Fracture after Knee Replacement
Fractures after knee replacement surgery, although rare, are a serious complication that can significantly affect recovery and mobility. A periprosthetic fracture, which occurs around the prosthetic knee joint, can happen during or after surgery, often as a result of trauma or weakened bones. This guide explains the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for fractures that occur after knee replacement surgery, aiming to help you understand how they are managed and what you can expect from recovery.
How Common It Is and Who Gets It? (Epidemiology)
Fractures after knee replacement surgery are uncommon but more likely to occur in certain patient populations. Older adults with weakened bones, particularly those with osteoporosis, are at a higher risk. Additionally, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, a history of prior knee surgeries, or those who are taking long-term steroid treatments may have an increased risk of periprosthetic fractures. Although fractures can occur at any time after surgery, they are more commonly seen in patients who experience a fall or trauma.
Why It Happens – Causes (Etiology and Pathophysiology)
Periprosthetic fractures typically occur when the bones around the knee joint become weakened due to various factors, including:
-
Osteoporosis: A condition that causes bones to become weak and brittle, increasing the risk of fractures.
-
Trauma: A fall or other physical trauma can put stress on the prosthetic joint and lead to fractures, particularly if the bones around the implant are already weakened.
-
Implant Loosening or Misalignment: If the prosthetic components become loose or were not properly aligned during surgery, it can increase the risk of fractures in the surrounding bone.
-
Inflammatory Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can lead to bone thinning and increase the risk of fractures.
-
Malalignment or Stress on the Knee: Misalignment of the knee components or undue stress on the joint may cause fractures over time.
How the Body Part Normally Works? (Relevant Anatomy)
The knee joint is a hinge joint formed by the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap). The femur and tibia are covered with articular cartilage to allow smooth movement, and the patella glides over the femoral surface. Knee replacement surgery involves removing the damaged portions of these bones and replacing them with prosthetic components. These prosthetic components are either fixed with bone cement (cemented) or press-fitted into the bone (cementless), and they restore the function and mobility of the knee joint.
What You Might Feel – Symptoms (Clinical Presentation)
The main symptom of a fracture after knee replacement is pain, which may be sudden or develop over time. Other symptoms include:
-
Pain: Persistent or worsening pain in the knee, particularly after physical activity or trauma.
-
Swelling: Swelling or fluid buildup around the knee joint, particularly after movement or weight-bearing activities.
-
Instability: A feeling that the knee is weak or giving way, making it difficult to walk or stand.
-
Difficulty Moving: The inability to bend or straighten the knee fully, often due to pain or mechanical blockages from the fracture.
-
Audible Sound: You may hear a crack or pop at the time of the fracture, particularly after a fall or sudden movement.
How Doctors Find the Problem? (Diagnosis and Imaging)
Diagnosis begins with a physical examination to assess knee stability, alignment, and signs of swelling. Imaging tests include:
-
X-rays: These are the first-line imaging tools used to check for fractures, implant malposition, or loosening.
-
MRI or CT Scans: These may be used to assess soft tissue damage, joint alignment, and to identify any damage to the bone around the prosthesis.
-
Bone Scans: In some cases, a bone scan can help identify fractures or signs of infection.
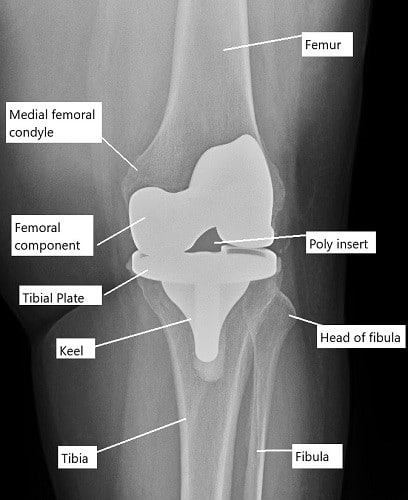
X-ray showing total knee replacement.
Classification
Fractures around the knee after surgery can be classified based on their location and severity:
-
Femoral Periprosthetic Fractures: These fractures occur in the femur, either above or below the femoral component. They are more common during or immediately after surgery.
-
Tibial Periprosthetic Fractures: These occur in the tibia, often as a result of misalignment or pre-existing bone weakness.
-
Patellar Periprosthetic Fractures: These fractures happen in the patella, often due to intraoperative injury or issues with patella resurfacing.
Femoral periprosthetic fractures
The fracture inner side of the lower end of the femur (medial femoral condyle) occurs mostly during the surgery. The management of femur periprosthetic fractures depends upon the location of the fracture and the stability of the prosthesis.
Non displaced stable periprosthetic fractures may be managed with nonoperative methods use as braces or casting. Fractures above the prosthesis with a stable prosthesis may be fixed with a nail or a metal plate which is fixed with screws.
A loose femoral component is managed with a revision involving a femoral component with a long stem. Rarely, an extensive fracture in the elderly may require the replacement of the entire lower end of the femur (distal femoral replacement).
Tibial periprosthetic fractures
Tibial fractures occur most commonly due to mal-aligned components or in patients with a prior history of tibial surgery. Nonsurgical treatment in the form of bracing/casting may be done for nondisplaced stable fracture. Unstable fractures with a stable prosthesis may be managed with plates, cables, wires, etc. Fractures with an unstable prosthesis are revised usually with a long stem prosthesis.
Patellar periprosthetic fractures
Kneecap (patella) fractures are common in cases where the patella is resurfaced with a plastic prosthetic component. Fractures of the patella occur commonly due to intraoperative surgical techniques. Damage to the blood supply of the patella may lead to patellar bone death and subsequent fracture.
Irregular resurfacing of the patella, inappropriate thickness of the residual patella, and the use of single peg implants have been associated with patellar periprosthetic fractures.
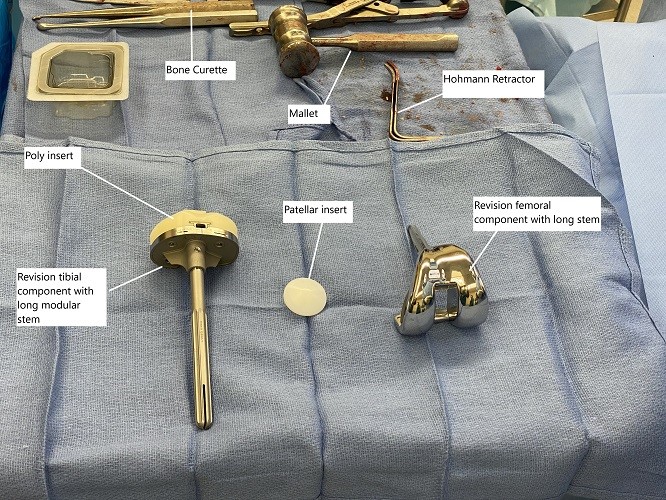
Intraoperative implants and instruments used in revision knee surgery.
Patellar fractures leading to disruption of the extensor mechanism (the ability to raise a straight leg), or with an unstable prosthesis are managed with surgical treatment. The surgical treatment may consist of removal of the patella, wire fixation, partial removal of the patella, revision of prosthesis, etc.
Stable fractures may be fixed with nonsurgical methods such as casting/bracing. Patients with periprosthetic patella fractures may complain of only minor pain in front of the knee as compared to tibial or femoral periprosthetic fractures where the pain is severe prompting a visit to the ER.
Do you have more questions?
How common are fractures after knee replacement surgery?
Fractures after knee replacement surgery are relatively uncommon, occurring in about 1-2% of cases.
What are the main risk factors for developing a fracture after knee replacement surgery?
The main risk factors include osteoporosis, previous knee surgeries, trauma during or after surgery, and improper alignment or placement of the knee implant.
Can fractures after knee replacement surgery occur years after the initial procedure?
Yes, fractures can occur years after knee replacement surgery, especially if the bones around the artificial joint weaken over time due to conditions like osteoporosis.
Are periprosthetic fractures more common in certain types of knee replacement implants?
Periprosthetic fractures can occur with any type of knee replacement implant, but some designs may have higher rates of fracture depending on factors like implant material, size, and surgical technique.
How soon after knee replacement surgery can a fracture occur?
Fractures can occur during the initial surgery or anytime during the post-operative period, ranging from days to years after the procedure.
What symptoms might indicate a fracture after knee replacement surgery?
Symptoms may include sudden pain, swelling, bruising, difficulty bearing weight on the affected leg, and in some cases, a popping or cracking sound at the time of injury.
Can fractures after knee replacement surgery be prevented?
While not all fractures can be prevented, certain measures like maintaining bone health, following post-operative instructions, and taking precautions to prevent falls can help minimize the risk.
How are fractures after knee replacement surgery diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans, and sometimes blood tests to assess bone health.
What are the treatment options for fractures after knee replacement surgery?
Treatment options include non-surgical approaches like immobilization with a brace or cast, surgical repair using implants like screws or plates, and in some cases, revision surgery to replace or revise the existing knee implant.
What is the typical recovery time after treatment for a fracture after knee replacement surgery?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the fracture, the type of treatment received, and individual factors like overall health and adherence to rehabilitation exercises. It can range from weeks to months.
Are there any long-term complications associated with fractures after knee replacement surgery?
Long-term complications may include persistent pain, stiffness, decreased range of motion, and an increased risk of future fractures or implant failure.
How successful are treatments for fractures after knee replacement surgery?
Success rates for treatment depend on various factors, including the severity of the fracture, the patient’s overall health, and the skill of the surgical team. Generally, early detection and appropriate treatment yield better outcomes.
Can physical therapy help with recovery after a fracture after knee replacement surgery?
Yes, physical therapy is an essential part of rehabilitation after a fracture. It helps improve strength, flexibility, and function in the affected knee joint.
Are there any restrictions on activities after treatment for a fracture after knee replacement surgery?
Your surgeon will provide specific guidelines based on the type of fracture and treatment received. In general, you may need to avoid high-impact activities and heavy lifting during the initial stages of recovery.
Is there a higher risk of developing another fracture after experiencing one after knee replacement surgery?
While there is a slightly increased risk of future fractures, especially if underlying bone health issues are present, proper treatment and preventive measures can help minimize this risk.
Can fractures after knee replacement surgery affect the longevity of the knee implant?
Fractures may compromise the stability and function of the knee implant, potentially leading to implant failure or the need for revision surgery in severe cases.
How can I improve bone health to reduce the risk of fractures after knee replacement surgery?
Strategies to improve bone health include maintaining a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, staying physically active, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and discussing bone health supplements with your healthcare provider if needed.
What should I do if I suspect I have a fracture after knee replacement surgery?
If you experience symptoms suggestive of a fracture, such as sudden pain or difficulty moving your knee, contact your doctor immediately for further evaluation and treatment.
Are there any lifestyle modifications I should consider after experiencing a fracture after knee replacement surgery?
Depending on your individual circumstances, your surgeon may recommend modifications such as using assistive devices like canes or walkers, making changes to your home environment to prevent falls, and avoiding activities that could put stress on the affected knee.
Can fractures after knee replacement surgery lead to chronic pain?
While it’s possible to experience chronic pain after a fracture, especially if complications arise or the fracture does not heal properly, prompt treatment and adherence to rehabilitation protocols can help minimize this risk.
What are the chances of needing revision surgery after experiencing a fracture after knee replacement surgery?
The likelihood of needing revision surgery depends on factors such as the severity of the fracture, the type of treatment received, and individual healing factors. Your surgeon can provide more information based on your specific situation.
Are there any experimental treatments or technologies being developed for fractures after knee replacement surgery?
Researchers are continually exploring new treatment options and technologies for fractures after knee replacement surgery, but currently, standard surgical techniques and implant designs remain the primary methods of treatment.

Dr. Mo Athar
A seasoned orthopedic surgeon and foot and ankle specialist, Dr. Mohammad Athar welcomes patients at the offices of Complete Orthopedics in Queens / Long Island. Fellowship trained in both hip and knee reconstruction, Dr. Athar has extensive expertise in both total hip replacements and total knee replacements for arthritis of the hip and knee, respectively. As an orthopedic surgeon, he also performs surgery to treat meniscal tears, cartilage injuries, and fractures. He is certified for robotics assisted hip and knee replacements, and well versed in cutting-edge cartilage replacement techniques.
In addition, Dr. Athar is a fellowship-trained foot and ankle specialist, which has allowed him to accrue a vast experience in foot and ankle surgery, including ankle replacement, new cartilage replacement techniques, and minimally invasive foot surgery. In this role, he performs surgery to treat ankle arthritis, foot deformity, bunions, diabetic foot complications, toe deformity, and fractures of the lower extremities. Dr. Athar is adept at non-surgical treatment of musculoskeletal conditions in the upper and lower extremities such as braces, medication, orthotics, or injections to treat the above-mentioned conditions.
