Microdiscectomy and laminectomy are two common surgical procedures used to treat conditions like lumbar radiculopathy caused by disc herniation or spinal stenosis. Both surgeries aim to decompress the spinal nerve roots, but they are performed in different ways and are suited for different causes of nerve compression. Microdiscectomy is focused on removing herniated disc material, while laminectomy involves increasing the space in the spinal canal to relieve pressure on the nerve roots.
How Common It Is and Who Gets It? (Epidemiology)
Both microdiscectomy and laminectomy are performed in patients with lumbar radiculopathy, a condition commonly seen in individuals between the ages of 30 and 50. It is especially common in people who engage in repetitive physical activities, heavy lifting, or those with degenerative disc disease. The conditions treated with these surgeries (disc herniation and lumbar stenosis) are common causes of low back pain and sciatica, affecting millions of people globally.
Why It Happens – Causes (Etiology and Pathophysiology)
- Lumbar Disc Herniation: When the inner material of an intervertebral disc (nucleus pulposus) pushes through the outer ring (annulus fibrosus), it can press on nearby spinal nerves, causing pain and dysfunction (radiculopathy). This is the primary condition treated by microdiscectomy.
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen can compress the spinal cord or nerve roots. The pressure may be caused by factors such as disc degeneration, bone spurs, or ligament thickening. Laminectomy surgery is often used to increase the space for the spinal nerves and alleviate symptoms.
Both conditions can result in symptoms like radiating pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the legs, commonly known as sciatica.
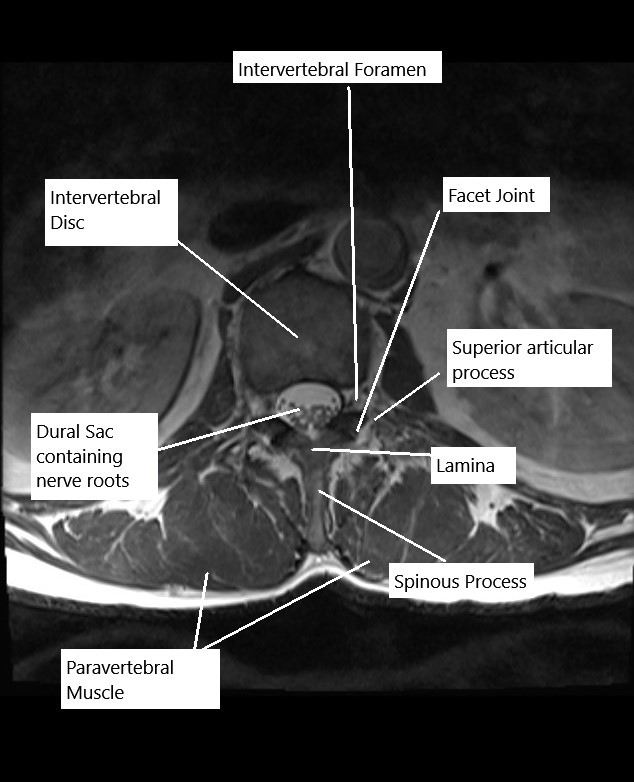
How the Body Part Normally Works? (Relevant Anatomy)
The lumbar spine consists of five vertebrae (L1-L5) and intervertebral discs that separate each vertebra. The spinal cord passes through the spinal canal, and spinal nerves exit through openings called foramina. These nerves control sensation and movement in the lower body, including the legs, feet, and pelvis. When discs herniate or the spinal canal narrows, it can compress the nerve roots, leading to pain and loss of function.
What You Might Feel – Symptoms (Clinical Presentation)
Both microdiscectomy and laminectomy are typically used to treat symptoms related to nerve compression, such as:
- Radicular Pain: Sharp, shooting pain that radiates down the leg (sciatica).
- Numbness or Tingling: Often in the buttocks, legs, or feet.
- Weakness: Difficulty moving the legs or feet, or a feeling of clumsiness or instability.
- Pain Aggravated by Activity: Such as walking, bending, or twisting.
How Doctors Find the Problem? (Diagnosis and Imaging)
- Physical Examination: Doctors assess nerve function, reflexes, strength, and pain levels.
- MRI: The most useful imaging technique for identifying herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and nerve compression.
- CT Scan: Helps in evaluating the bony structures and assessing stenosis.
- X-rays: Can reveal spinal alignment issues, bone spurs, or signs of degeneration.
- Electromyography (EMG): To evaluate nerve damage and function, confirming radiculopathy.
Classification
Microdiscectomy and laminectomy are both classified based on the type of surgery and approach:
- Microdiscectomy: Removal of herniated disc material to relieve nerve pressure.
- Laminectomy: Removal of part or all of the lamina (the back portion of the vertebra) to create more space in the spinal canal.
Both procedures can be performed via traditional open methods or minimally invasive techniques.
Other Problems That Can Feel Similar (Differential Diagnosis)
Conditions that mimic the symptoms of lumbar radiculopathy include:
- Piriformis Syndrome: Compression of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle in the buttocks.
- Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Pain in the lower back or buttocks that may radiate into the legs.
- Facet Joint Syndrome: Degeneration or arthritis of the facet joints, often causing pain similar to that of sciatica.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Nerve damage outside the spine can cause similar symptoms in the legs and feet.
Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Care
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening back muscles and improving posture to relieve pressure on the spine.
- Medications: Pain relief from NSAIDs or corticosteroids.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: To reduce inflammation around the spinal nerves.
- Nerve Blocks: For targeted pain relief in the affected area.
Surgical Care
- Microdiscectomy: A minimally invasive procedure focused on removing herniated disc material to relieve pressure on the nerve roots.
- Laminectomy: A surgery that removes part of the lamina (or the entire lamina) to increase the space in the spinal canal, alleviating pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
Recovery and What to Expect After Treatment
- Microdiscectomy:
- Recovery is typically quick, with most patients returning to light activities within 1-2 weeks.
- Full recovery may take several weeks, with physical therapy to strengthen the back muscles and improve flexibility.
- Laminectomy:
- Recovery can take a bit longer compared to microdiscectomy due to the more extensive nature of the procedure.
- Patients are typically able to return to daily activities within 4-6 weeks, with full recovery taking a few months.
Both procedures are often performed as outpatient surgeries, allowing patients to return home the same day or the day after surgery.
Possible Risks or Side Effects (Complications)
Potential complications include:
- Infection: At the surgical site.
- Nerve Injury: Damage to the spinal cord or nerve roots is rare but possible.
- Dural Tear: Accidental puncture of the protective covering around the spinal cord (dura mater).
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after the procedure.
- Recurrent Herniation: A small percentage of patients may experience another disc herniation at the same level.
Long-Term Outlook (Prognosis)
Both microdiscectomy and laminectomy have high success rates in relieving symptoms of lumbar radiculopathy. Most patients experience significant pain relief and improved function, with a return to normal activities. However, some patients may develop recurrent symptoms or require additional surgery, especially if there is ongoing spinal degeneration or instability.
Out-of-Pocket Costs
Medicare
CPT Code 63030 – Lumbar Microdiscectomy: $225.06
CPT Code 63020 – Cervical Microdiscectomy: $271.49
CPT Code 63040 – Thoracic Microdiscectomy: $335.83
CPT Code 63047 – Lumbar Laminectomy: $271.76
CPT Code 63045 – Cervical Laminectomy: $319.26
CPT Code 63046 – Thoracic Laminectomy: $303.41
Under Medicare, 80% of the approved amount for these procedures is covered once the annual deductible has been met. The remaining 20% is typically the patient’s responsibility. Supplemental insurance plans—such as Medigap, AARP, or Blue Cross Blue Shield—typically cover this 20%, meaning most patients will have little to no out-of-pocket expenses for Medicare-approved spinal surgeries. These supplemental plans coordinate directly with Medicare to ensure full coverage for the procedures.
If you have secondary insurance—such as Employer-Based coverage, TRICARE, or Veterans Health Administration (VHA)—it functions as a secondary payer once Medicare has processed the claim. After your deductible is satisfied, these secondary plans may cover any remaining balance, including coinsurance or small residual charges. Most secondary insurance plans have a modest deductible, typically between $100 and $300, depending on the specific policy and network status.
Workers’ Compensation
If your lumbar, cervical, or thoracic spine condition requiring these procedures is work-related, Workers’ Compensation will cover all treatment-related costs, including surgery, hospitalization, and rehabilitation. You will have no out-of-pocket expenses under an accepted Workers’ Compensation claim.
No-Fault Insurance
If your spinal condition or injury is the result of a motor vehicle accident, No-Fault Insurance will cover all medical and surgical expenses, including discectomy and laminectomy procedures. The only possible out-of-pocket cost may be a small deductible depending on your policy terms.
Example
David, a 60-year-old patient with cervical disc degeneration, underwent cervical microdiscectomy (CPT 63020) and lumbar laminectomy (CPT 63047) to relieve nerve compression. His estimated Medicare out-of-pocket costs were $271.49 for the cervical discectomy and $271.76 for the lumbar laminectomy. Since David had supplemental insurance through Blue Cross Blue Shield, the 20% not covered by Medicare was fully paid, leaving him with no out-of-pocket expenses for the procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q. How long does recovery take after microdiscectomy or laminectomy?
A. Most patients recover within 1-2 weeks for microdiscectomy and 4-6 weeks for laminectomy, although full recovery may take a few months depending on the procedure and individual health.
Q. What are the main differences between microdiscectomy and laminectomy?
A. Microdiscectomy is focused on removing herniated disc material to relieve nerve pressure, while laminectomy involves removing part or all of the lamina to create more space in the spinal canal.
Q. Is there a risk of needing another surgery in the future?
A. While rare, some patients may experience recurrent herniation or other complications that require additional surgery, especially if spinal instability is present.
Summary and Takeaway
Microdiscectomy and laminectomy are highly effective surgical options for treating lumbar radiculopathy. The choice of procedure depends on the underlying cause of nerve compression. Microdiscectomy is ideal for disc herniations, while laminectomy is typically used for spinal stenosis or when more space is needed in the spinal canal. Both surgeries offer high success rates, though the recovery times and risks vary depending on the procedure.
Who Performs This Treatment? (Specialists and Team Involved)
Both procedures are typically performed by:
- Spine Surgeons: Orthopedic or neurosurgeons specializing in spinal disorders.
- Anesthesiologists: For managing anesthesia during the procedure.
- Physical Therapists: To assist in post-operative rehabilitation and recovery.
When to See a Specialist?
If you experience persistent or worsening lower back pain, leg pain, numbness, or weakness, and conservative treatments have failed, consult a spine specialist to determine if surgery is necessary.
When to Go to the Emergency Room?
Seek emergency care if you experience:
- Sudden loss of bladder or bowel control.
- Severe, unmanageable pain.
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the legs or feet.
What Recovery Really Looks Like?
Recovery is typically quick for microdiscectomy, with most patients returning to light activities within 1-2 weeks. Laminectomy recovery takes a bit longer, but most patients can return to normal activities within 4-6 weeks.
What Happens If You Ignore It?
Ignoring symptoms of nerve compression can lead to worsening pain, permanent nerve damage, and loss of mobility. Early surgical intervention often leads to better outcomes and faster recovery.
How to Prevent It?
Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and strengthening the muscles that support the spine can help prevent conditions that lead to lumbar radiculopathy.
Nutrition and Bone or Joint Health
A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone health and helps prevent degenerative changes in the spine.
Activity and Lifestyle Modifications
After surgery, engage in light activities like walking or swimming to maintain flexibility and strength, while avoiding heavy lifting or high-impact exercises during recovery.
Do you have more questions?
Which procedure has a faster recovery time?
Microdiscectomy generally has a faster recovery time due to its minimally invasive nature and smaller incisions.
What are the main benefits of a microdiscectomy?
Benefits include smaller incisions, reduced tissue damage, less postoperative pain, and a quicker recovery period.
What are the potential complications of a laminectomy?
Complications can include infection, blood clots, nerve damage, and spinal instability.
What is the success rate of microdiscectomy in relieving pain?
Microdiscectomy has a high success rate, with most patients experiencing significant relief from leg pain (sciatica).
What is the recovery process like for microdiscectomy?
Recovery involves gradual resumption of activities, physical therapy, and avoiding heavy lifting or twisting movements for several weeks.
What activities should be avoided after a laminectomy?
Patients should avoid heavy lifting, bending, twisting, and high-impact activities until cleared by their surgeon.
How do I manage pain after surgery?
Pain management may include medications, ice packs, and gentle stretching exercises as advised by your surgeon.
How effective is laminectomy in treating spinal stenosis?
Laminectomy is highly effective in relieving symptoms of spinal stenosis, particularly leg pain and weakness.
Can I expect complete relief of symptoms after these surgeries?
Many patients experience significant symptom relief, though some may have residual pain or other symptoms depending on the severity and duration of their condition.
What lifestyle changes should I make after surgery?
Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking can help prevent recurrence of spinal issues.
Are there any alternatives to these surgeries?
Alternatives include physical therapy, medications, epidural steroid injections, and less invasive procedures like percutaneous discectomy.
How do I know if I am a candidate for microdiscectomy?
Candidates typically have a herniated disc causing significant nerve compression and have not responded to conservative treatments like physical therapy or medications.
How soon can I start driving after surgery?
Patients can typically resume driving once they are no longer taking narcotic pain medications and feel comfortable, usually around 2-4 weeks post-surgery.
What kind of anesthesia is used during these surgeries?
Both procedures are usually performed under general anesthesia.

