Hip Resurfacing vs Total Hip Replacement
Hip resurfacing is a surgical alternative to total hip replacement, offering a less invasive approach to managing hip arthritis. While total hip replacement involves the complete removal of the femoral head, hip resurfacing preserves the femoral neck, capping the head of the femur with a prosthetic. This procedure is ideal for younger, more active patients who wish to preserve as much bone as possible, which is important for future procedures if necessary.
How Common It Is and Who Gets It? (Epidemiology)
Hip resurfacing is typically recommended for younger patients (under 60 years) with hip arthritis, especially those who are more active and have good bone strength. Patients with a higher BMI or those with significant deformities may not be suitable candidates. It is especially beneficial for individuals with a good quality femur and for those who may need a future hip replacement revision.
Why It Happens – Causes (Etiology and Pathophysiology)
The most common cause of hip arthritis leading to hip resurfacing is osteoarthritis, where the articular cartilage deteriorates, causing bone-on-bone friction. Other causes include trauma (e.g., fractures or dislocations), childhood hip diseases, or conditions like avascular necrosis. In these cases, the femoral head loses its smooth surface, leading to pain, stiffness, and difficulty in performing daily activities.
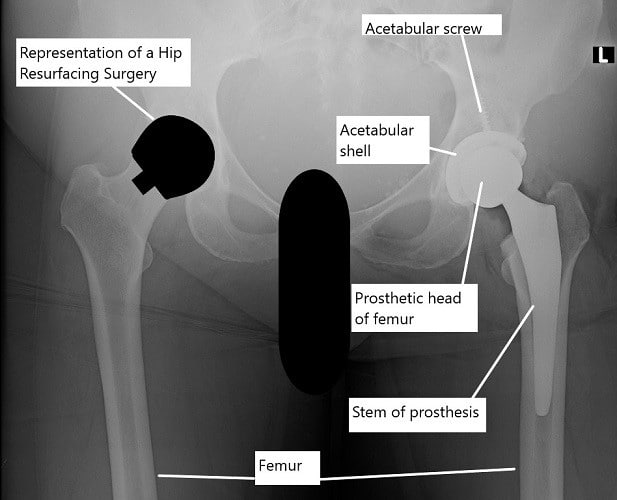
X-ray showing a total hip replacement on the left hip and an illustration of hip resurfacing on the right hip.
How the Body Part Normally Works? (Relevant Anatomy)
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint, where the femoral head (ball) fits into the acetabulum (socket) of the pelvis. The smooth articular cartilage on the ball and socket allows frictionless movement. In hip arthritis, this cartilage is worn away, resulting in painful bone friction, affecting joint function.
What You Might Feel – Symptoms (Clinical Presentation)
-
Pain: Particularly in the groin, outer thigh, or buttocks.
-
Stiffness: Difficulty bending, squatting, and walking.
-
Loss of mobility: Limited range of motion in the affected hip.
-
Night pain: Some patients experience pain even when not bearing weight on the hip.
How Doctors Find the Problem? (Diagnosis and Imaging)
-
Physical examination: To assess joint range of motion and areas of tenderness.
-
X-rays: To visualize joint space narrowing and signs of arthritis.
-
MRI: For a detailed view of soft tissues and early-stage changes in the hip joint.
Procedure Types or Techniques (Classification)
-
Hip Resurfacing: Replaces only the ball of the femur, preserving the femoral neck and socket.
-
Total Hip Replacement (THR): Involves replacing both the femoral head and acetabulum (socket) with prosthetic components.
Other Problems That Can Feel Similar (Differential Diagnosis)
-
Trochanteric bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa on the outside of the hip can mimic hip pain.
-
Labral tears: A tear in the hip labrum can cause hip pain and limited range of motion.
-
Low back issues: Conditions like sciatica or lumbar spine problems may cause referred pain to the hip area.
Treatment Options
Non-surgical: Includes medications (NSAIDs, acetaminophen), physical therapy, weight management, and cortisone injections.
Surgical: If non-surgical treatments fail, surgery (hip resurfacing or THR) is considered.
Recovery and What to Expect After Surgery
-
Initial recovery: Hospital stay for 1-2 days, with most patients able to bear weight on the hip immediately following surgery (with crutches).
-
Physical therapy: Begins shortly after surgery, focusing on strength, mobility, and regaining range of motion.
-
Full recovery: Most patients see significant improvement within 3-6 months, with the potential for resuming normal activities like walking, swimming, and golfing.
Possible Risks or Side Effects (Complications)
-
Fractures: A small risk of femoral neck fractures post-surgery.
-
Infection: A risk with any surgical procedure.
-
Metal ion release: As hip resurfacing involves a metal-on-metal implant, some patients may experience elevated levels of metal ions in their blood, leading to inflammation or implant loosening.
-
Leg length discrepancy: May occur if the femoral head or implant is not properly aligned during surgery.
Long-Term Outlook (Prognosis)
-
Pain relief: Most patients experience significant pain relief and improved function.
-
Longevity: Hip resurfacing implants generally last 15-20 years, but the possibility of future revision surgery is greater in younger, more active patients.
-
Functional recovery: Patients typically return to a range of low-impact activities, but high-impact sports should be avoided to prolong the implant’s lifespan.
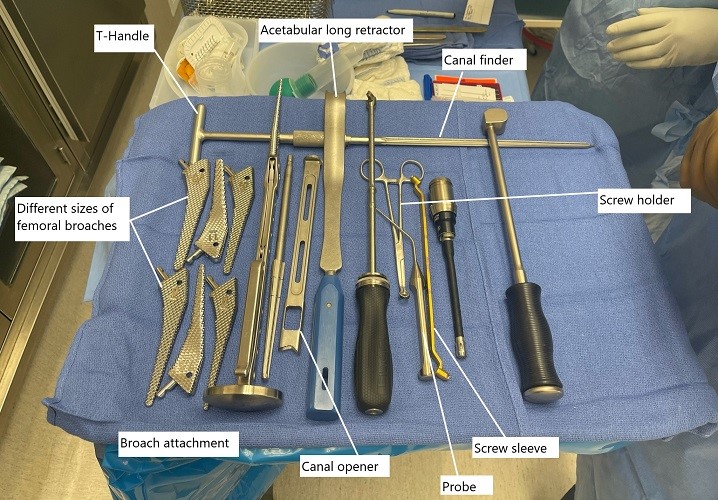
Intraoperative image showing instruments used in total hip replacement.
Out-of-Pocket Cost
Medicare
CPT Code 27130 – Hip Resurfacing (Total Hip Arthroplasty via Anterior or Posterior Approach): $303.45
Medicare Part B typically covers 80% of the approved cost for this procedure once your annual deductible has been met, leaving you responsible for the remaining 20%. Supplemental Insurance plans such as Medigap, AARP, or Blue Cross Blue Shield generally cover that remaining 20%, minimizing or eliminating out-of-pocket expenses for Medicare-approved surgeries. These plans work in coordination with Medicare to fill the coverage gap and reduce patient costs.
If you have Secondary Insurance, such as TRICARE, an Employer-Based Plan, or Veterans Health Administration coverage, it serves as a secondary payer. These plans typically cover any remaining coinsurance or small deductibles, which usually range between $100 and $300, depending on your plan and provider network.
Workers’ Compensation
If your hip resurfacing surgery is required due to a work-related injury or degenerative condition caused by your job, Workers’ Compensation will cover all medical expenses, including surgery, rehabilitation, and follow-up care. You will not have any out-of-pocket expenses, as the employer’s insurance carrier directly covers all approved treatments.
No-Fault Insurance
If your hip resurfacing is needed due to an automobile accident, No-Fault Insurance will typically cover the full cost of treatment, including surgery and postoperative care. The only potential out-of-pocket cost may be a small deductible or co-payment depending on your insurance policy.
Example
Rachel Mitchell required hip resurfacing surgery (CPT 27130) due to hip arthritis. Her estimated Medicare out-of-pocket cost was $303.45. Since Rachel had supplemental insurance through Blue Cross Blue Shield, her remaining balance was fully covered, leaving her with no out-of-pocket expenses for the procedure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q. How long does recovery take?
A. Full recovery typically takes 3-6 months, but patients may be able to return to non-impact activities sooner.
Q. Will I be able to walk right away?
A. Yes, most patients are able to walk with crutches immediately after surgery, bearing weight on the hip.
Q. Can I return to sports?
A. Low-impact activities like swimming, biking, and walking are encouraged, but high-impact activities should be avoided.
Summary and Takeaway
Hip resurfacing is a viable option for younger, active patients with hip arthritis who want to preserve their bone structure. It offers faster recovery and fewer complications compared to total hip replacement, making it an excellent choice for those seeking joint preservation.
Clinical Insight & Recent Findings
When considering hip replacement options, patients aged 65 or older have the choice between total hip arthroplasty (THA) and hip resurfacing arthroplasty (HRA). A recent study comparing these two procedures found that HRA led to superior functional outcomes, with better mobility and reduced pain at the one- and two-year follow-ups.
Patients undergoing HRA also demonstrated greater activity levels as measured by the Lower Extremity Activity Scale (LEAS). However, the study emphasized the importance of careful patient selection, as older patients with conditions like osteoporosis or renal insufficiency may face greater risks with HRA.
While HRA provided favorable results in this study, the decision should always be based on individual health assessments and surgical considerations. (“Study on outcomes of total hip replacement vs hip resurfacing for patients over 65 – see PubMed.“)
Who Performs This Surgery? (Specialists and Team Involved)
Orthopedic surgeons specializing in hip replacements perform this surgery. The surgical team may include anesthesiologists, surgical assistants, and physical therapists.
When to See a Specialist?
If you are experiencing persistent hip pain and have not found relief through conservative treatments, consult an orthopedic specialist to discuss your surgical options.
When to Go to the Emergency Room?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience sudden, severe hip pain or signs of infection (e.g., fever, redness, swelling) after surgery.
What Recovery Really Looks Like?
The recovery process involves limited weight-bearing, physical therapy, and follow-up visits to ensure proper healing. Most patients regain substantial mobility and function within a few months.
What Happens If You Delay Surgery?
Delaying hip resurfacing can lead to further joint degeneration, increased pain, and decreased function, potentially requiring a more invasive procedure later.
How to Prevent Recurrence or Failure?
Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding high-impact activities, and following your surgeon’s post-surgery instructions can help ensure the long-term success of the implant.
Nutrition and Bone or Joint Health
Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is important for bone health. Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption to support healing.
Activity and Lifestyle Modifications
Post-surgery, engage in low-impact activities like swimming or cycling, and avoid activities that put excessive strain on the hip joint, such as heavy lifting or running.
Do you have more questions?
Are there any specific lifestyle modifications or restrictions that patients should follow after undergoing hip resurfacing surgery, and for how long should these precautions be maintained?
Patients may need to follow certain lifestyle modifications or restrictions after hip resurfacing surgery to promote proper healing and prevent complications. These may include avoiding high-impact activities, maintaining a healthy weight, and adhering to postoperative rehabilitation guidelines. These precautions may need to be followed for several weeks to months, depending on individual recovery progress.
What are the key differences in postoperative pain management between hip resurfacing surgery and total hip replacement, and how does this impact the patient’s recovery experience?
Postoperative pain management strategies may differ between hip resurfacing surgery and total hip replacement, depending on factors such as surgical technique and patient preferences. Understanding these differences can help patients prepare for their recovery experience and manage pain effectively during the healing process.
How long does it typically take for patients to resume normal daily activities, such as walking, driving, and returning to work, after undergoing hip resurfacing surgery?
The time it takes for patients to resume normal daily activities after hip resurfacing surgery can vary depending on individual factors such as overall health, surgical technique, and postoperative rehabilitation progress. Patients should discuss their specific recovery timeline with their surgeon to set realistic expectations and plan accordingly.
What are the potential signs of complications or implant failure that patients should watch out for after undergoing hip resurfacing surgery, and when should they seek medical attention?
Patients should be aware of potential signs of complications or implant failure after hip resurfacing surgery, such as persistent pain, swelling, instability, or limited range of motion in the hip joint. It’s important to seek medical attention promptly if any concerning symptoms arise to ensure timely evaluation and appropriate management.
Are there any long-term lifestyle modifications or precautions that patients should consider adopting to prolong the lifespan of their hip resurfacing implant and minimize the risk of complications?
Adopting long-term lifestyle modifications or precautions can help prolong the lifespan of a hip resurfacing implant and reduce the risk of complications. These may include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular low-impact exercise, avoiding activities that place excessive stress on the hip joint, and attending regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon for monitoring.
How does the cost of hip resurfacing surgery compare to total hip replacement, and are there any factors that may influence the overall cost, such as insurance coverage or hospital fees?
The cost of hip resurfacing surgery may vary depending on factors such as geographic location, surgeon experience, hospital fees, and insurance coverage. Patients should consult with their healthcare provider and insurance company to understand the potential costs associated with the procedure and explore available financing options or assistance programs if needed.
What are the potential benefits of undergoing hip resurfacing surgery in terms of preserving bone stock and facilitating future revision surgeries, particularly for younger patients?
– Hip resurfacing surgery offers potential benefits in terms of preserving bone stock and facilitating future revision surgeries, which may be particularly advantageous for younger patients who are more likely to require additional procedures over their lifetime. Understanding these benefits can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment options.
How does the rehabilitation process after hip resurfacing surgery differ from that of total hip replacement, and what specific exercises or activities are typically recommended to promote optimal recovery?
The rehabilitation process after hip resurfacing surgery may differ from that of total hip replacement based on factors such as surgical technique and patient factors. Physical therapy exercises and activities may be tailored to the individual patient’s needs and goals, focusing on improving strength, flexibility, and mobility in the hip joint while minimizing stress on the surgical site.
What are the potential risks or complications associated with delaying or avoiding hip resurfacing surgery for patients who may benefit from the procedure, and how can patients weigh the risks and benefits of treatment timing?
Delaying or avoiding hip resurfacing surgery for patients who may benefit from the procedure can carry risks such as worsening symptoms, decreased quality of life, and potential progression of joint damage. Patients should work closely with their healthcare provider to assess the risks and benefits of treatment timing based on their individual circumstances and treatment goals.
Are there any alternative treatments or therapies available for patients who may not be suitable candidates for hip resurfacing surgery, and how do these options compare in terms of effectiveness and risks?
Patients who are not suitable candidates for hip resurfacing surgery may have alternative treatment options available, such as total hip replacement, conservative management, or other surgical interventions. These options should be discussed with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action based on the patient’s individual needs and preferences.
What are the key factors that patients should consider when deciding between hip resurfacing surgery and total hip replacement, and how can patients weigh these factors to make an informed decision?
– Patients should consider factors such as age, bone quality, activity level, anatomical considerations, and potential long-term outcomes when deciding between hip resurfacing surgery and total hip replacement. Consulting with a healthcare provider and discussing the risks, benefits, and potential outcomes of each procedure can help patients make an informed decision that aligns with their individual needs and goals
How does hip resurfacing surgery impact the range of motion and stability of the hip joint compared to total hip replacement, and what implications does this have for patients’ functional abilities and activities of daily living?
Understanding how hip resurfacing surgery affects the range of motion and stability of the hip joint compared to total hip replacement can help patients anticipate changes in their functional abilities and activities of daily living postoperatively. Patients may need to adjust their expectations and lifestyle based on these differences to optimize their recovery and overall outcomes.
What are the potential limitations or contraindications for hip resurfacing surgery, and how does the presence of certain medical conditions or anatomical factors influence candidacy for the procedure?
Identifying potential limitations or contraindications for hip resurfacing surgery is crucial for determining patient candidacy and minimizing the risk of complications. Factors such as underlying medical conditions, bone quality, anatomical abnormalities, and lifestyle considerations may impact eligibility for the procedure and should be carefully evaluated during the preoperative assessment.
How does the recovery timeline for hip resurfacing surgery compare to that of total hip replacement, and what factors contribute to variations in recovery duration among patients?
Understanding the typical recovery timeline for hip resurfacing surgery and the factors that influence variations in recovery duration can help patients set realistic expectations and monitor their progress postoperatively. Factors such as surgical technique, preoperative health status, adherence to rehabilitation protocols, and individual healing responses can all affect the pace and success of recovery.
Are there any specific dietary recommendations or nutritional considerations that patients should follow before and after undergoing hip resurfacing surgery to support optimal healing and recovery?
Nutrition plays a critical role in supporting optimal healing and recovery after hip resurfacing surgery. Patients may benefit from following a balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals to promote tissue repair, immune function, and overall health. Consulting with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian can help patients develop personalized dietary recommendations based on their individual needs and surgical goals.
What are the potential effects of hip resurfacing surgery on patients’ mobility, independence, and quality of life compared to total hip replacement, and how do these factors influence treatment decisions and patient satisfaction?
Assessing the potential effects of hip resurfacing surgery on patients’ mobility, independence, and quality of life relative to total hip replacement can inform treatment decisions and enhance patient satisfaction. Patients may prioritize different outcomes based on their lifestyle, preferences, and treatment goals, and understanding the potential impact of each procedure can help align expectations and optimize postoperative outcomes.
How does the risk of implant wear and failure differ between hip resurfacing surgery and total hip replacement, and what factors contribute to the long-term durability of each type of implant?
Comparing the risk of implant wear and failure between hip resurfacing surgery and total hip replacement can help patients understand the factors that influence the long-term durability of each type of implant. Factors such as implant design, material composition, patient activity level, and surgical technique can all affect the risk of wear and failure over time and should be considered when evaluating treatment options.
What are the potential implications of hip resurfacing surgery for patients’ future joint health and mobility, particularly in terms of the risk of revision surgery, implant longevity, and functional outcomes over time?
Understanding the potential implications of hip resurfacing surgery for patients’ future joint health and mobility is important for informed decision-making and long-term treatment planning. Patients should consider factors such as the risk of revision surgery, implant longevity, and functional outcomes over time when weighing the benefits and risks of the procedure and discussing their preferences with their healthcare provider.
How does the skill and experience of the surgeon performing hip resurfacing surgery impact patient outcomes and the risk of complications, and what criteria should patients consider when selecting a surgeon for the procedure?
The skill and experience of the surgeon performing hip resurfacing surgery can significantly influence patient outcomes and the risk of complications. Patients should carefully evaluate a surgeon’s expertise, training, and surgical volume when selecting a provider for the procedure to ensure optimal results and minimize the risk of adverse events.
What are the potential implications of hip resurfacing surgery for patients’ participation in high-impact activities, sports, or strenuous physical occupations, and how should patients approach returning to these activities postoperatively?
Patients considering hip resurfacing surgery should be aware of the potential implications for their participation in high-impact activities, sports, or strenuous physical occupations. While hip resurfacing may offer certain advantages for younger, more active patients, it’s essential to discuss realistic expectations and activity modifications with a healthcare provider to minimize the risk of implant wear, dislocation, or other complications during recovery and beyond.
What ongoing monitoring or follow-up care is typically recommended for patients after undergoing hip resurfacing surgery, and how does this contribute to the long-term success and durability of the implant?
Ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are essential components of postoperative management for patients who have undergone hip resurfacing surgery. Regular appointments with a healthcare provider allow for the assessment of implant function, detection of potential complications, and implementation of preventive measures to optimize long-term success and durability. Patients should adhere to recommended follow-up schedules and communicate any concerns or changes in symptoms to their healthcare team promptly.

Dr. Mo Athar
[et_pb_button admin_label="Button" button_url="https://www.cortho.org/general-appointment/" url_new_window="off" button_text="Schedule an Appointment" button_alignment="center" background_layout="light" custom_button="on" button_text_color="#FFFFFF" button_bg_color="#02770B" button_border_color="#FFFFFF" button_letter_spacing="1" button_font="Arial" button_on_hover="on" button_text_color_hover="#FFFFFF" button_bg_color_hover="#02770B" button_letter_spacing_hover="1" /]
