Conservative / Non-operative Treatment of Sciatica
Most of the patients of sciatica get better with nonoperative treatment. The word sciatica refers to the pain along the distribution of the sciatic nerve. The medical terminology for sciatica is lumbar radiculopathy. It is usually present on one side only.
Sciatica is a pain that starts from the lower back and radiates into either leg. It usually radiates along the outside or the back of the thigh and leg. It can also radiate along the inner leg or the front of the inner thigh depending on the level involved. The pain can go over the front of the foot or into the sole.
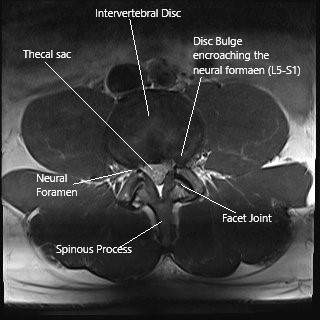
Axial section of the spine at L5-S1 level on an MRI
This radiating pain can be associated with tingling or numbness. Occasionally, there may be some weakness in the toes also. Rarely, a profound weakness can be found in the ankle, knee or the hip.
The prevalence of sciatica or lumbar radiculopathy is about 10 per thousand patients and may be more commonly involved in women. In patients presenting with sciatica, 90% do have lumbar disc herniationhttps://www.cortho.org/spine/herniated-disc/. Approximately 5% of people will experience sciatica in their lifetime.
The pain is due to a combination of inflammation and decreased blood supply to the nerve root commonly known as a nerve root irritation. The most common cause of this irritation is disc herniation. Other uncommon causes can be facet arthritis and synovial cyst.
Sciatica occurs in relatively younger people. Sciatica may be associated with back pain, but it can also present without back pain. Rarely, a sciatica may be associated with sudden or progressive neurological deficit in the form of weakness or involvement of bowel or bladder.
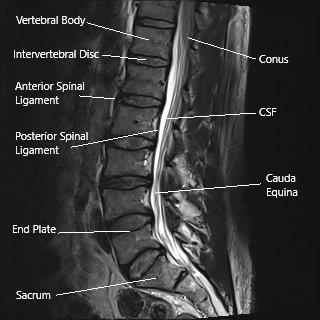
Sagittal section of the lumbar spine on an MRI.
The sciatica is mostly treated conservatively, especially the initial phase. Mode of treatment includes medications, physical therapy, chiropractor and acupuncture among others.
Medications that can be used for sciatica include nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medications like naproxen or ibuprofen, narcotic medications like tramadol, oxycodone and hydrocodone. Oral steroids in the form of Medrol Dosepak can be used. Occasionally, the medications can be supplemented with gabapentin or pregabalin or tricyclic antidepressants with good results. Pharmacological treatment of radiculopathy may also involve use of tricyclic antidepressants like amitriptyline, anticonvulsants like gabapentin and pregabalin.
Physical therapy can be initiated in patients with sciatica. The therapy includes isometric and isotonic exercises to strengthen their muscles of the back, abdominals and obliques. It also includes stretching as well as pain modalities like ultrasound, interferential therapy, heat and cold therapy, TENS unit etc.
Alternative therapies including massage, acupuncture, acupressure as well as chiropractic care are sometimes being found useful. The patient can have one or a combination of these therapies. Traction can also be used in the treatment of sciatica.
The therapy needs to be continued for 4 to 8 weeks for good results. Patients who do not improve or deteriorate with therapy should seek attention and see their spine surgeon. Short-term rest for up to 1 to 2 days has been proven in the treatment of sciatica. Long-term rest more than 2 days has not been found beneficial, but rather has been found detrimental in the management of back pain and sciatica.
Surgical treatment of sciatica is only needed if all the conservative managements have failed and the pain affects the activities of daily living as well as work. Patients presenting with sciatica associated with sudden or progressive neurological deficit in the form of weakness or involvement of bowel or bladder may need urgent surgery to stop the progression and optimize the conditions for recovery.
Minimal Invasive pain intervention for Sciatica
There are multiple minimal invasive pain interventions that have been tried in patients with lumbar radiculopathy or sciatica. These include epidural steroid injection (ESI), selective nerve root block (SNRB), disc decompression surgery using laser (laser discectomy), radiofrequency coblation (nucleoplasty), intradiscal oxygen ozone (O3) as alternatives to surgical treatment.
Researchers have shown consistent results from steroid injections, either epidural or selective nerve root block. Other procedures have also been used with limited success.
To perform an epidural injection, a needle is introduced from the back into the spine just outside the dura or the linings of the nerve roots and steroid mixed with local anesthetic is infiltrated. This steroid spreads out to bathe the nerve roots at that level as well as the levels above and below leading to decrease in inflammation. This causes improvement in symptoms and decrease in pain.
Epidural injection can be given through three different approaches namely caudal, interlaminar or transforaminal. Various steroids can be used including triamcinolone, methylprednisolone, betamethasone and dexamethasone.
Selective nerve root block is usually performed over the nerve root involved. A needle is put near the nerve root and a small amount of steroid with local anesthetic is injected. Selective nerve root block is a selective procedure and is diagnostic along with being therapeutic hence identifying the nerve root causing the problem.
These procedures are relatively safe procedures with good success rate. Complications of these procedures may include inadvertent injection of steroid into the dura or vessel, which can sometimes be catastrophic. Other complications include worsening of the pain, non-recovery or no benefit from the pain after the injections.
Patients who undergo epidural injection or nerve root block should maintain a pain diary and check and document their pain at 2 hours, 4 hours after the procedure as well as twice daily for the next 2 to 3 weeks. These patients can restart physical therapy within 3 to 5 days of the procedure.
Do you have more questions?
What causes sciatica?
Sciatica is most commonly caused by a herniated disc in the spine, bone spurs, or spinal stenosis, all of which can compress the sciatic nerve. Other causes include muscle spasms, pregnancy, or piriformis syndrome.
Can sciatica go away on its own?
Yes, in many cases, sciatica can improve on its own within a few weeks with rest, self-care measures, and conservative treatments. However, if the pain persists or worsens, it’s important to seek medical attention.
How is sciatica diagnosed?
Sciatica is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to identify the cause of nerve compression.
What are the most effective non-surgical treatments for sciatica?
Effective non-surgical treatments include physical therapy, medications (such as NSAIDs and muscle relaxants), epidural steroid injections, chiropractic care, acupuncture, and lifestyle modifications like weight management and exercise.
How does physical therapy help with sciatica?
Physical therapy helps by strengthening the muscles supporting the spine, improving flexibility, and encouraging proper posture, which can alleviate pressure on the sciatic nerve and reduce pain.
Are there specific exercises I should avoid if I have sciatica?
Avoid exercises that put excessive strain on your lower back, such as heavy lifting, high-impact activities, and bending or twisting movements. Always consult a physical therapist before starting any new exercise regimen.
How long does it take for epidural steroid injections to work?
Epidural steroid injections typically begin to relieve pain within 1 to 3 days, with peak effects around one week. Relief can last anywhere from several days to a few months.
Can medications completely relieve sciatica pain?
Medications can help manage the pain and inflammation associated with sciatica, but they may not completely eliminate the pain, especially if the underlying cause, like a herniated disc, is not addressed.
What are the risks of epidural steroid injections?
While generally safe, risks include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and headaches. Discuss these risks with your doctor to determine if this treatment is right for you.
Can chiropractic care worsen sciatica?
When performed by a qualified chiropractor, spinal adjustments are generally safe and can relieve sciatica. However, inappropriate or overly aggressive manipulations could potentially worsen symptoms, so it’s important to work with a licensed professional.
Is acupuncture effective for treating sciatica?
Acupuncture can be an effective complementary treatment for sciatica, helping to reduce pain and improve function by stimulating the body’s natural pain-relieving mechanisms.
How do lifestyle modifications help with sciatica?
Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and practicing good posture, can reduce the strain on your spine and lower your risk of recurring sciatica.
Should I use heat or ice for sciatica pain?
Both heat and ice can be beneficial. Ice is typically used in the initial stages to reduce inflammation, while heat can help relax tight muscles and increase blood flow to the affected area after the acute phase.
Can sciatica be prevented?
While not all cases of sciatica can be prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, proper lifting techniques, and good posture can reduce the risk of developing sciatica.
How do I know when it’s time to consider surgery for sciatica?
Surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments have failed to relieve symptoms after several months, or if you experience severe pain, significant weakness, loss of bowel or bladder control, or signs of cauda equina syndrome.
What is the success rate of conservative treatments for sciatica?
Conservative treatments are successful in managing sciatica symptoms in approximately 80-90% of cases. The success largely depends on the severity of the condition and adherence to treatment plans.
How often should I do physical therapy exercises?
It’s generally recommended to perform physical therapy exercises daily or as advised by your physical therapist. Consistency is key to seeing improvements.
Will sciatica come back after treatment?
Sciatica can recur, especially if the underlying causes, such as poor posture or a sedentary lifestyle, are not addressed. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regular exercise can help prevent recurrence.
Can I continue to work with sciatica?
Many people with sciatica can continue working with modifications to their activities, such as avoiding heavy lifting or prolonged sitting. Discuss with your doctor or physical therapist for specific advice based on your condition.
Is bed rest recommended for sciatica?
Prolonged bed rest is not recommended for sciatica. While short periods of rest may help, staying active with gentle movements and walking is generally better for recovery.
Can sciatica cause permanent nerve damage?
In severe cases, untreated sciatica can lead to permanent nerve damage, resulting in chronic pain, muscle weakness, or loss of sensation in the affected leg.
How do I manage sciatica pain at night?
To manage sciatica pain at night, try sleeping on your side with a pillow between your knees, using a firm mattress, and avoiding positions that exacerbate the pain. Heat therapy before bed may also help.
Should I continue treatment even if my symptoms improve?
Yes, continuing treatment after symptoms improve is important to prevent recurrence. This includes maintaining an exercise routine, practicing good posture, and following any other advice from your healthcare provider.
What are the signs that my sciatica is improving?
Signs of improvement include reduced pain intensity, increased mobility, less frequent flare-ups, and a return to normal activities without discomfort.

Dr. Vedant Vaksha
I am Vedant Vaksha, Fellowship trained Spine, Sports and Arthroscopic Surgeon at Complete Orthopedics. I take care of patients with ailments of the neck, back, shoulder, knee, elbow and ankle. I personally approve this content and have written most of it myself.
Please take a look at my profile page and don't hesitate to come in and talk.
