Wrist pain is a common condition that affects all age groups. A number of different causes may lead to wrist pain. The pain may arise suddenly after an injury or may develop over time due to repetitive stress or arthritis.
Daily activities such as driving, writing, typing, playing sports, gripping, etc require proper functioning of both the hand and wrist. Wrist pain, therefore, may have a significant impact on our everyday activities.
The wrist joint is made of a number of small joints connecting the forearm with the hand. There are 8 bones in each wrist connecting with bones of lower forearm and hand. Besides bones, there are tendons and ligaments forming an essential part of the wrist joint. Various structures such as nerves and blood vessels pass across the wrist joint in a small space.
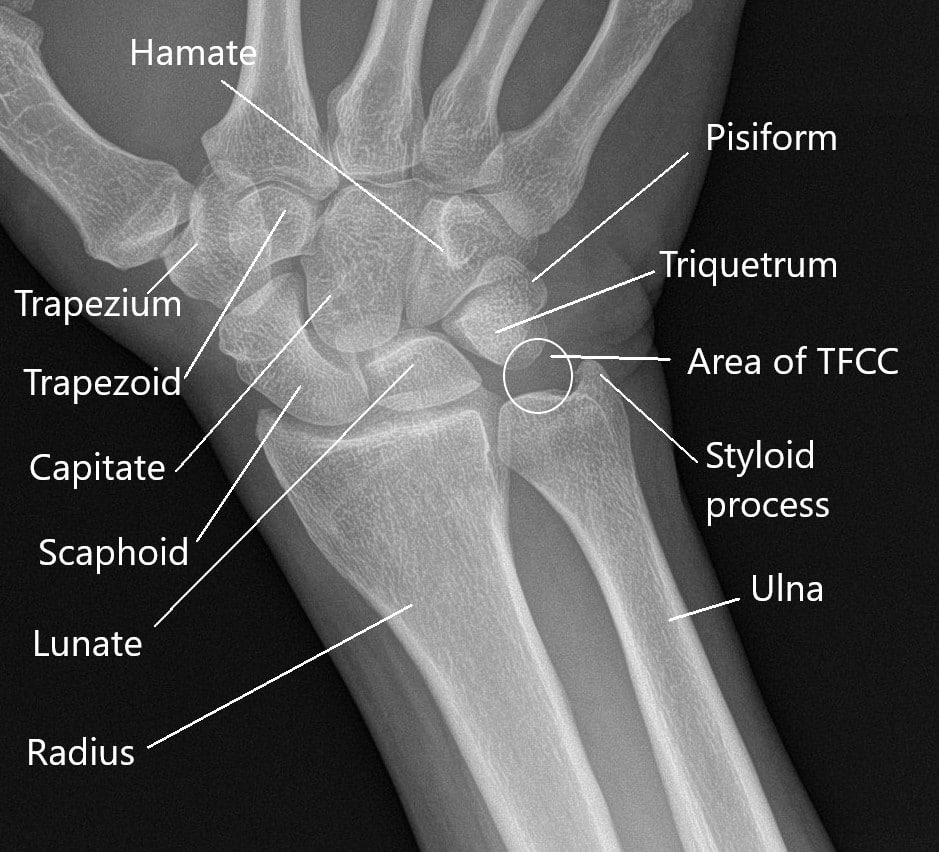
X-ray of the wrist showing anatomy of the wrist.
The tendon is a tough connective tissue that connects the muscle to the bone. Similarly, ligaments are a tough tissue that connects one bone with another. The small bones with their articular cartilage form a joint with one another. The small joints in the wrist work in unison for smooth movements of the wrist.
Causes
Hand and wrist pain is commonly associated with injury but a number of other causes may lead to wrist hand.
- Trauma or injury to the bones, ligaments, or tendons of the wrist may cause sudden pain in the wrist. Injury may result in sprains, strains, or fractures. Scaphoid bone fractures in the wrist require special attention. The scaphoid fractures are not evident until a few days on X-ray.
- Triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is a small tissue that provides a cushion to the small bones on the pinky side. Tears of TFCC may cause chronic pain and instability.
- Cysts are small fluid-filled sacs that may cause pain and swelling. Ganglion cysts are usually located on the opposite side of the palm. It is a result of swelling of the covering of the tendons passing over and under the wrist. The fluid is similar to the fluid inside the joints.
- Overuse and repetitive motions may result in inflammation and swelling of the tissues around the wrist. Certain activities such as writing, typing, knitting, racquet sports, cutting hair involve repeated wrist motion which may cause inflammation.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs due to compression of the median nerve as it passes through a small canal in the wrist.Overuse and repetitive activities such as typing may result in swelling of the tendons around the nerve. The median nerve gets entrapped and compressed within the small space.
- Kienbock disease is the avascular necrosis of the lunate bone in the wrist. The blood supply of the bone gets disrupted which results in bone death. The lunate plays an important role in the smooth movements of other bones. The disease usually affects young adults.
- Osteoarthritis is a wear and tear disease of the cartilage and surrounding structures. The condition mostly affects the older age group of patients. Other joints may be involved as well. Although the causes are multifactorial, the disease may run in some families.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease where the body’s own cells destroy tissues. Multiple joints are involved and commonly both the wrist joints may get involved.
- Psoriatic arthritis is another disease of the immune system associated with the skin disease psoriasis.
Gout is a condition resulting from excess uric acid deposition in joints. Other joints are involved as well. High protein-rich foods, water pills (diuretic), alcohol consumption, and chemotherapy are risk factors. - Tendonitis is the inflammation of tendons. Diabetics and pregnant women are more prone to develop tendonitis of the wrist with subsequent carpal tunnel syndrome.
- De Quervain’s disease affects the side of the wrist near the thumb. There is inflammation and fluid accumulation in the covering of the tendons.
Symptoms
The symptoms of wrist pain are wide-ranging depending upon the cause of the condition.
- Pain is the most common symptom. The pain resulting from wrist injuries may be sharp in character. The part of the injured wrist is usually tender to pressure. The pain from osteoarthritis may be dull in character.
- The swelling of the wrist in addition to pain is present in injuries and inflammatory conditions.
- Stiffness of the wrist joint may result from a chronic condition. The patient is unable to move the wrist in the normal range of motion.
- Pins and needles usually result from carpal tunnel syndrome. Additionally, the patients may complain of numbness of the pinky, ring, part of the middle finger and the thumb. Numbness and tingling sensation may accompany pain, especially at night.
- Loss of function in the form of gripping, writing, driving may result from pain, swelling, stiffness, or numbness.
Diagnosis
A physician visit is required for the diagnosis and management of wrist pain. A thorough history regarding the onset of wrist pain is obtained. The physician will then examine the wrist to look for tender points and swelling. The range of motion, deformity, and the strength of the hand and forearm muscles are assessed with special tests.
Radiological examination is generally undertaken. An X-ray helps to locate any fractures and signs of arthritis. A CT scan is helpful to look for fractures not visible on an X-ray. MRI helps to look for inflammation and swellings of the wrist as well as the nerve entrapments.
Ultrasound examination is done to look for superficial swellings, cysts, and tendons. The physician may also request nerve conduction studies to look for nerve entrapment. Additionally, blood examination may be done to rule out systemic illness.
Nonsurgical Management
The treatment options of wrist pain depend upon the cause of wrist pain. Simple muscle strains and sprains can be effectively managed at home.
- Rest to the wrist is important to reduce further damage to the joint.
- Activity adjustment or completely stopping the activity causing wrist pain is necessary to stop further progression.
- Icing is used for sudden injuries to reduce swelling and pain. Heat therapy may be used in chronic conditions to reduce pain and promote healing.
- Splints and casts are sometimes used to provide rest to the injured part while it heals.
- Therapy is helpful to strengthen and stretch the muscles around the wrist. Physical therapy also aids in increasing the range of motion of the wrist.
- Medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs are used to reduce pain and inflammation of the wrist. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis may require the use of drugs known as disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Surgical Management
Certain conditions require surgical management, these surgeries can be done via an open incision or an arthroscope. Wrist fractures that cannot be managed with a cast or splint are operated upon. They may require fixation with hardware fixed to the bone.
An arthroscope is a special instrument consisting of a minute camera. The camera is inserted inside the wrist to look for possible causes of wrist pain. The camera images are displayed via a live feed on a large display. Arthroscopy is the gold standard for diagnosing wrist conditions.
The added advantage of arthroscopy is using miniature instruments to fix any encountered injury or disease. Various conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome can be surgically fixed with an arthroscope. Consider visiting an orthopedic surgeon specialized in sports injuries if you have wrist pain for proper diagnosis or treatment.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
