Swelling after Knee Replacement
Knee pain is a frequent issue for many individuals. Intense pain, or discomfort that disrupts daily life or is accompanied by symptoms like swelling, redness, or warmth, should prompt a consultation with a healthcare professional.
At Complete Orthopedics, we have a specialized team ready to address various types of knee pain, providing surgical treatments if needed. Our services are available throughout New York City and Long Island at six different hospitals, ensuring top-notch surgical and orthopedic solutions. Appointments with our expert surgeons can be made online or by calling us.
Learn about common causes of knee pain and review the treatment options we offer, including when surgery might be necessary.
Overview
Total knee replacement is a common orthopedic surgery and one of the most successful surgeries in medicine. Complications after knee replacement surgery are rare but persistent pain or swelling are the most common complaints after knee replacement.
While some swelling is normal even up until 6 months post-surgery, swelling may also occur as a result of serious complications such as deep vein thrombosis or prosthetic joint infection.
Arthritis of the knee joint is the most common indication for replacement surgery. During replacement surgery, the surgeon gives an incision in front of the knee and cuts/separates tissues to reach the diseased knee joint. During the entire surgery, the patient remains under either general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia.

X-ray showing a total knee replacement.
The surgeon further proceeds to cut and remove the diseased ends of the thigh bone and the shin bone. The removed ends are replaced with metal alloy and plastic parts. The prosthetic joint functions to recreate the motion and alignment of the natural joint.
Swelling and pain are the most common complaints after knee replacement. The swelling is normal and is usually moderate to severe in the first week but gradually decreases for the next weeks and months. Mild swelling may persist normally as long as six months post-surgery.
Swelling is defined as a protuberance of a body. In the case of the knee after replacement surgery, the swelling occurs as a result of the accumulation of excess fluid in the tissue of the knee joint. During surgery, the skin, soft tissues, and bones are cut to perform the surgery. As they take time to heal, there may be excess fluid accumulation in the tissue as a part of the inflammatory chain leading to healing.
The swelling persists even after the skin incision heals as the tissues in the body take a long time to get back to their condition before the surgery. The patients may complain of swelling around their knees, below or above their knees. The swelling may get worse at the end of the day with activity.
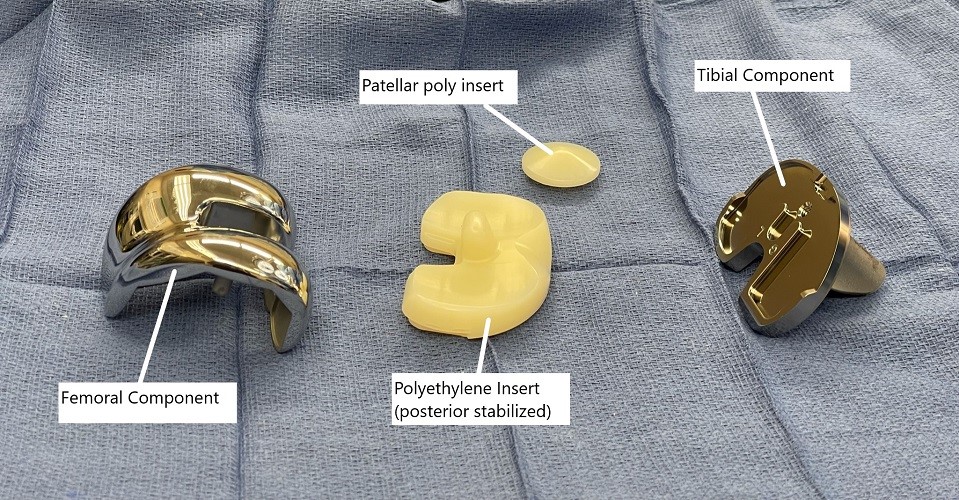
Intraoperative image showing knee replacement implants.
What Causes Knee Swelling?
After knee replacement surgery, it’s normal for the knee area to swell due to the body’s natural response to surgery and the trauma inflicted on the tissues during the procedure. Factors such as the type of surgery, the patient’s health status, and the surgical techniques used can influence the extent and duration of swelling.
Surgical Impact: The physical manipulation of bone and tissue during surgery causes an inflammatory response.
Fluid Accumulation: The body’s response includes increasing fluid in the knee area to aid in healing, which contributes to swelling.
Blood Vessel Changes: Surgery can affect blood flow dynamics around the knee, further contributing to fluid buildup.
The swelling may also be caused as a result of deep vein thrombosis. Deep thrombosis occurs as a result of the formation of a blood clot inside the veins of the legs. Major surgery such as knee replacement is a significant risk factor for deep vein thrombosis.
The blood clot formed in the leg may cause swelling of the leg especially the calf region. The swelling may extend above the knee. The blood clot may travel up the veins and to the lungs, a condition known as pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism may lead to shortness of breath and may be fatal if not treated.
Progression and Measurement of Swelling
Swelling typically peaks within the first few days after surgery. Studies have shown that:
Immediate Post-Op: Swelling is considerable, as the body reacts to the surgical trauma.
First Few Weeks: Swelling gradually decreases as the healing process progresses, although some level of swelling may persist.
Long-Term: Even months after surgery, a slight swelling can remain but should progressively lessen as recovery continues.
Monitoring swelling is crucial for assessing the healing process. Methods such as bioimpedance spectrometry, which measures fluid changes in tissues, help in quantifying swelling and guiding rehabilitation.
While the normal swelling after knee replacement surgery gradually improves, at times the swelling may represent a serious pathology such as deep vein thrombosis or infection. The infection of the prosthetic joint may occur in the immediate postoperative period, in a few weeks/months after the surgery or even years after the surgery.
The swelling of the knee joint secondary to infection may present with redness and pain. The infection may also cause fever and in severe cases of infection, a discharge may be present. The swelling associated with infection is due to the inflammation and fluid formation secondary to bacterial activity. The infected prosthetic joint needs blood and radiological investigations as well as need revision surgery.
Risk Factors for Increased Swelling
Certain factors can increase the risk or extent of swelling, including:
- Pre-Existing Health Conditions: Conditions like diabetes or heart disease can affect how the body handles fluid and healing.
- Activity Level: Both excessive activity and inadequate movement post-surgery can exacerbate swelling.
- Nutrition and Medication: Diet and medications affect inflammation and fluid balance in the body.
Managing and Reducing Swelling
Effective management of knee swelling post-surgery is pivotal for a successful recovery. Approaches include:
- Elevation and Ice: Regularly elevating the affected leg and applying ice can significantly reduce swelling.
- Compression Garments: These can help in maintaining fluid flow and reducing excessive swelling.
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to manage swelling and pain.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises improve circulation, enhance muscle strength, and facilitate fluid drainage from the leg.
Regular icing is recommended for the management of swelling after knee replacement. The patients are advised to apply an ice pack as cold temperature helps in the control of both pain and swelling. Icing induces narrowing of the blood vessels in the region and that leads to decrease the flow of fluid to the area and decreases the swelling.
Similarly, patients are advised to slightly elevate their leg just above their heart level. The elevation helps in flow of the fluid back to the body from the legs. The patients after knee replacement surgery are advised ankle pumps and other home exercises.
Ankle pumps involve pushing the ankles down and up repeatedly. The movement of the ankle brought about by the contraction of the calf muscles not only decreases the swelling but also helps in preventing deep vein thrombosis. The patients may also use compression stockings to decrease swelling. Compression stockings also help decrease the incidence of deep vein thrombosis.
Patients are advised to do ankle pumps and start moving as soon as possible after the knee surgery to prevent deep vein thrombosis. Patients are usually able to walk the day of the surgery or the next day.
Besides movement, the patients are prescribed a blood-thinning medication such as aspirin or enoxaparin to decrease the chances of blood clots. Compression stocking (TED stocking) may also help to prevent deep vein thrombosis after knee replacement surgery.
Swelling after knee replacement surgery is common but it is important to bring the swelling to your surgeon’s attention in case of swelling is increasing or associated with other symptoms.
Conclusion
Understanding the dynamics of knee swelling after replacement surgery helps in managing expectations and optimizing recovery strategies. With proper care, monitoring, and adherence to post-operative instructions, the impact of swelling can be minimized, paving the way for a smoother recovery and return to activity.
Do you have more questions?
What exactly causes the body to react with swelling after knee replacement surgery?
Swelling is a natural part of the body’s inflammatory response to surgery, where increased fluid and white blood cells are sent to the knee to aid in healing and fight any potential infection.
Are there specific surgical techniques that reduce the risk of severe swelling?
Yes, minimally invasive surgical techniques and careful management of tissue handling can reduce the extent of trauma and, subsequently, swelling.
How long does swelling usually last after knee replacement?
Typically, swelling peaks within the first few days post-surgery and gradually decreases over the following weeks, but some mild swelling can persist for several months.
Can swelling affect the long-term outcome of my knee replacement?
Persistent or excessive swelling can potentially impact the healing process and knee function, but with proper management, long-term outcomes are generally very good.
What are the best ways to measure knee swelling at home?
Measuring the circumference of the knee with a tape measure at regular intervals can provide a quantitative way to track changes in swelling.
Is there a difference in swelling between robotic-assisted and traditional knee surgery?
Robotic-assisted surgery may result in less tissue damage and therefore potentially less swelling, although individual results can vary.
Does the type of knee implant affect swelling?
The type of implant itself typically does not directly affect swelling; however, the technique and accuracy of implant placement might.
What medications are best for controlling swelling after knee surgery?
NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) are commonly used to reduce swelling and pain, but they should be taken under the guidance of a healthcare provider due to potential side effects.
How can I differentiate between normal swelling and an infection?
Normal swelling should gradually improve with time and respond to elevation and ice. If swelling is accompanied by increased pain, redness, or warmth, or if it worsens suddenly, it may indicate an infection.
Should I be concerned if one leg is more swollen than the other after bilateral knee replacements?
It’s not uncommon for one knee to swell more than the other, but significant differences should be evaluated by your surgeon.
Can diet affect swelling after knee replacement?
Yes, a diet high in sodium can exacerbate swelling, while foods rich in anti-inflammatory agents like omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce it.
How does physical therapy help manage swelling?
Physical therapy helps by promoting fluid drainage through movement and strengthening exercises, which also improve joint function and range of motion.
What role does compression therapy play in managing swelling?
Compression garments or bandages help reduce swelling by preventing fluid accumulation in the tissue around the knee.
When should I be able to stop using ice on my knee?
Ice can be used in the initial weeks post-surgery as needed to help control swelling and pain, typically decreasing in frequency as the swelling subsides.
Is elevation really effective for swelling?
Yes, elevating the leg above the level of the heart helps reduce the gravitational pull on fluids, decreasing swelling.
Can massage therapy reduce swelling after knee replacement?
Gentle massage may help by encouraging fluid movement away from the knee, but it should be performed by a professional familiar with post-operative care.
What are the signs that swelling is not resolving normally?
Persistent swelling, increased pain, decreased mobility, or signs of infection are indications that the swelling isn’t resolving as expected and should be checked by a healthcare provider.
Can I take diuretics to help with swelling?
Diuretics are not typically recommended for swelling due to knee surgery, as they can lead to other complications. It’s best to manage swelling through elevation, ice, and mobility.
What if the swelling suddenly increases a few weeks after surgery?
An increase in swelling after initial improvement could indicate activity-related inflammation or a complication such as an infection or blood clot, and should be evaluated urgently.
Are there any exercises I should avoid to prevent worsening the swelling?
High-impact activities like running or jumping should be avoided in the early post-operative period to prevent exacerbatingthe swelling. Gentle stretching and low-impact activities like walking and cycling are encouraged.
Can weather affect knee swelling after surgery?
Yes, changes in atmospheric pressure and humidity can affect joint swelling. Some patients report increased swelling in colder or damp weather.
Should I use heat or cold to treat the swelling?
In the initial post-operative phase, cold is generally recommended to reduce swelling and numb pain. Heat may be used later in the recovery to aid muscle relaxation and improve circulation once the acute swelling has subsided.
What are the consequences of not managing swelling effectively?
Poor management of swelling can lead to stiffness, reduced mobility, prolonged recovery, and in some cases, chronic swelling.
How soon after surgery can I expect my knee to look ‘normal’ again?
Most of the noticeable swelling subsides within the first few months, but complete recovery and the return to a ‘normal’ appearance can take up to a year, depending on various factors including the individual’s health and adherence to rehabilitation.
Is there a correlation between swelling and scar tissue formation?
Yes, excessive or prolonged swelling can lead to increased scar tissue formation, which might affect the knee’s function and range of motion. Proper management of swelling helps to minimize this risk.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
