Unstable Knee – Causes and Management
If knee discomfort escalates, disrupts daily routines, or is accompanied by swelling and redness, it is essential to see a healthcare professional. At Complete Orthopedics, our specialized team is dedicated to managing injuries to the posterior cruciate ligament through personalized strategies and surgical interventions. We aim to comprehend your symptoms, pinpoint the root causes, and suggest appropriate therapies or operations.
Our centers are located throughout New York City and Long Island, linked to six leading hospitals, providing access to superior knee care. You can book an appointment with our orthopedic specialists either online or via phone. Explore the reasons and treatments for knee pain and understand when surgical intervention is the most effective solution.
Overview
The knee joint is the largest joint of the body. The knee helps in day to day activities such as walking, sitting, climbing stairs, running, etc. The unstable knee is the feeling of the knee giving away. Also known as buckling of the knee, it is usually associated with pain and swelling.
Anatomy
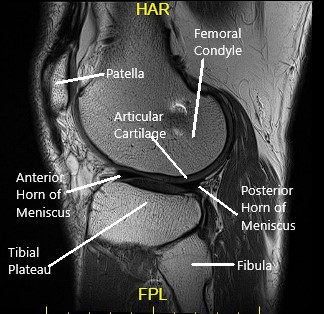
The knee is a large weight-bearing hinge joint formed by the thigh bone, kneecap and shin bone. The various structures forming the joint are:
- Articular cartilage is a glistening white smooth tissue covering the ends of bones. It is toughened yet flexible enough to cushion the gliding of the bones reducing friction and acting as a shock absorber.
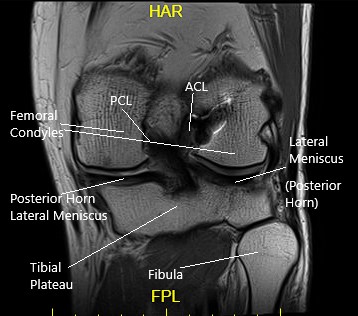
- The menisci are pads of tissue between the joint dampening the impact. Both the meniscus and cartilage have a very limited blood supply, therefore, limiting any healing if subjected to damage.
- Ligaments are tough tissues connecting one bone to another. Ligaments prevent slipping one bone over the other, maintaining stability.
- Synovium is a thin tissue lines the inside of the joint secreting a watery thin, sticky, clear lubrication called synovial fluid. Just like machine oil, it helps in the smooth movement of the joint.
- The lower end of the thigh bone and upper part of the shin bone along with the kneecap form the joint. The muscles attached to them help to bend or straighten the knee joint. Proper alignment between both is necessary to perform the movements.
Ligaments
The ligaments of the knee along with the meniscus provide stability to the knee. Tears or rupture of the ligaments and menisci are the most common cause of knee buckling.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
The ACL runs from the front and middle of the tibia to the outer and backward side of the femur. The ligament provides stability mainly in the front and back of the knee. The ligament also stabilizes the rotatory movement of the knee.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
The PCL is present behind the knee joint. Along with ACL, it provides stability in the front and back of the knee. Similar to ACL, the PCL also provides rotational stability.
Medial & Lateral Collateral Ligaments
The medial collateral ligament provides stability on the inner side of the knee. Similarly, the lateral collateral ligament provides stability on the outer side of the knee.
Causes of unstable knee
Twisting injuries or sudden forces on the knee in some positions may lead to tears or complete rupture of the ligaments.
The ACL is commonly injured during the sudden twisting of the knee during non-contact sports. The ACL tear is usually associated with a medial collateral ligament and medial meniscus injury. The PCL injury is associated with a violent force acting in front of the knee. The PCL injury may occur isolated or associated with other injuries.
The medial collateral ligament is injured by a force acting on the outer side of the knee. The knee opens up on the inner side with the rupture of the medial collateral ligament. Meniscus injuries may occur with small twisting/turning forces acting while playing field sports or running.
Anterior Instability
Instability in the front may be due to injury of a number of structures such as:
- ACL
- Lateral capsular (partial or complete)
- Medial capsular (partial or complete)
Posterior Instability
Instability behind the knee may be due to injury to :
- PCL
- Arcuate complex (partial or complete)
- Posterior oblique ligament (partial or complete)
Medial Instability
Instability on the inner side of the knee is due to injury of :
- Medial collateral ligament
- Medial capsular ligament
- ACL
- Posterior oblique ligament
- Sometimes PCL
Lateral Instability
Instability on the outer side of the knee is due to injury of :
- Lateral collateral ligament
- Lateral capsular
- ACL
- Biceps tendon
- Arcuate complex (partial or complete)
- ITB (Iliotibial band)
Symptoms
The instability is often described as a feeling of the knee giving away or buckling. The instability is more evident in activities that require turning/twisting of the knee such as getting out of a vehicle. The buckling is mostly associated with knee pain and swelling of the knee.
Impact on Daily Life
The effects of knee instability are multifaceted. Physically, it can lead to a reduction in mobility and an avoidance of activities that require knee stability, such as sports or even walking on uneven surfaces. Psychologically, it can cause fear of falling and decreased confidence in one’s ability to perform daily tasks, leading to social withdrawal and a reduced quality of life.
Diagnosis
The patient’s knee is thoroughly examined by the orthopedic surgeon. The physical examination involves a detailed history of the events leading to the injury. Special tests are done to look for instability in the various range of motion.
Radiological tests are usually done after clinical examination. An X-ray gives information about any fractures or arthritis of the knee joint. An MRI is able to detect any minor tears/rupture of the ligaments or a torn meniscus. The gold standard test for the diagnosis of knee instability is an arthroscopic examination.
Treatment
The treatment options depend upon the severity of the injury and the structure damaged.
Most of the medial collateral ligament tears and isolated PCL injuries can be managed conservatively. Conservative management involves knee braces, rest, icing, compression and elevation, and anti-inflammatory drugs. Physical therapy is aimed at strengthening the muscles around the knee.
Surgical treatments for knee instability is mostly carried out with an arthroscope. A tiny instrument about the size of a pencil is inserted in the shoulder joint. The instrument has magnifying lenses and a camera.
The video feed is displayed on a large monitor. The operating surgeon utilizes the live video feed to guide minuscule instruments to repair the ligament injury.
Postop, the patient undergoes rehabilitation in the form of physical therapy and home exercise program to regain maximum function and strength.
Conclusion
Knee instability is a complex issue that requires a multifaceted approach for effective management. Understanding the causes and impacts of this condition is essential for those affected by it. With appropriate treatment and preventive measures, individuals with knee instability can lead active and fulfilling lives.
Do you have more questions?
What exactly causes the knee to become unstable?
Knee instability is commonly caused by damage to ligaments such as the ACL, degenerative changes from osteoarthritis, or weakness in the muscles around the knee. It can also result from acute injuries or chronic wear and tear.
Are there specific exercises to prevent knee instability?
Yes, exercises focusing on strengthening the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles can help stabilize the knee. Balance exercises and core strengthening are also beneficial.
How is knee instability diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, patient history, and imaging tests like MRI or X-rays to assess ligament damage and joint status.
Can knee instability lead to other knee problems?
Yes, it can lead to increased wear and tear in the knee joint, exacerbate conditions like osteoarthritis, and increase the risk of falls and other injuries.
What are the treatment options for severe knee instability?
Severe instability might require surgical interventions such as ligament reconstruction or knee replacement, depending on the underlying cause.
How effective are knee braces in managing instability?
Knee braces can be very effective in providing support and stability, especially during activities that put stress on the knee.
What is the role of physical therapy in treating knee instability?
Physical therapy is crucial for strengthening the muscles around the knee, improving flexibility, and teaching stabilizing techniques to protect the joint.
Can knee instability be completely cured?
While some causes of instability can be effectively treated, chronic conditions like osteoarthritis may require ongoing management.
Is knee instability common in athletes?
Yes, athletes, particularly those involved in high-impact sports or activities that involve rapid direction changes, are at higher risk of developing knee instability.
What lifestyle changes can help manage knee instability?
Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding high-impact activities, and regular knee-strengthening exercises can help manage symptoms.
How long does it take to recover from a procedure to correct knee instability?
Recovery times can vary widely based on the specific procedure, ranging from a few weeks to several months.
Are there age-specific concerns regarding knee instability?
Older adults may experience more pronounced effects due to muscle weakness and degenerative changes, while younger individuals may suffer from instability primarily due to injuries.
Can knee instability affect balance and coordination?
Yes, instability can significantly impact balance and coordination, increasing the risk of falls and affecting the ability to perform daily activities.
What are the signs that knee instability is worsening?
Increased frequency of knee giving way, heightened pain, swelling, and reduced mobility are signs that instability may be worsening.
Are there non-surgical treatments that can be effective?
Besides physical therapy and braces, treatments like corticosteroid injections, NSAIDs, and lifestyle modifications can be effective non-surgical options.
What is ACL reconstruction?
ACL reconstruction is a surgical procedure used to replace a torn anterior cruciate ligament, a common cause of knee instability.
How does obesity affect knee instability?
Obesity increases stress on the knee joints, exacerbating instability and associated symptoms like pain and reduced function.
Can knee instability be a sign of more serious health issues?
While it often relates to local issues within the knee, severe or unexplained instability should be evaluated to rule out other health problems.
What are the risks of surgery for knee instability?
Risks include infection, nerve damage, blood clots, and the potential for continued instability or pain.
How do I know if my knee instability is due to osteoarthritis?
A diagnosis typically involves evaluating symptoms like joint stiffness, pain during activity, and reviewing imaging studies.
What advancements are being made in treating knee instability?
Advances include new surgical techniques, better diagnostic tools, and developments in regenerative medicine like stem cell therapy.
Is swimming good for knee instability?
Yes, swimming is an excellent low-impact exercise that can strengthen the muscles around the knee without putting excessive stress on the joint.
How often should I perform stability exercises for my knee?
Frequency can vary based on individual needs, but generally, stability exercises should be performed 2-3 times per week, gradually increasing intensity and complexity under professional guidance.
What dietary considerations can help with knee health and stability?
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and adequate hydration can support joint health and potentially reduce symptoms related to knee instability.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
