structure and Patient Informed Assent for Narcotic Treatment Structure.
-
Doctors’ ought to be proficient about and keep up with consistence with significant Government and state-controlled substance regulation and guidelines.
-
The objective is to change to the principles of care recognized underneath and stay away from unexpected discontinuation of narcotics in patients who have been getting long haul treatment before the inception of the New York Non-Intense Torment Clinical Treatment Rules.
-
Thought of other co-grim circumstances that need to be tended to (for instance, sorrow, uneasiness, grim stoutness), with fitting references as shown.
Ongoing, Long-Term Opioid Management
Overview of Ongoing, Long-Term Opioid Management
When a choice is made to establish as well as proceed (for those specialists who didn’t begin these meds) constant narcotic treatment, the doctor is answerable for regularly observing the wellbeing and adequacy (worked on tolerant capability and agony control/help) of continuous treatment.
Principles for Safe Management include:
-
Long haul narcotic treatment ought to just be started based on an unequivocal choice and understanding between the patient and doctor (Patient Informed Assent for Narcotic Treatment Structure [Appendix F] and Patient Understanding for Narcotic Treatment Structure [Appendix G]).
-
When narcotic portion, type, or patient condition changes, the Patient Informed Assent for Narcotic Treatment also, Patient Comprehension for Narcotic Treatment structures should be refreshed and appropriately endorsed by the patient and the doctor.
-
Remedies from a solitary expert and a solitary drug store.
-
Doctors’ ought to recommend opiates in consistence with state and Government regulation.
-
Most minimal conceivable viable portion. The peculiarity of resilience should be offset with relief from discomfort. Procedures to accomplish the most minimal conceivable successful portion might incorporate narcotic pivots, periodic narcotic portion decreases, or conceivable reinstitution of already fruitful treatment plans.
-
Proceeding with audit of in general treatment plan in regard to nonopioid method for torment control and upkeep of practical status to incorporate ID or potentially continuation of suitable adjuvant non-narcotic treatments steady with proposals in the New York Non-Intense Agony Clinical Therapy Rules to assuage torment and help the patient adapt to the condition.
-
All endeavors to empower and support dynamic activity (as gone against to aloof) to empower and uphold patient self-management.
-
A few pieces of these rules suggest thought of reference to experts in Agony Medication or potentially Fixation Medication. These suggestions ought not be viewed as inseparable from a proposal to tighten, deprescribe or end a particular medicine. Rather, they are a suggestion to enroll extra ability.
-
Observing/Screening
-
Progressing survey/reassessment and documentation of relief from discomfort, practical status, suitable prescription use, and antagonistic secondary effects, occasionally and as justified by evolving conditions (torment force, level of capability, progress toward objectives). This should be reported at every patient experience.
-
Chance appraisal/separation for directing way to deal with recurrence of observing:
-
In patients at generally safe for antagonistic results and on stable portions of narcotics, checking at any rate when each three to a half year might be adequate.
-
Patients with earlier history of a habit-forming jumble, utilized in an occupation requesting smartness, more established patients, patients with shaky or useless social climate and those with comorbid mental or clinical conditions require more incessant observing.
-
For patients at an exceptionally high gamble for unfavorable results, week after week observing and ecomanagement with a doctor spend significant time in compulsion medication might be a sensible procedure.
-
Checking of conduct for indications of conceivable substance misuse demonstrating an expanded gamble for habit and conceivable requirement for discussion with a doctor spend significant time in fixation medication.
-
Pee drug testing ought to be performed arbitrarily at least one time each year and even more oftentimes as considered proper by the recommending doctor concurring to gamble with class (See Table 4: UDT Dangers and Recurrence of Testing).
-
It is suggested that unannounced pill counts be proceeded as demonstrated by risk class or risk factors. For atypical way of behaving, unannounced pill counts are unequivocally suggested.
-
On the off chance that no obvious explanations for portion decrease or cessation of narcotics are distinguished, and the patient illustrates benefit from the narcotic treatment (upheld by approved proportions of moved along capability and torment), continuation of narcotics can be fitting. Progressing treatment, be that as it may, requires progressing appraisal/observing.
-
Utilize restricted to limit of two narcotics:
-
-
A long-acting narcotic for upkeep of relief from discomfort what’s more, a short-acting narcotic for restricted salvage use when torment surpasses the standard level.
-
If more than two narcotics are being considered for long haul use, or then again on the off chance that patients are requiring > 50 Prescription/24hrs, a second assessment from an expert who is Board Affirmed in Compulsion Medication or Agony Medication is unequivocally suggested.
-
All narcotic meds ought to be utilized with alert in patients with a potential for misuse.
-
Buccal-conveyed drugs ought not be utilized in this populace.
-
Acetaminophen cautioning with mix items: hepatotoxicity can result from delayed utilization of portions in abundance of suggested greatest day to day portions of acetaminophen, including over the counter meds. (See Segment F.1.e.i, “Acetaminophen”)
-
What our office can do if you have workers compensation injuries
We have the experience to help you with their workers compensation injuries. We understand what you are going through and will meet your medical needs and follow the guidelines set by the New York State Workers Compensation Board.
We understand the importance of your workers compensation cases. Let us help you navigate through the maze of dealing with the workers compensation insurance company and your employer.
We understand that this is a stressful time for you and your family. If you would like to schedule an appointment, please contact us so we will do everything we can to make it as easy on you as possible.

Dr. Nakul Karkare
I am fellowship trained in joint replacement surgery, metabolic bone disorders, sports medicine and trauma. I specialize in total hip and knee replacements, and I have personally written most of the content on this page.
You can see my full CV at my profile page.
