Minimally Invasive Total Hip Replacement
Minimally invasive total hip replacement is a surgical technique used to perform a total hip replacement using smaller incisions as compared to the traditional approach. The minimally invasive technique also utilizes less cutting of the tissues besides a smaller skin incision.
The technique is fairly recent as compared to the traditional hip replacement technique. While minimally invasive hip replacement offers a lot of benefits compared to the traditional approach, the technique may not be best suited for all patients.
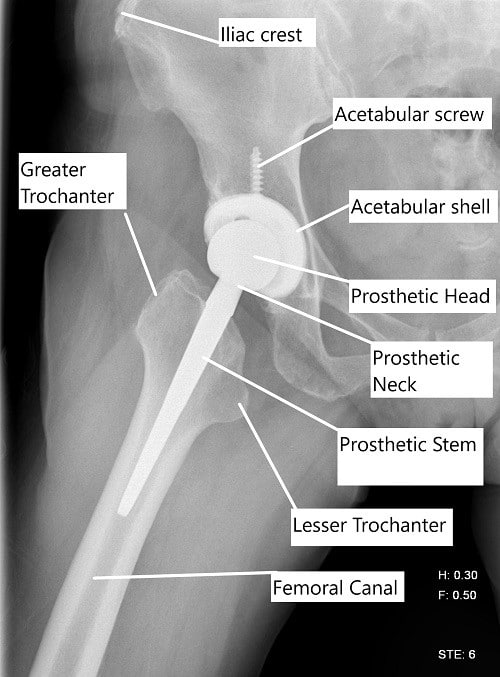
X-ray showing a lateral view of a total hip replacement.
Hip replacement surgery is most often performed for the management of end-stage arthritis of the hip joint. The surgery involves the removal of the diseased ends of the bones that form the hip joint. Prosthetic metal and plastic parts are then capped over the bony ends to recreate the function of the natural joint.
Minimally invasive surgery
The prosthetic implants used in a minimally invasive hip replacement surgery are the same as the ones used in a traditional approach. The instruments used in the minimally invasive technique are however different from the ones used in the traditional approach.
Special instruments may be utilized to help the surgeon perform the surgery through a smaller incision. The special instruments are useful while preparing the bony socket and the femoral canal for the implants.
Generally, minimally invasive surgery is only advised in patients who require a primary uncemented hip replacement, are physiologically younger, have a thin physique with relatively normal hip anatomy.
Minimally invasive surgery is not recommended in patients undergoing revision surgery or complex primary hip replacement surgery. Patients that require revision hip replacement or complex primary hip replacement need a significantly larger exposure of the hip joint to perform the surgery.
The technique is also not advised in patients who may have undergone any kind of prior hip/thigh surgery such as osteotomy, fracture fixation with screws/nails/plates, etc. Obese, highly muscular, and patients with multiple medical co-morbidities are also not good candidates for minimally invasive surgery.
Patients with a bone tumor, metabolic bone disease such as osteoporosis, inflammatory arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis who may need a hip replacement are also not good for a minimally invasive technique. Similarly, patients with severe hip deformities such as contractures or bony fusion of the hip may require an extensive approach used in traditional surgery.
Technique differences
During a traditional hip replacement surgery, the surgeon gives an incision that may be approximately 10-12 inches long. The incision in the common posterior approach is given at the back of the hip joint. The incision in anterior hip replacement is given in the groin area and given at the side of the hip joint in the direct lateral approach.
The neck of the femur is cut to free the head which is subsequently extracted out. The acetabulum socket is then prepared through serial reaming which is usually followed by the preparation of the femoral canal.
An acetabular shell is usually press-fitted in the bony socket or may be fixed with bone cement. A femoral prosthetic stem is press-fitted in the femoral canal and is capped with a prosthetic head of the femur. The prosthetic head is then relocated in the prosthetic cup.
In the case of minimally invasive surgery, the skin incision is usually half the size of the incision used in the traditional approach. The surgeon may utilize minimally invasive techniques through either of the approaches used in the traditional hip replacement.
Surgeons may also use a double incision, with an incision in front of the hip and the back. The incision in the groin is used for the preparation of the bony acetabulum and prosthetic cup placement. Similarly, the incision in the back is used for femoral canal preparation and the placement of the femoral component.
Advantages
The smaller skin incision used in minimally invasive surgery leads to a smaller surgical scar. During minimally invasive technique fewer tissues are cut/separated which leads to less intraoperative blood loss. Additionally, the patients may have a shortened postoperative recovery. The technique preserves the abductor muscles at the side of the hip joint that is important for normal walking.
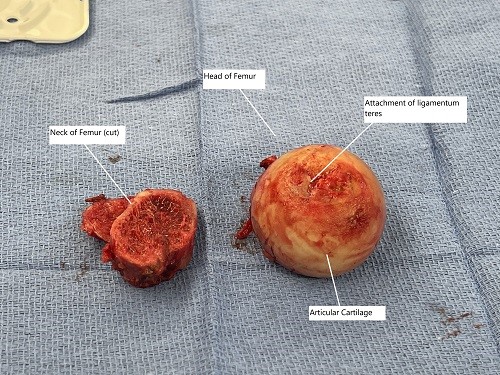
Intraoperative image showing the removed head of the femur and the neck of the femur.
Limitations
The exposure to the joint is greatly reduced in a minimally invasive technique. The limited exposure may potentially lead to mal-aligned implants. Proper positioning of the implants is necessary to prevent prosthetic hip dislocation and ensure a stable range of motion.
The minimally invasive technique utilizes special instruments to perform the surgery through a narrow field. The instruments may put stress on the tissues and the skin that may be double the stresses in the traditional approach. The additional stress on the skin and the tissue may lead to problems of wound healing and tissue damage.
The narrow field of surgery in a minimally invasive technique may increase the chances of damage to the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, femoral nerve, or the sciatic nerve depending upon the approach used in surgery. The technique may also increase the chances of an intraoperative prosthetic joint fracture.
Conclusion
Hip replacement surgery is one of the most successful surgeries in the history of medicine. The traditional approach has been proved to be highly effective in numerous long-term studies. The minimally invasive technique requires a significant amount of training by the surgeon to master the technique.
The minimally invasive technique offers advantages over the traditional approach; there is not enough data to conclusively state that it is more beneficial than the traditional approach. Speak with your operating surgeon regarding the type of surgery that may be best suited in your case.
Do you have more questions?
What is the typical recovery time for patients undergoing minimally invasive total hip replacement surgery?
Recovery time can vary depending on individual factors, but many patients are able to return to normal activities within a few weeks to months after surgery.
Are there any specific post-operative rehabilitation exercises recommended for patients undergoing minimally invasive total hip replacement?
patients typically undergo physical therapy to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the hip joint following surgery.
How does minimally invasive total hip replacement differ from traditional hip replacement surgery?
Minimally invasive techniques involve smaller incisions and less disruption to surrounding tissues, potentially leading to shorter hospital stays, faster recovery, and less post-operative pain compared to traditional surgery.
What are the potential risks and complications associated with minimally invasive total hip replacement?
While complications are rare, they can include infection, blood clots, implant loosening, nerve injury, or fracture. Your surgeon will discuss these risks and how they are minimized during the procedur
Can minimally invasive total hip replacement be performed on patients with severe hip arthritis or other underlying conditions?
Yes, in many cases, minimally invasive surgery is suitable for patients with severe hip arthritis or other conditions affecting the hip joint.
How is the accuracy of implant placement ensured during minimally invasive total hip replacement?
Advanced imaging techniques and robotic-assisted technology may be used to ensure precise implant placement and optimal alignment of the hip joint.
What type of anesthesia is typically used for minimally invasive total hip replacement surgery?
Patients may receive either general anesthesia or regional anesthesia, depending on their medical history and the preference of the surgical team.
How soon after surgery can patients expect to experience pain relief and improved mobility?
Many patients experience significant pain relief and improved mobility shortly after surgery, with continued improvement over the following weeks and months.
Are there any specific lifestyle modifications or precautions recommended for patients following minimally invasive total hip replacement?
Patients may be advised to avoid high-impact activities and certain movements that could put excessive stress on the hip joint. Your surgeon will provide guidance based on your individual circumstances.
What factors determine whether a patient is a suitable candidate for minimally invasive total hip replacement?
Factors such as the severity of hip arthritis, overall health, bone quality, and lifestyle goals are considered when determining candidacy for surgery.
How long do the benefits of minimally invasive total hip replacement typically last?
The benefits of surgery can be long-lasting, providing patients with improved function and pain relief for many years. However, individual results may vary.
What pre-operative preparations are necessary for patients undergoing minimally invasive total hip replacement?
Pre-operative preparations may include medical evaluations, imaging tests, cessation of certain medications, and lifestyle modifications to optimize surgical outcomes.
Are there any dietary restrictions or nutritional guidelines that patients should follow before or after surgery?
While there are no specific dietary restrictions, maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients can support the healing process and overall recovery.
How is post-operative pain managed for patients undergoing minimally invasive total hip replacement?
Pain management techniques may include a combination of oral medications, regional anesthesia, nerve blocks, or other modalities to ensure patient comfort during recovery.
What are the potential benefits of minimally invasive total hip replacement compared to traditional surgery?
Potential benefits include smaller incisions, reduced tissue damage, faster recovery, shorter hospital stays, and less post-operative pain.
Can minimally invasive total hip replacement be performed as an outpatient procedure?
In some cases, minimally invasive surgery may be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home on the same day as surgery.
What follow-up care is necessary after minimally invasive total hip replacement surgery?
Follow-up care typically involves regular post-operative appointments with your surgeon to monitor healing, address any concerns, and track your progress.
How soon can patients resume driving and other normal activities after minimally invasive total hip replacement?
Patients may be able to resume driving and light activities within a few weeks after surgery, with more strenuous activities gradually introduced as healing progresses.
Are there any age restrictions for patients undergoing minimally invasive total hip replacement?
Age alone is not a determining factor for candidacy, as suitability for surgery depends on overall health and individual circumstances.
Can minimally invasive total hip replacement be performed using robotic-assisted technology?
Yes, robotic-assisted technology may be used to enhance precision and accuracy during minimally invasive hip replacement surgery.
How is infection risk minimized during minimally invasive total hip replacement surgery?
Strict adherence to sterile techniques, antibiotic prophylaxis, and other infection prevention protocols are utilized to minimize the risk of surgical site infections.
Are there any long-term complications associated with minimally invasive total hip replacement?
While complications are rare, long-term issues such as implant wear, loosening, or dislocation may occur in some patients, necessitating further evaluation and management.
What is the success rate of minimally invasive total hip replacement surgery?
Minimally invasive hip replacement surgery has generally high success rates, with many patients experiencing significant improvement in pain and function following the procedure.
How soon can patients expect to return to work or other regular activities after minimally invasive total hip replacement surgery?
Return to work and other regular activities can vary depending on individual factors such as job requirements, overall health, and the type of activities involved. However, many patients are able to resume normal activities within a few weeks to months after surgery.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
