Hip Bursitis
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs in the body that help in the smooth gliding of the muscles, tendons, ligaments over the bony prominences. There are two major bursae in the hip joint, the trochanteric bursa and the iliopsoas bursa. Inflammation of the bursae is a common cause of hip pain. The pain may be managed with medications, change of activity, injections, and rarely surgery.
The inflammation of these bursae causes bursitis. The inflammation may occur as a result of wear and tear, irritation, or direct trauma/injury to the region. During inflammation, the body tries to repair the damage to the bursae that may cause swelling and pain.
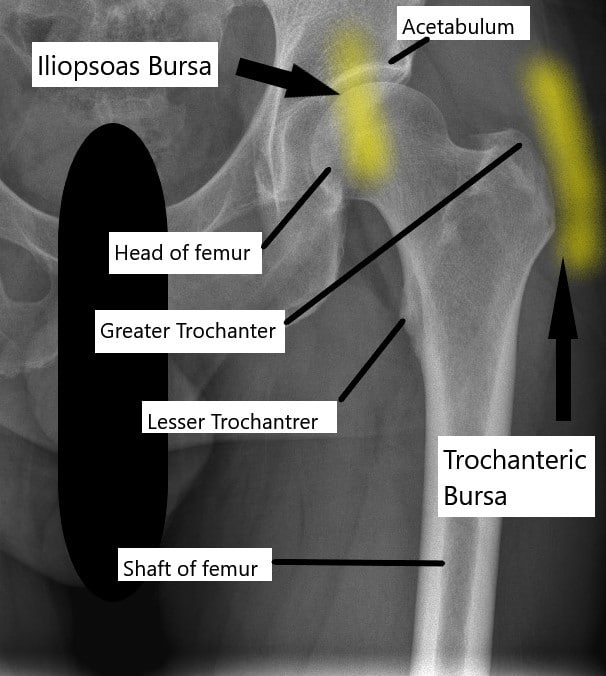
X-ray of the hip joint and its relation to the trochanteric bursa and iliopsoas bursa.
Trochanteric bursa
The trochanteric bursae is a small sac of fluid present at the side of the hip joint. The bursae allow the smooth gliding between the hip abductor muscles, tensor fascia, and the greater trochanter. The greater trochanter is bony prominence at the upper end of the thigh bone at the side of the hip joint.
Iliopsoas bursa
The iliopsoas bursa helps in the smooth gliding of the iliopsoas tendon over the front of the hip joint. The bursa may get inflamed and cause pain and tenderness. The pain is typically situated in front of the hip joint.
Causes
- A direct injury to the hip region may cause inflammation of the bursae. The injury may be associated with a fall or maybe sustained playing contact sports or during a motor vehicle accident.
- Repetitive motion about the hip joint may cause irritation of the bursae. The iliotibial band passes on the side of the trochanteric bursae and repetitive motion leading to sliding of the band over the bursae may cause inflammation. Activities such as running, jogging, athletics, cycling, etc. are the usual culprits.
- Inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis make the bursae more liable to be inflamed.
- Abnormal deposition of calcium in the tendons that pass over the bursae may irritate the bursae and cause inflammation.
- Any prior surgeries around the hip joint may lead to bursitis. Additionally, any birth deformities or a complication of total hip replacement that may cause leg length discrepancy may also lead to hip bursitis.
Symptoms
Patients with trochanteric bursitis may complain of sharp pain on the side of the hip. The pain may also be described as a dull ache spreading over the side of the hip. The pain is more severe with activities such as walking, running, climbing stairs, etc.
The pain associated with the iliopsoas bursa is repeated in the groin region in front of the hip joint. The pain of bursitis in both cases may get worse at night especially on sleeping on the side of the inflamed bursa.
Diagnosis & Management
The diagnosis of hip bursitis is made by the physician after eliciting the history of events leading up to the current symptoms and a thorough physical examination. During the physical examination, the physician may perform tests to localize the pain. Radiological tests in the form of X-ray, CT scan, or MRI may be performed to help in the diagnosis in cases where the physical examination is inconclusive.
The management of hip bursitis is mainly nonoperative. The patients are advised to modify their physical activity in cases where repetitive motion leads to inflammation of the bursa. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications such as naproxen and ibuprofen may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and pain.
The prolonged intake of NSAID medications may however cause stomach ulcers and may increase the risk of bleeding. The NSAID medications are therefore prescribed only for a short period of time.
Physical therapy may help to increase the flexibility and the strength of the muscles around the hip joint that may reduce the risk of bursitis. Similarly, icing may be helpful in acute cases of bursitis. The icing helps by reducing inflammation and soothing the nerves to help reduce pain.
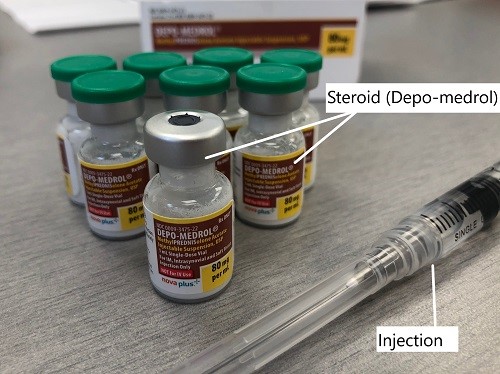
Depo-Medrol used as a steroid shot in cortisone injection.
Cortisone steroid injections mixed with a numbing medication such as lidocaine may lead to temporary or permanent relief from bursitis. The steroid in the injection helps to reduce the inflammation, while the lidocaine helps by immediately numbing the nerves around the bursa leading to pain relief. The steroid injection may provide relief for a few days, weeks, or months. The steroid injection may be repeated if needed in some cases.
Surgical management of hip bursitis is rare but may be performed using keyhole surgical techniques using an arthroscope. The surgeon makes a small incision in the hip region and inserts a miniature camera along with instruments. The surgeon may then open up and remove the offending bursa. The surgery may be performed in an outpatient setting and patients are up and walking the day of the procedure.
Do you have more questions?
What are the typical symptoms of hip bursitis, and how can I differentiate them from other hip-related conditions?
Understanding the specific symptoms of hip bursitis and how they differ from other hip conditions can help in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on distinguishing between various hip-related issues.
Is there a risk of developing chronic hip bursitis, and what steps can I take to prevent its recurrence?
Chronic hip bursitis is a possibility for some individuals, especially if underlying factors contribute to its development. Your healthcare provider can offer recommendations on preventive measures and lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Are there specific ergonomic or lifestyle changes I can make to alleviate hip bursitis symptoms during daily activities?
Modifying daily activities and ergonomics can help reduce strain on the hip joint and alleviate bursitis symptoms. Your healthcare provider or physical therapist can provide personalized recommendations based on your lifestyle and needs.
How long does it typically take to recover from hip bursitis, and what factors may influence the duration of recovery?
Recovery from hip bursitis can vary depending on individual factors such as the severity of inflammation, adherence to treatment, and underlying health conditions. Your healthcare provider can provide an estimate of the recovery timeline and factors that may affect it.
What are the potential side effects or risks associated with cortisone steroid injections for hip bursitis, and how common are they?
Cortisone steroid injections can provide relief from hip bursitis symptoms but may also carry risks or side effects. Understanding these potential complications can help you make informed decisions about treatment options. Your healthcare provider can discuss the risks and benefits of cortisone injections.
Are there any alternative or complementary therapies, such as acupuncture or chiropractic care, that may help alleviate hip bursitis symptoms?
Some individuals may find relief from hip bursitis symptoms through alternative or complementary therapies. Discussing these options with your healthcare provider can help determine if they are suitable for your situation and if they can be integrated into your treatment plan.
Can hip bursitis affect my ability to perform specific activities or sports, and are there modifications I should consider to prevent exacerbating the condition?
Hip bursitis may impact your ability to engage in certain activities or sports, depending on the severity of symptoms and underlying factors. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on activity modifications to minimize discomfort and prevent worsening of the condition.
How can I manage pain and discomfort associated with hip bursitis at home, and are there specific self-care strategies I should follow?
Implementing self-care strategies at home can help manage pain and discomfort associated with hip bursitis. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on effective home remedies, such as rest, ice therapy, and gentle stretching exercises.
Are there any specific warning signs or red flags that indicate a worsening of hip bursitis or the development of complications?
Being aware of potential warning signs or red flags can help you recognize when hip bursitis may be worsening or when complications may be developing. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on what to watch for and when to seek medical attention.
What are the potential effects of hip bursitis on my mobility and daily activities, and how can I maintain independence during the recovery process?
Understanding how hip bursitis may affect mobility and daily activities can help you develop strategies to maintain independence during the recovery process. Your healthcare provider or physical therapist can provide guidance on adaptive techniques and assistive devices, if necessary.
Are there any dietary or nutritional recommendations that may help support healing and reduce inflammation associated with hip bursitis?
Certain dietary and nutritional factors may play a role in supporting healing and reducing inflammation associated with hip bursitis. Your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can offer personalized recommendations based on your overall health and specific needs.
Can hip bursitis cause referred pain or discomfort in other areas of the body, and how can I distinguish between primary and referred pain?
Hip bursitis may sometimes cause referred pain or discomfort in other areas of the body, which can complicate diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the characteristics of primary and referred pain can help you and your healthcare provider differentiate between the two and identify the underlying cause of your symptoms.
What role does posture play in managing hip bursitis, and are there specific ergonomic adjustments I should make to alleviate symptoms?
Posture can impact hip bursitis symptoms, and making ergonomic adjustments may help alleviate discomfort. Your healthcare provider or a physical therapist can provide guidance on maintaining proper posture and making ergonomic modifications to your work or home environment.
Is there a risk of developing complications, such as infection or chronic inflammation, as a result of untreated or poorly managed hip bursitis?
Untreated or poorly managed hip bursitis may increase the risk of complications, including infection or chronic inflammation. Understanding these potential risks can underscore the importance of seeking timely treatment and adhering to recommended management strategies.
What steps can I take to optimize the effectiveness of physical therapy or rehabilitation exercises for hip bursitis, and how can I ensure proper technique and progression?
Maximizing the effectiveness of physical therapy or rehabilitation exercises is crucial for managing hip bursitis and promoting recovery. Your physical therapist can provide guidance on proper technique, progression of exercises, and strategies to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
Are there any specific precautions or limitations I should be aware of when engaging in physical activity or exercise to prevent exacerbating hip bursitis?
Understanding precautions and limitations when engaging in physical activity or exercise can help prevent exacerbation of hip bursitis symptoms. Your healthcare provider or physical therapist can provide personalized recommendations based on your condition and activity level.
What are the potential long-term implications of hip bursitis, and how can I minimize the risk of recurrence or complications over time?
Considering the potential long-term implications of hip bursitis can help you take proactive steps to minimize the risk of recurrence or complications. Your healthcare provider can offer guidance on lifestyle modifications, preventive measures, and ongoing management strategies to support long-term joint health.
Are there any alternative treatments or therapies, such as acupuncture, massage therapy, or herbal supplements, that may complement conventional medical approaches for managing hip bursitis?
Exploring alternative treatments or therapies alongside conventional medical approaches may provide additional relief for hip bursitis symptoms. Your healthcare provider can help evaluate the safety and efficacy of alternative therapies and incorporate them into your treatment plan, if appropriate.
How can I effectively communicate with my healthcare provider about my hip bursitis symptoms, treatment preferences, and concerns?
Effective communication with your healthcare provider is essential for optimizing your hip bursitis treatment and addressing any concerns or preferences you may have. Asking questions, expressing your needs, and actively participating in shared decision-making can help ensure that your treatment plan aligns with your goals and values.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
